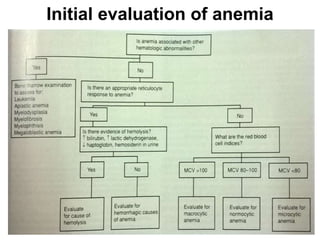
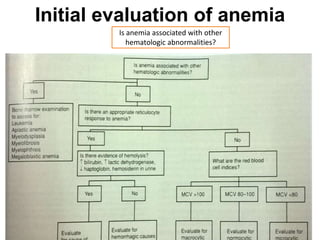
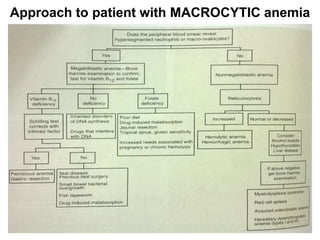
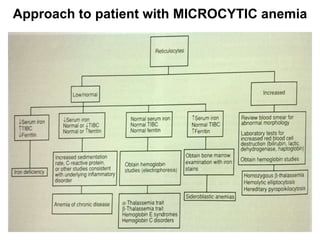
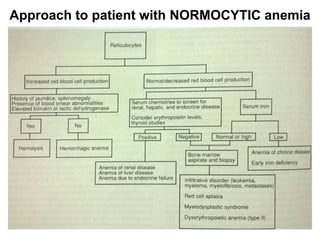
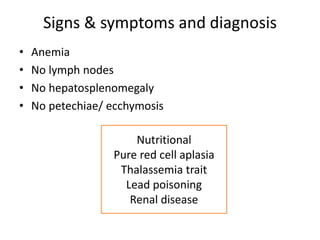
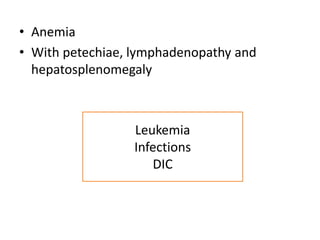
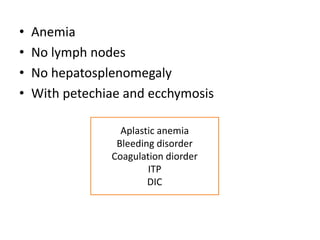
The document discusses the approach to evaluating and diagnosing anemia. It defines anemia as a reduction in hemoglobin or red blood cell volume below normal levels. The evaluation involves taking a thorough history including symptoms, medications, travel, diet and family history. A physical exam evaluates for pallor, jaundice, organomegaly and bruising. Initial labs help classify anemia as macrocytic, microcytic or normocytic. Further testing is then guided by these characteristics to identify potential causes such as nutritional deficiencies, bleeding disorders, infections, liver or bone marrow diseases.