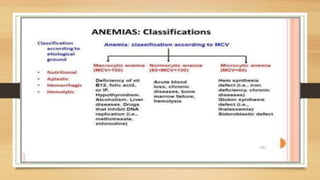
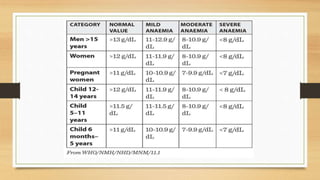
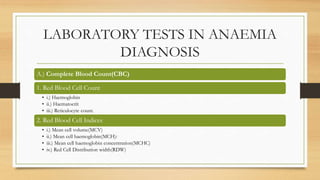
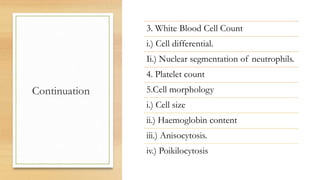
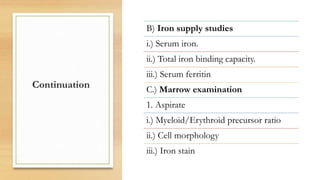
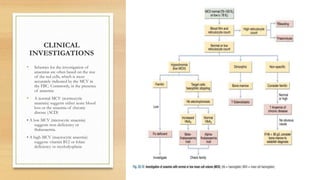
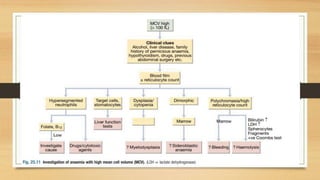
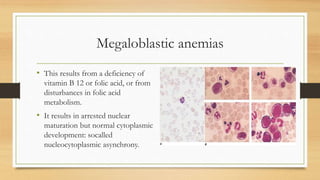
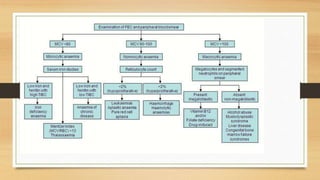
This document provides an overview of anaemia, including its definition, epidemiology, etiology, clinical features, investigations, diagnosis, treatment, complications and prevention. Anaemia is defined as a low level of hemoglobin in the blood. It affects about 30% of the global population and is commonly caused by multiple factors like nutritional deficiencies, blood loss, and increased red blood cell destruction. Clinical features are non-specific and include pallor, fatigue, and breathlessness. Investigations include complete blood count, peripheral smear, iron studies, and bone marrow examination. Treatment involves identifying and treating the underlying cause, as well as oral or intravenous iron, folic acid, vitamin B12 supplementation, or blood transfusions as needed.