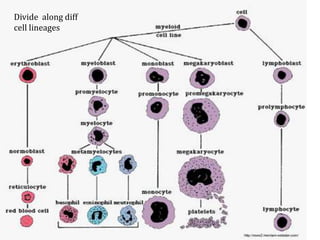
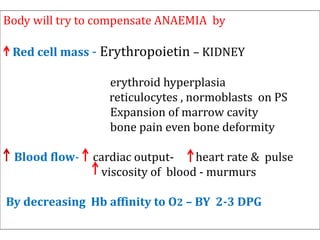
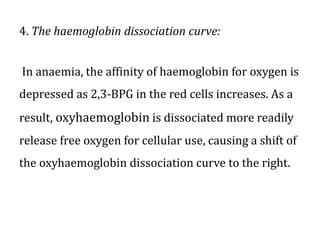
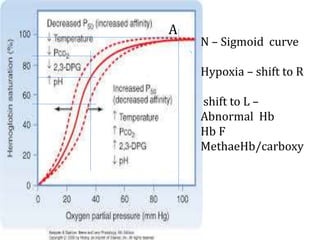
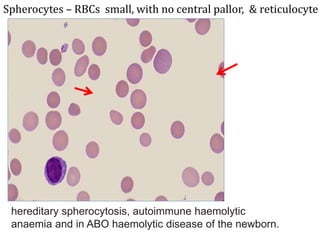
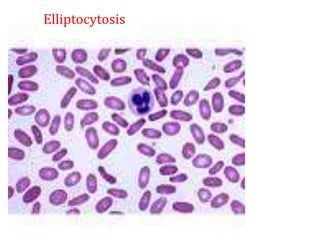
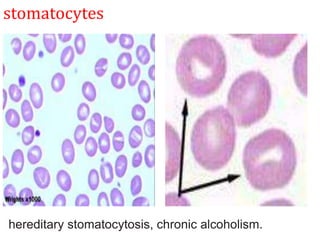
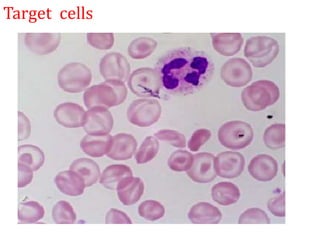
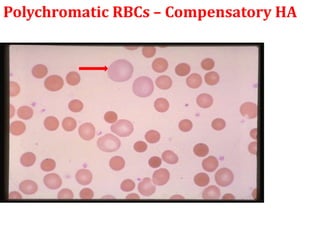
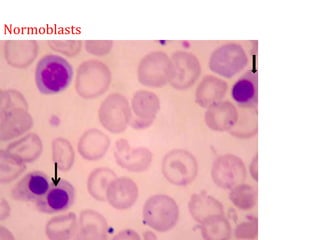
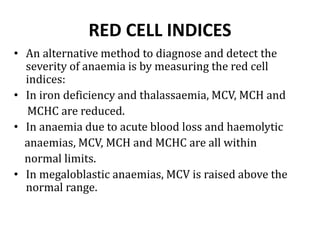
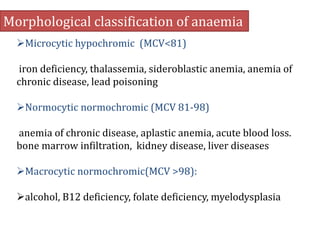
This document provides an overview of anemia, including its classification, causes, clinical features, laboratory diagnosis, and pathophysiology.
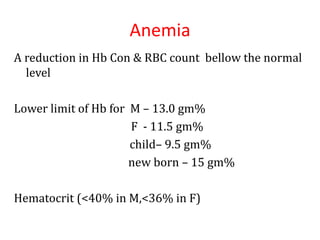
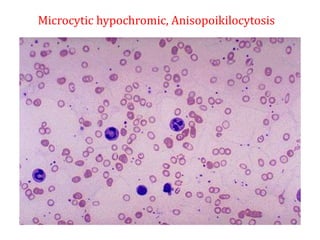
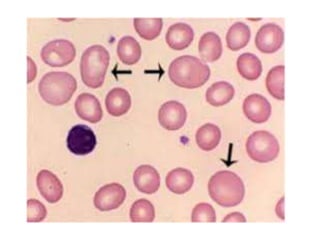
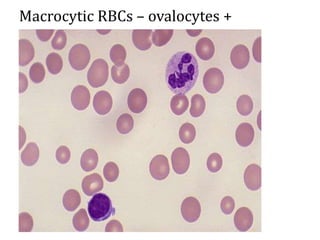
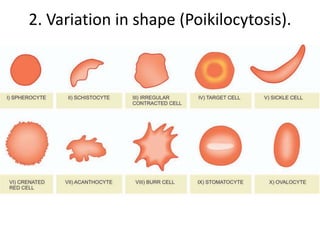
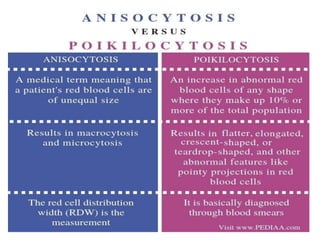
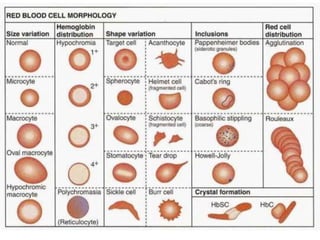
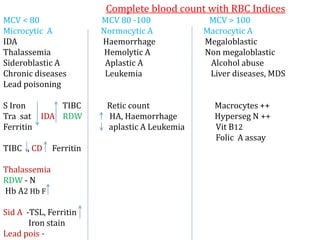
Anemia is defined as a hemoglobin level below the normal range based on age and sex. It can be classified based on red blood cell size (microcytic, normocytic, macrocytic) or pathophysiology (blood loss, impaired RBC production, increased RBC destruction). Common causes include iron deficiency, B12/folate deficiency, blood loss, hemolytic disorders, and bone marrow disorders.
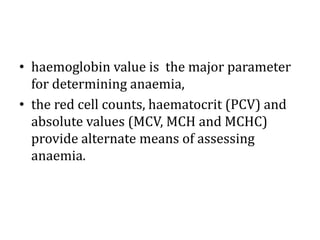
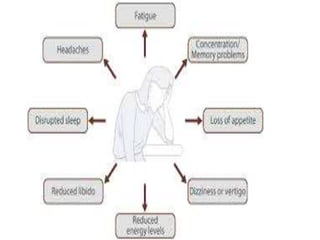
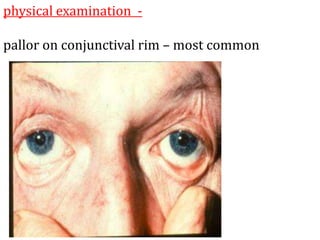
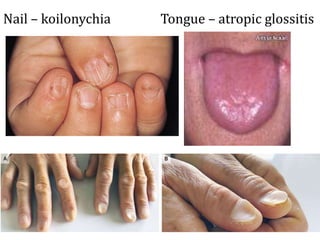
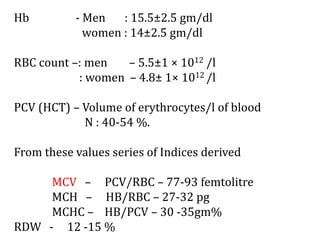
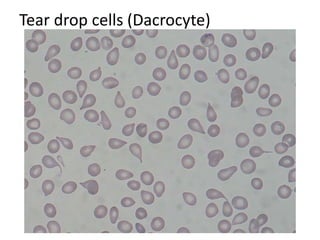
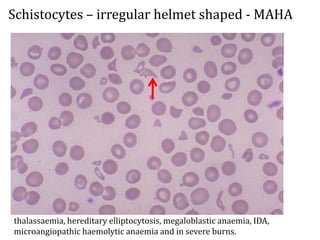
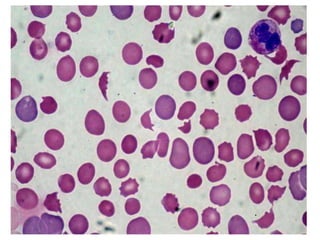
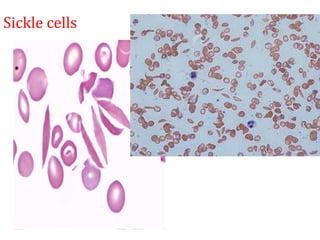
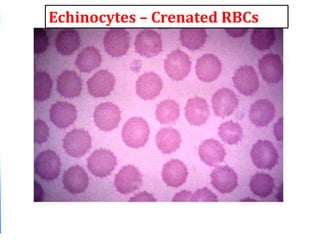
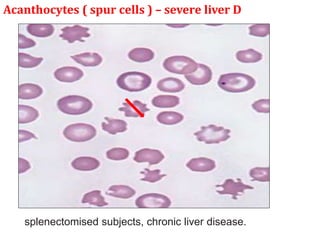
Clinical features depend on the severity and speed of onset of anemia. Laboratory evaluation includes complete blood count, RBC indices, peripheral smear, and additional