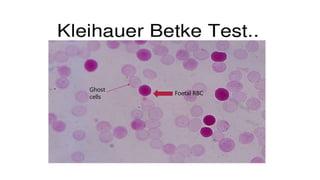
Rh isoimmunization occurs when a Rh-negative mother develops antibodies against Rh-positive fetal red blood cells. This can cause hemolytic disease in future Rh-positive pregnancies. Prophylaxis with Rh immunoglobulin is highly effective at preventing sensitization. For sensitized pregnancies, maternal anti-D titers and fetal middle cerebral artery Doppler are used to monitor for anemia. Severe anemia may require cordocentesis or intrauterine transfusions. After delivery, affected newborns may need exchange transfusions or other supportive care to manage hyperbilirubinemia and anemia. Prompt and specialized treatment can help prevent complications in isoimmunized pregnancies.