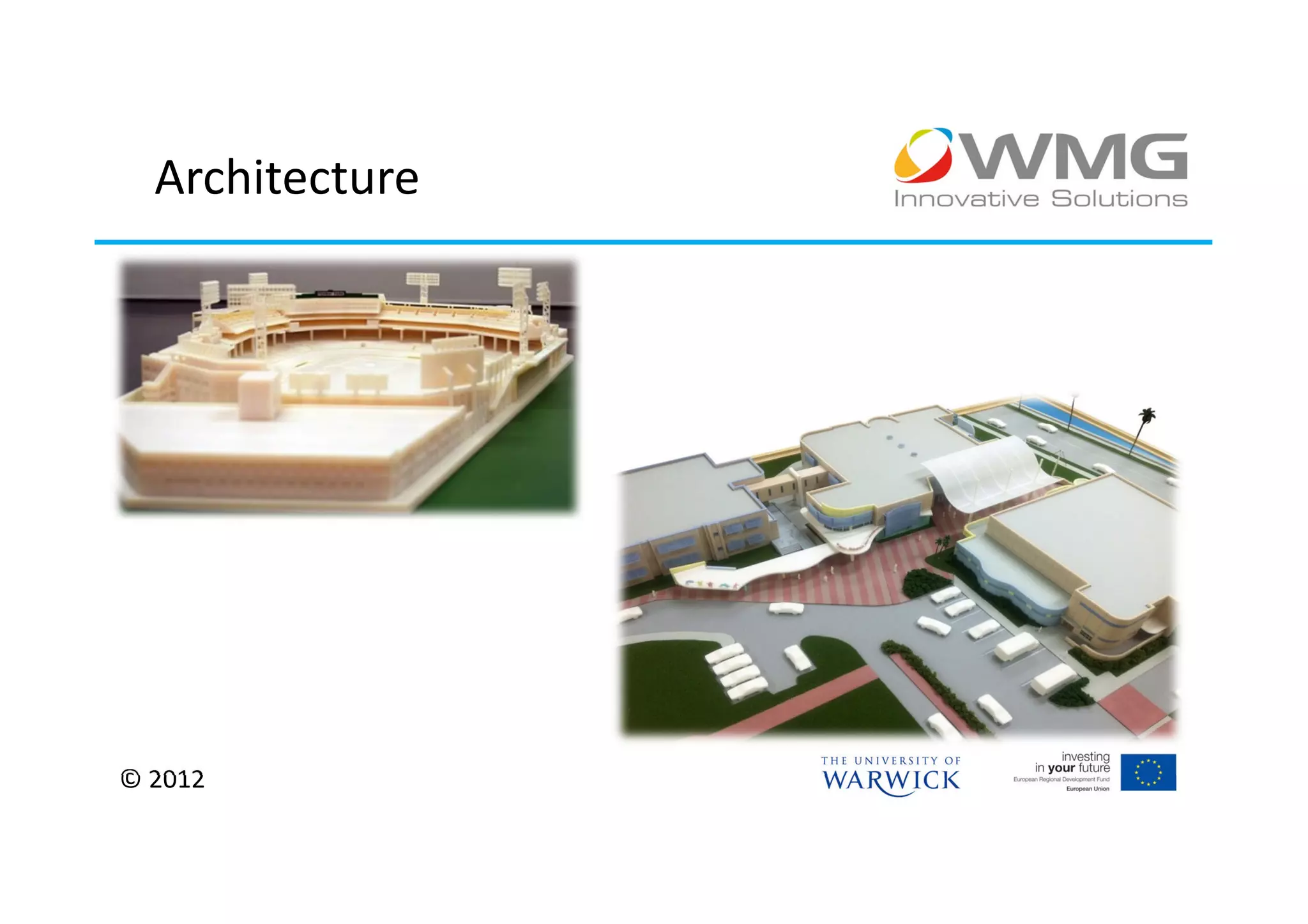
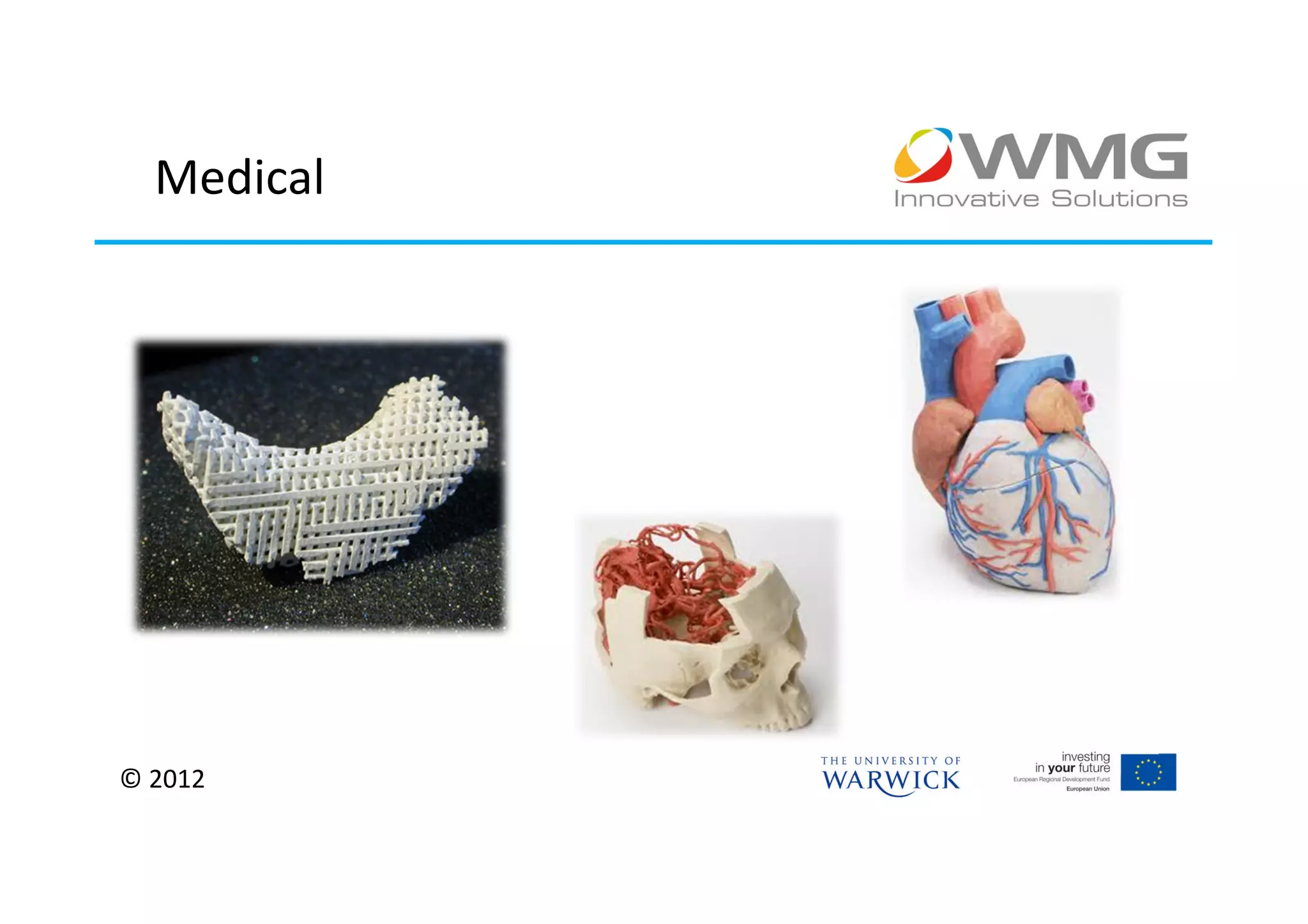
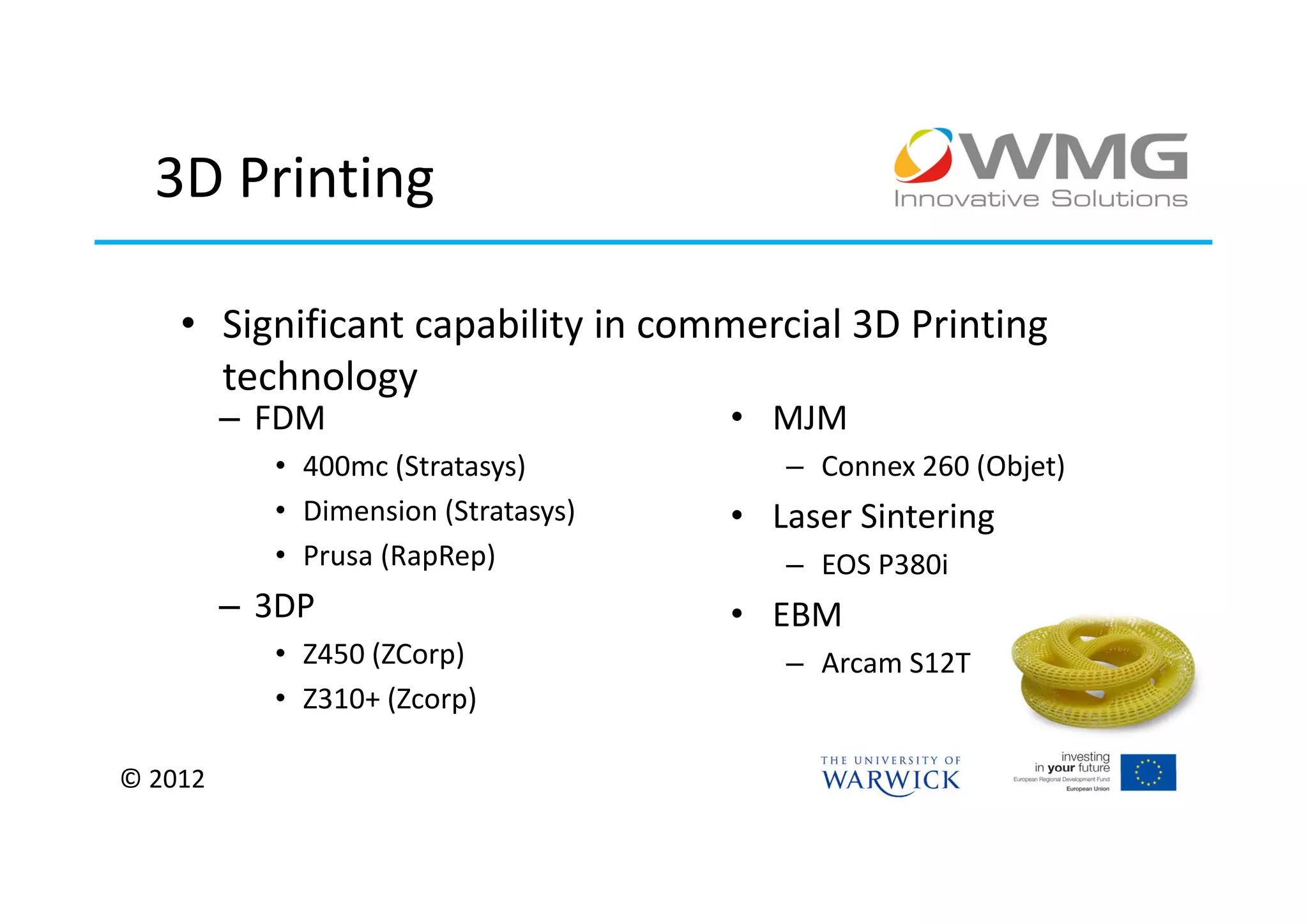
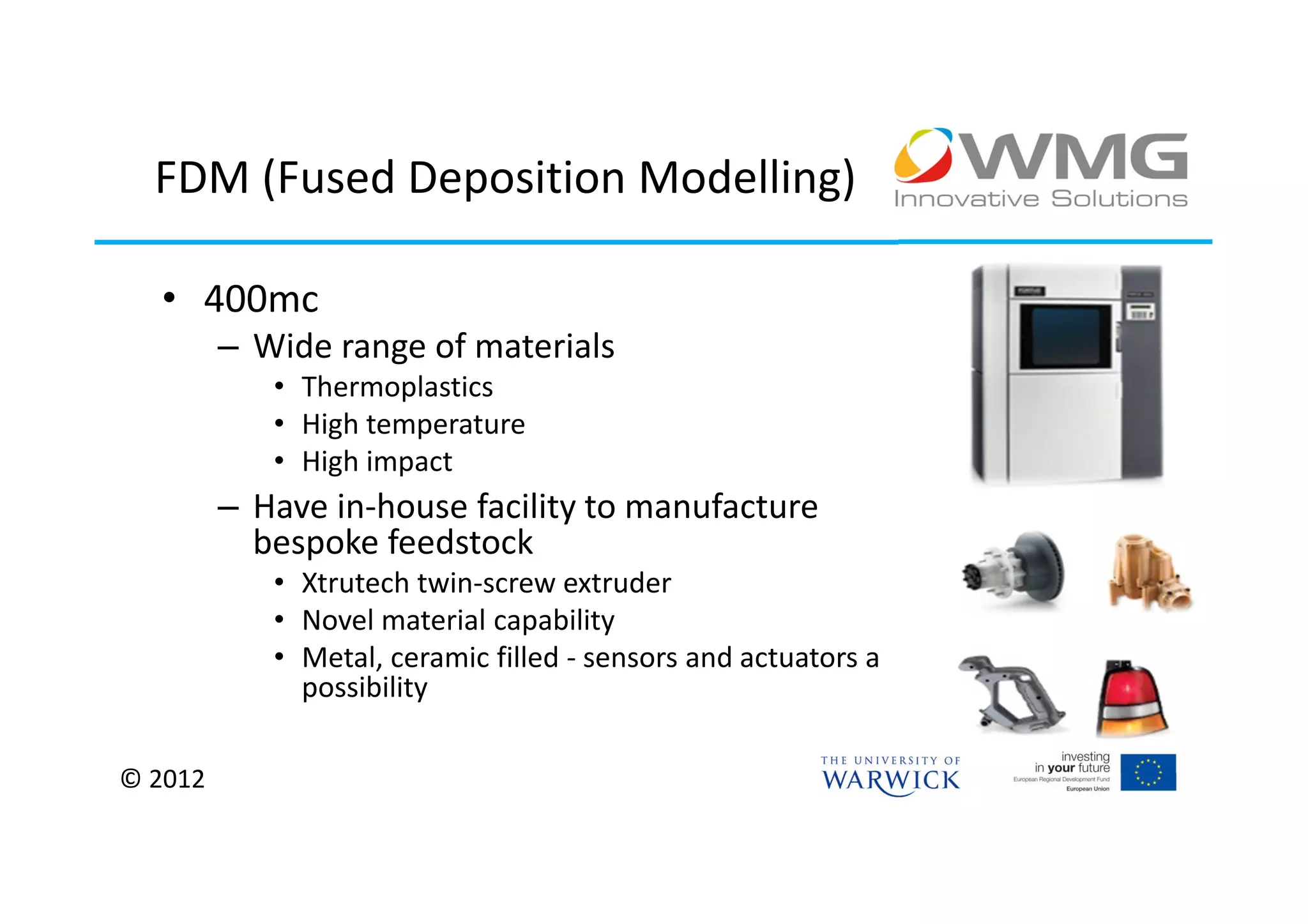
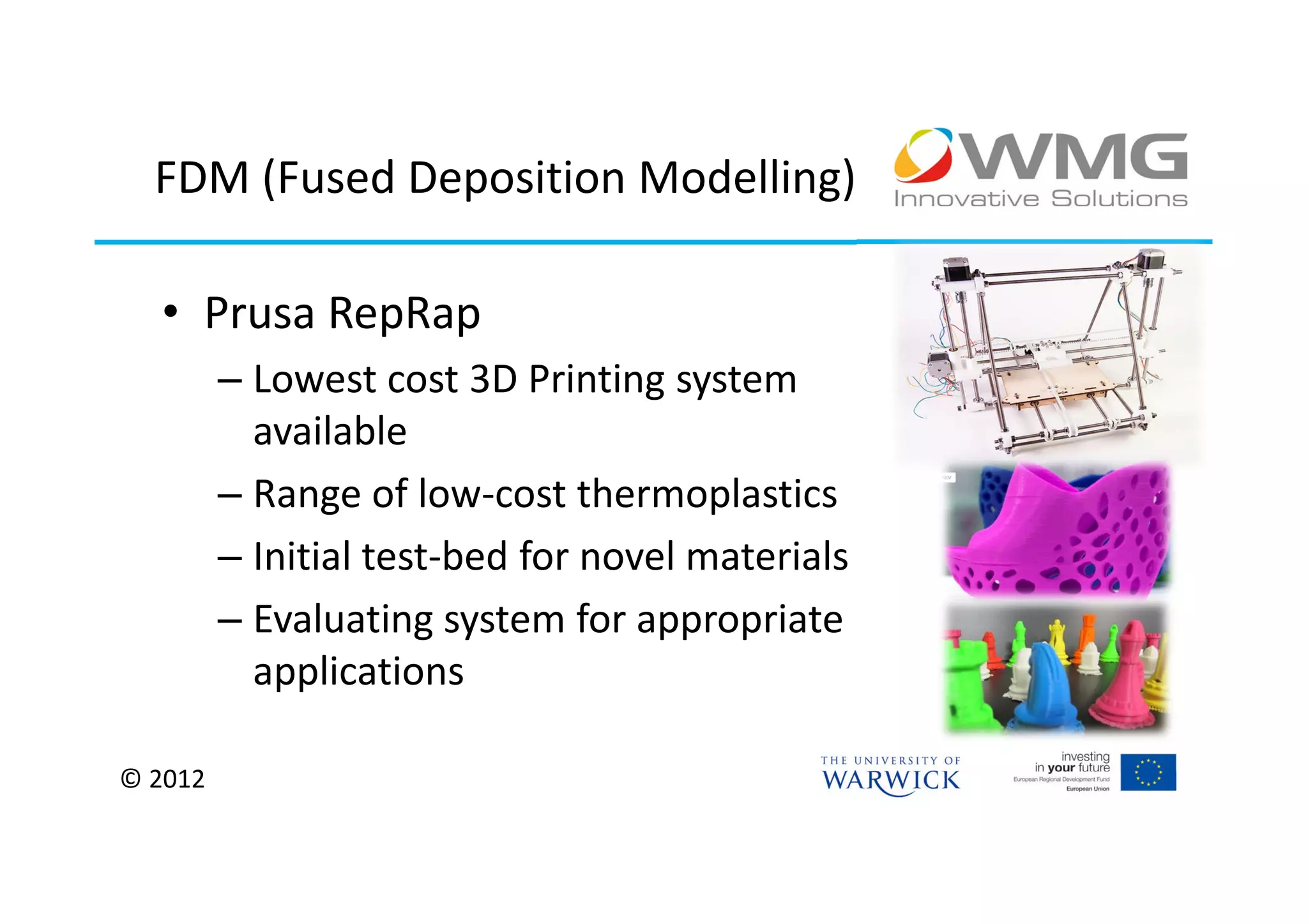
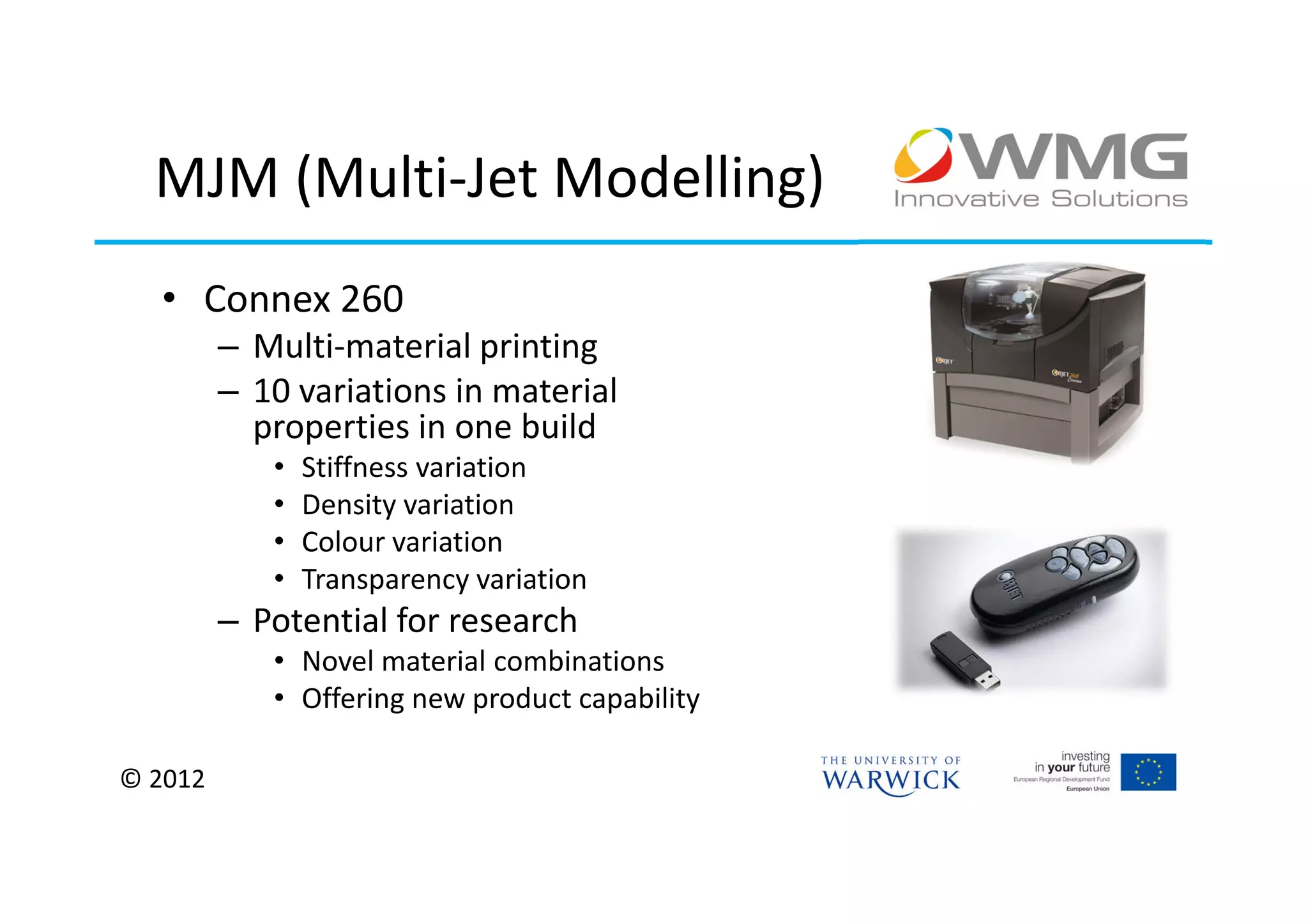
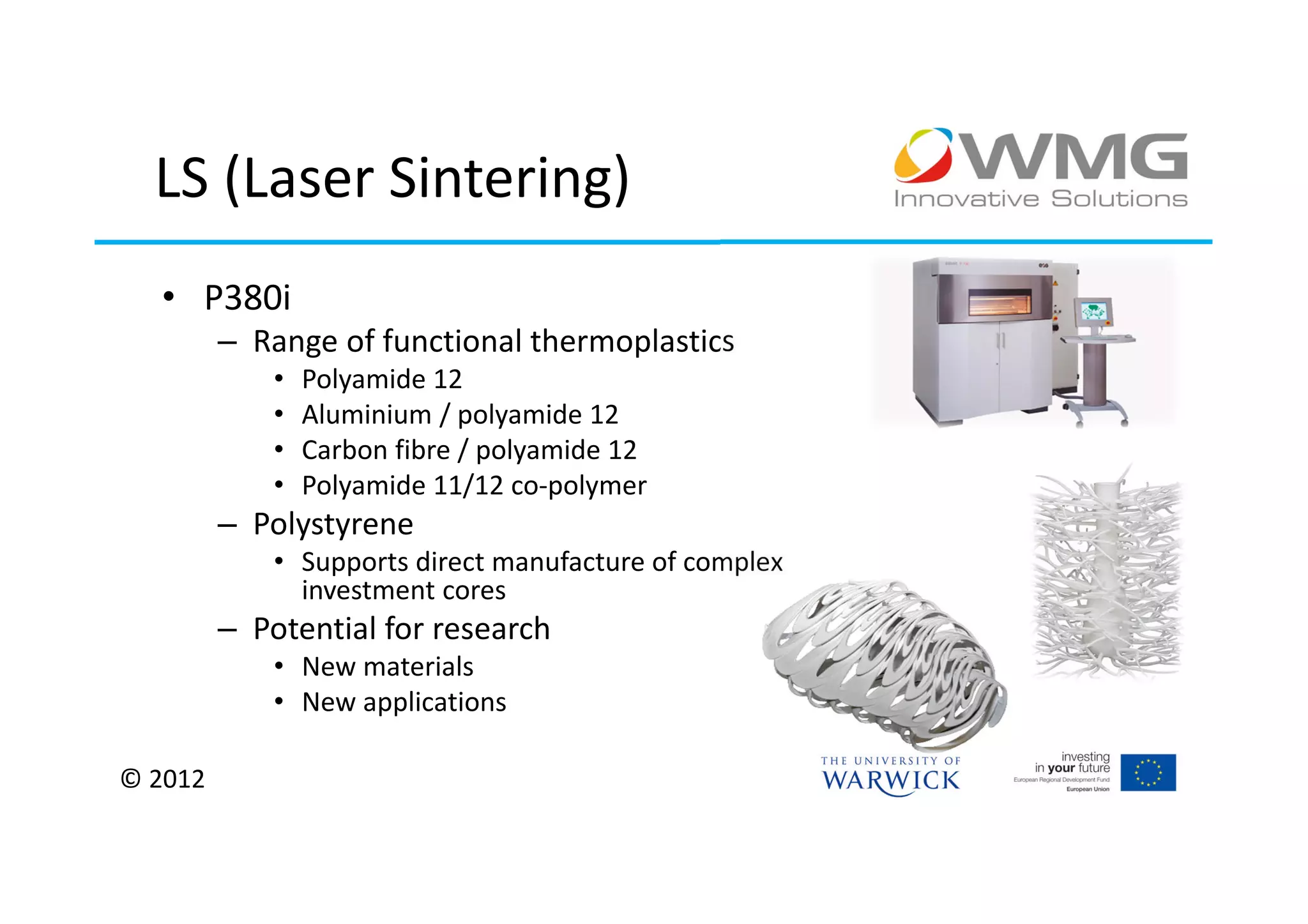
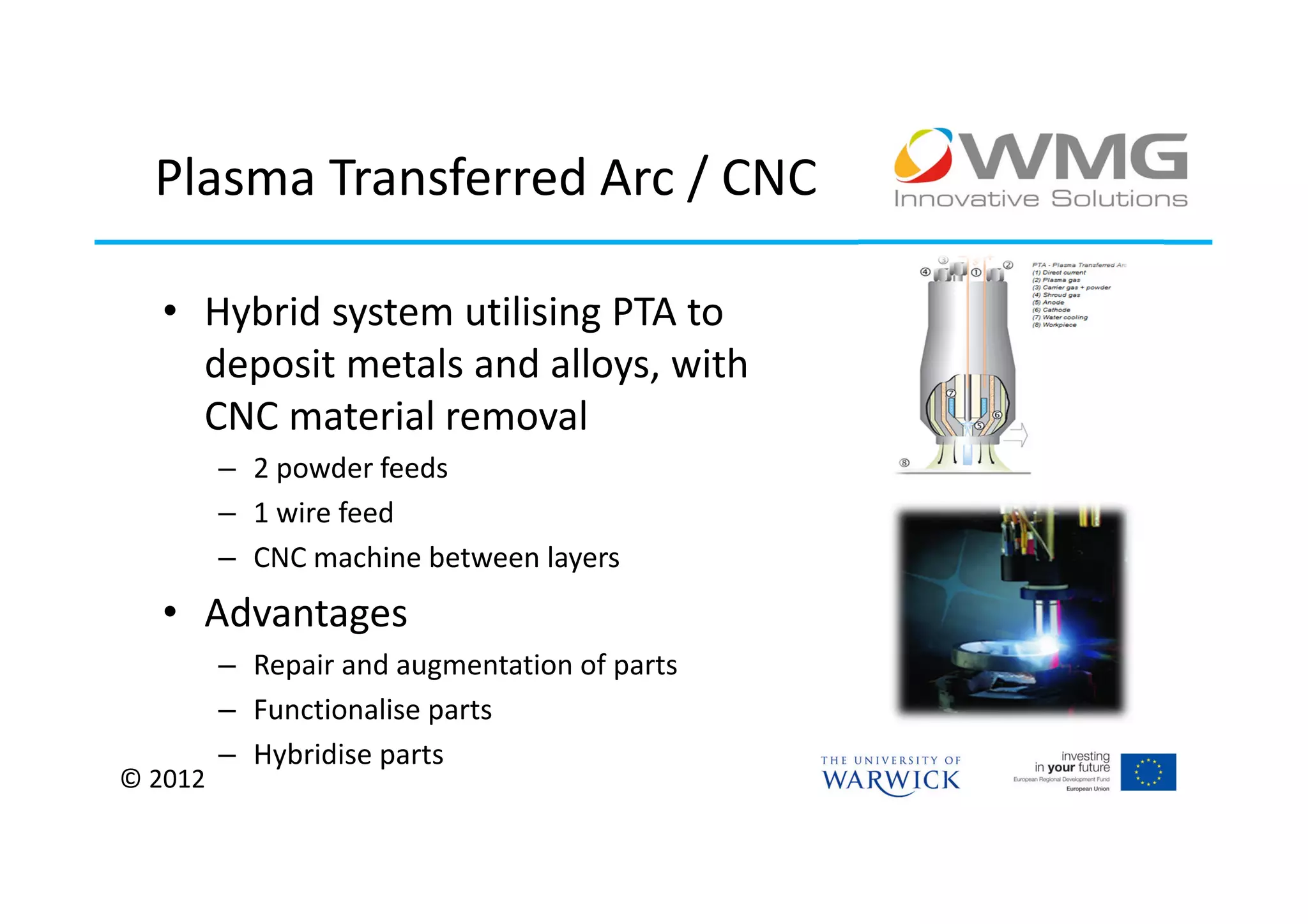
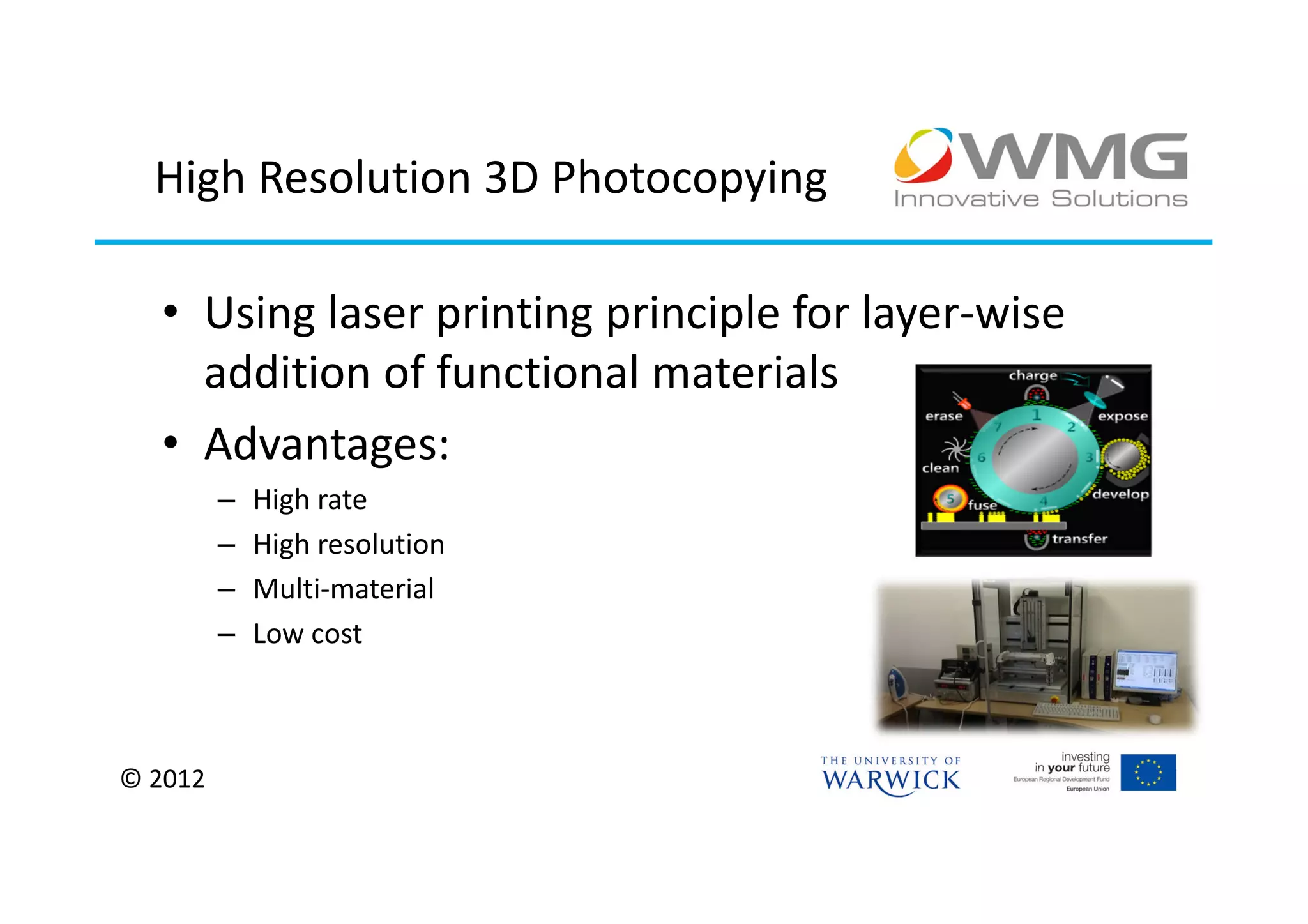
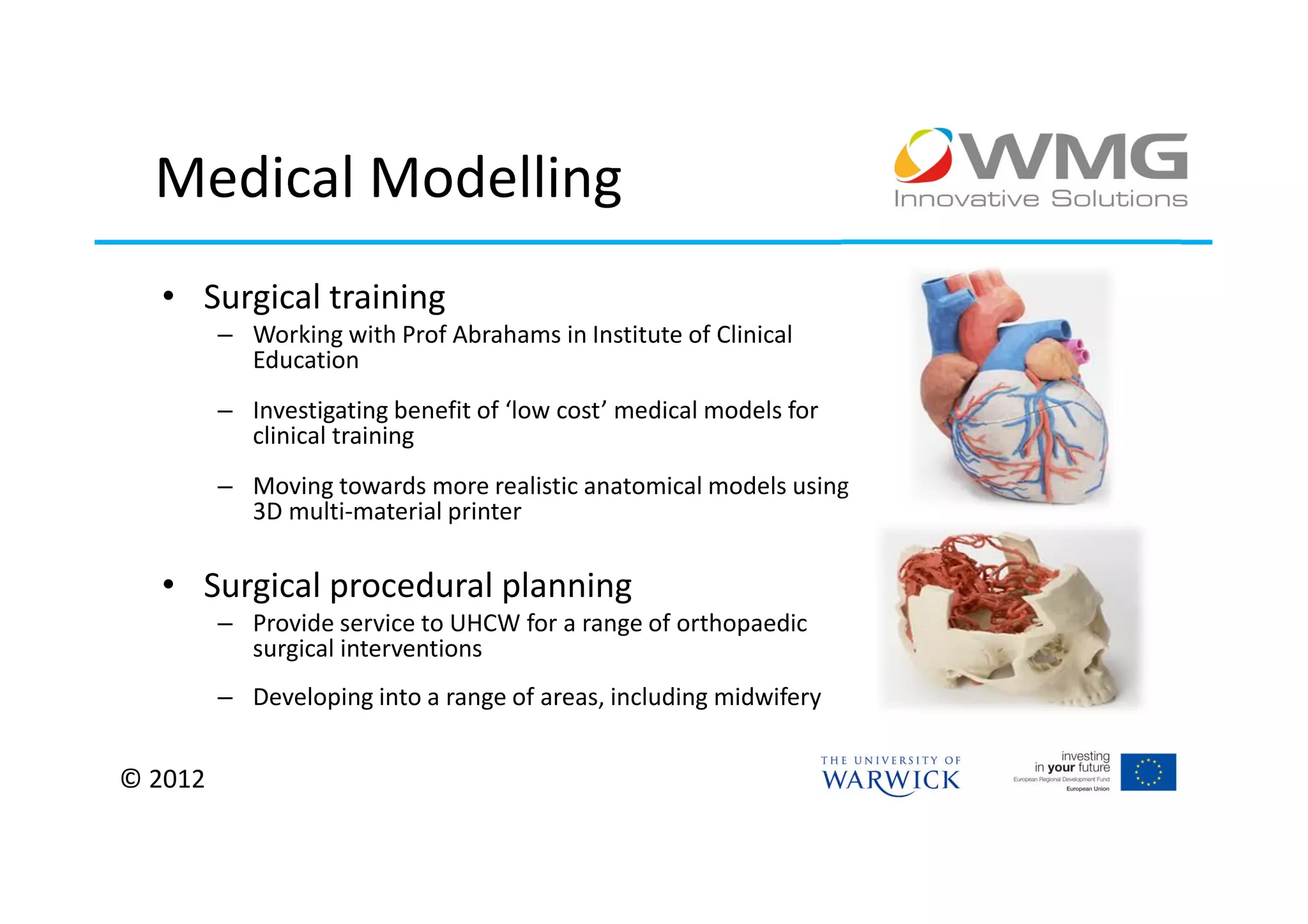
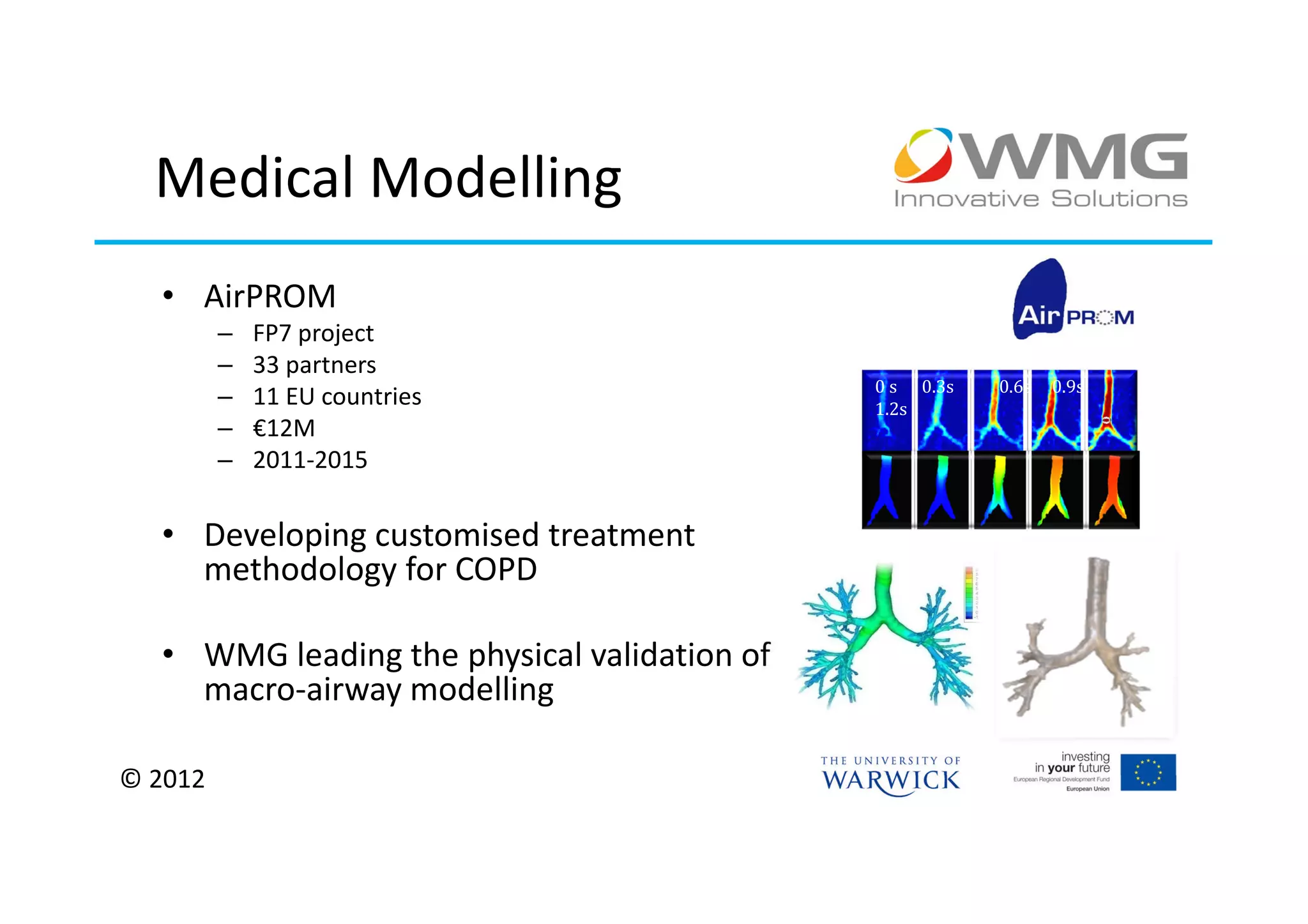
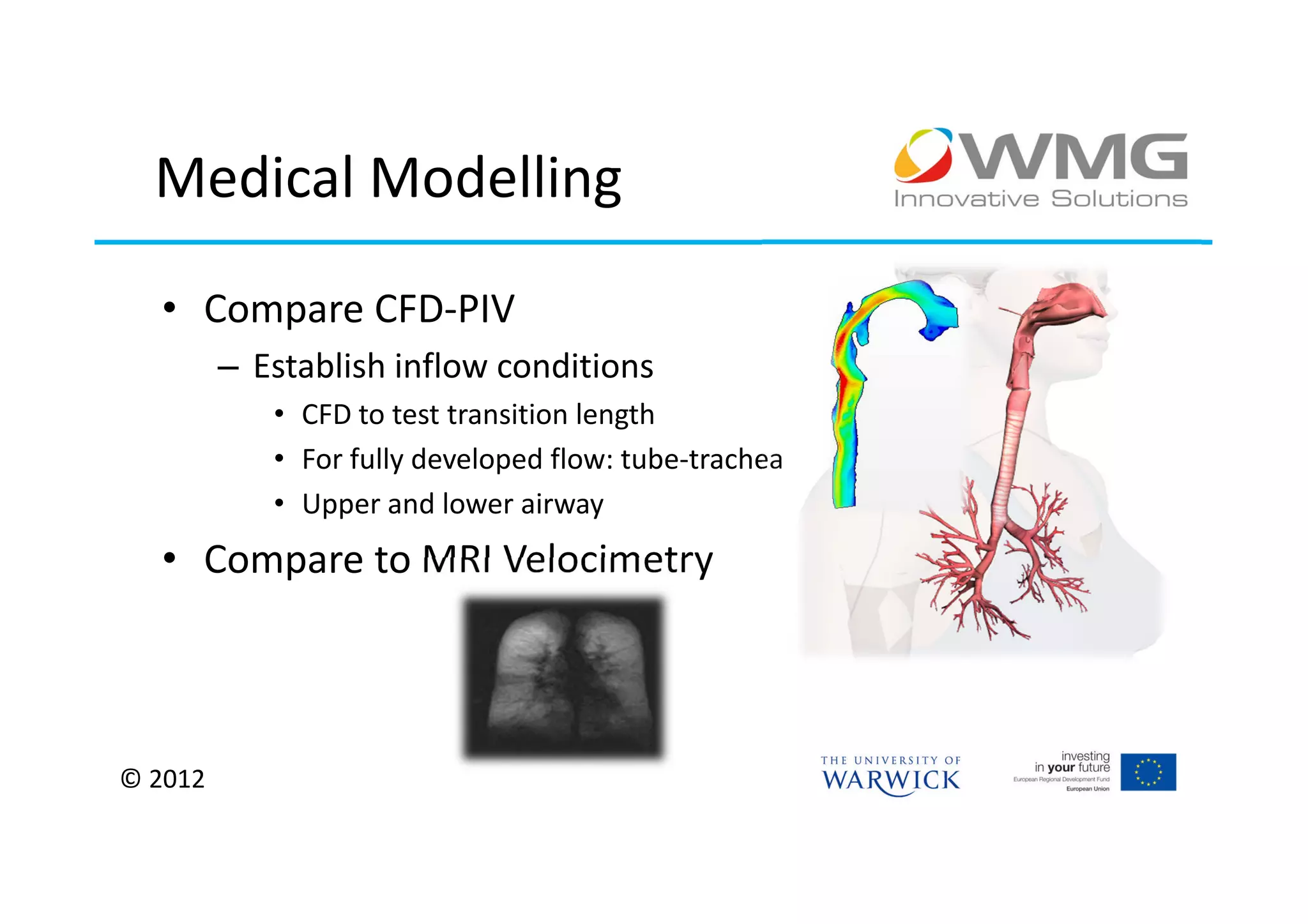
The document discusses various applications of 3D printing including architecture, marketing, medicine, furniture, fashion, animation, and small-medium enterprises. It then details the 3D printing capabilities at IIPSI including fused deposition modeling (FDM), multi-jet modeling (MJM), laser sintering, and electron beam melting. Research activities exploring metallic and composite 3D printing, high resolution hybrid deposition, medical modeling, and low cost 3D printing are also summarized.