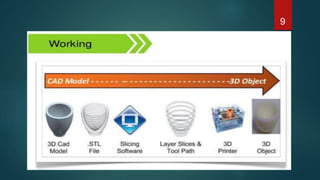
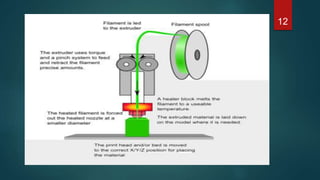
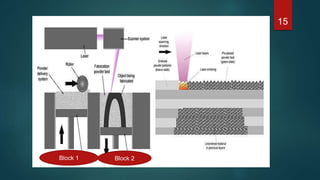
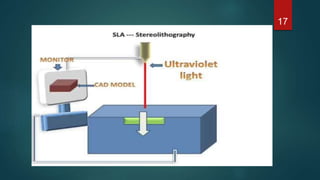
This document provides an overview of 3D printing. It discusses the history of 3D printing, how 3D printing works by building objects layer by layer, and common 3D printing processes like fused deposition modeling, selective laser sintering, and stereolithography. The document also outlines advantages such as reducing waste and allowing for testing of designs before production. Limitations include the costs of materials and equipment as well as speed. Applications of 3D printing span various fields like art, music, engineering, automotive, and medicine. In conclusion, 3D printing offers benefits of time, cost, and resource savings for manufacturing.