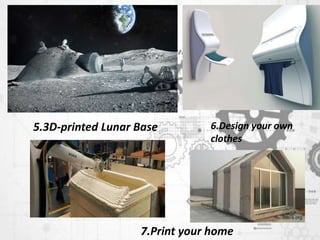
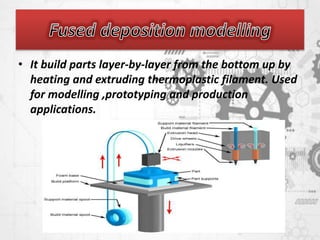
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, involves using 3D modeling software to slice a digital design into layers, then depositing materials layer by layer to construct a physical object. Common materials used include plastics, metals, concrete, and potentially human tissue. The key advantages of 3D printing include the ability to customize products, produce prototypes rapidly and at low cost, and eliminate storage and shipping costs. Potential future applications include producing complex engine and aircraft parts, 3D printed lunar bases, and even printing entire homes.









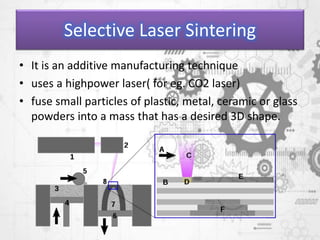
![Stereolithography
• stereolithography apparatus, optical fabrication, photo-
solidification, or resin printing
• form of 3D printing technology used for
creating models, prototypes, patterns, and production parts
in a layer by layer fashion
• using photopolymerization, a process by which light causes
chains of molecules to link, forming polymers.[1] Those
polymers then make up the body of a three-dimensional
solid](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-181110132604/85/Presentation1-ppt-3-d-printing-11-320.jpg)



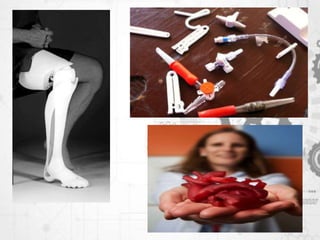
![7.).Medical
• BIOPRINTING
• Three dimensional (3D) bioprinting is the utilization of 3D
printing and 3D printing–like techniques to combine cells,
growth factors, and biomaterials to fabricate biomedical
parts that maximally imitate natural tissue
characteristics.[1] Generally, 3D bioprinting utilizes the layer-
by-layer method to deposit materials known as bioinks to
create tissue-like structures that are later used in medical
and tissue engineering fields. Bioprinting covers a broad
range of biomaterials.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-181110132604/85/Presentation1-ppt-3-d-printing-16-320.jpg)