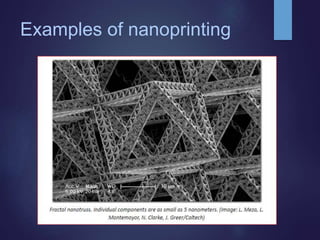
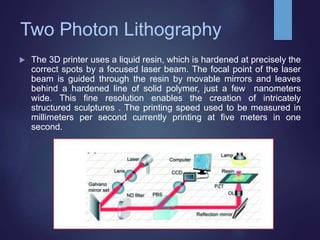
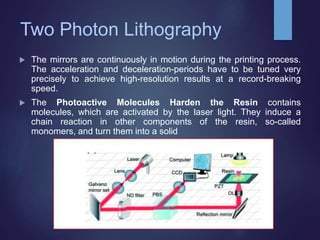
Nano 3D printing utilizes two-photon lithography to create intricate nanostructures with remarkable precision and speed, enabling applications in fields like medicine and biosensors. A breakthrough at the Vienna University of Technology has significantly increased the printing speed, allowing for the fabrication of highly detailed objects within minutes. This advanced manufacturing technology promises improved efficiency and less waste in nanofabrication, mirroring the benefits seen in traditional additive manufacturing.