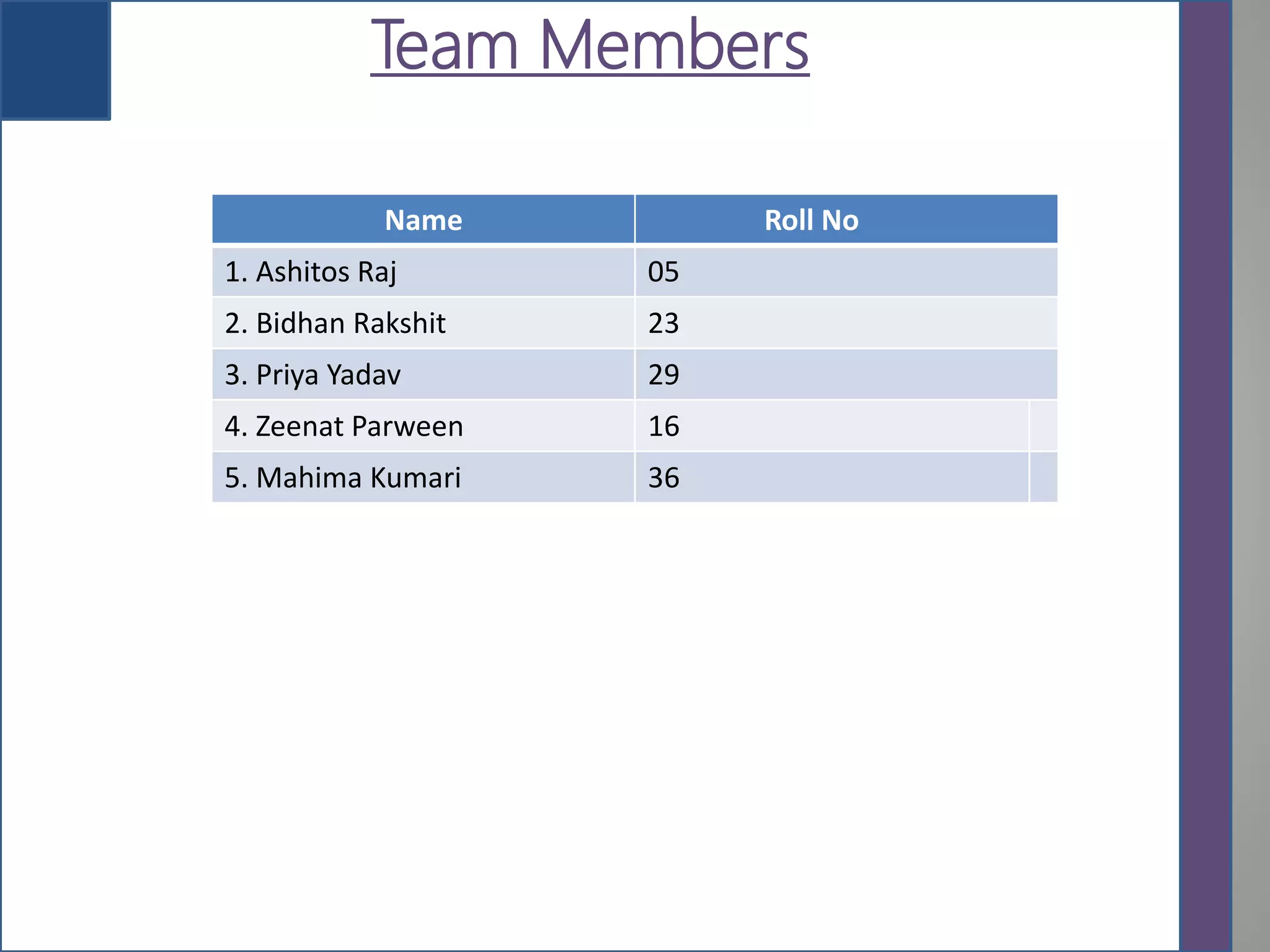
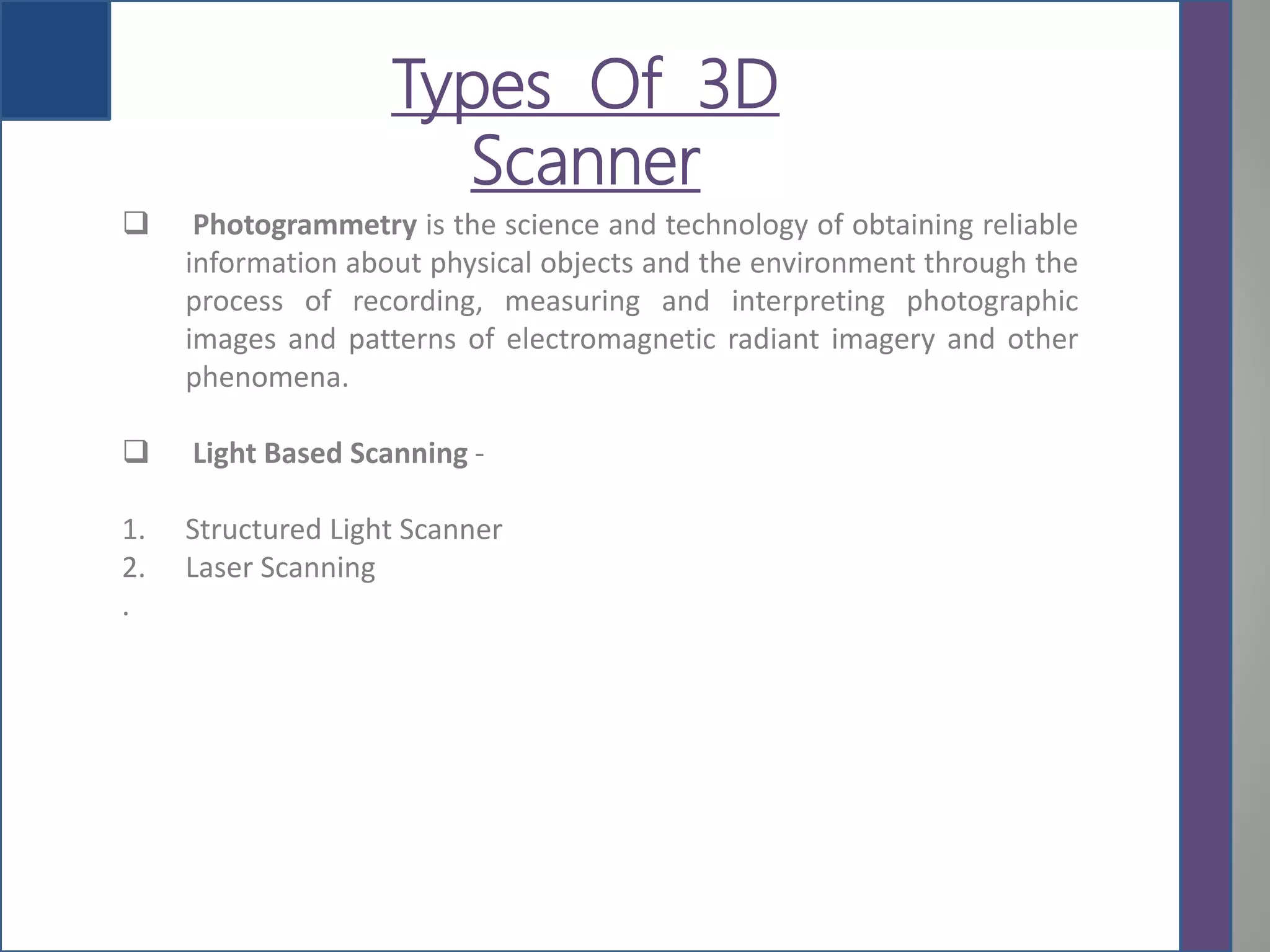
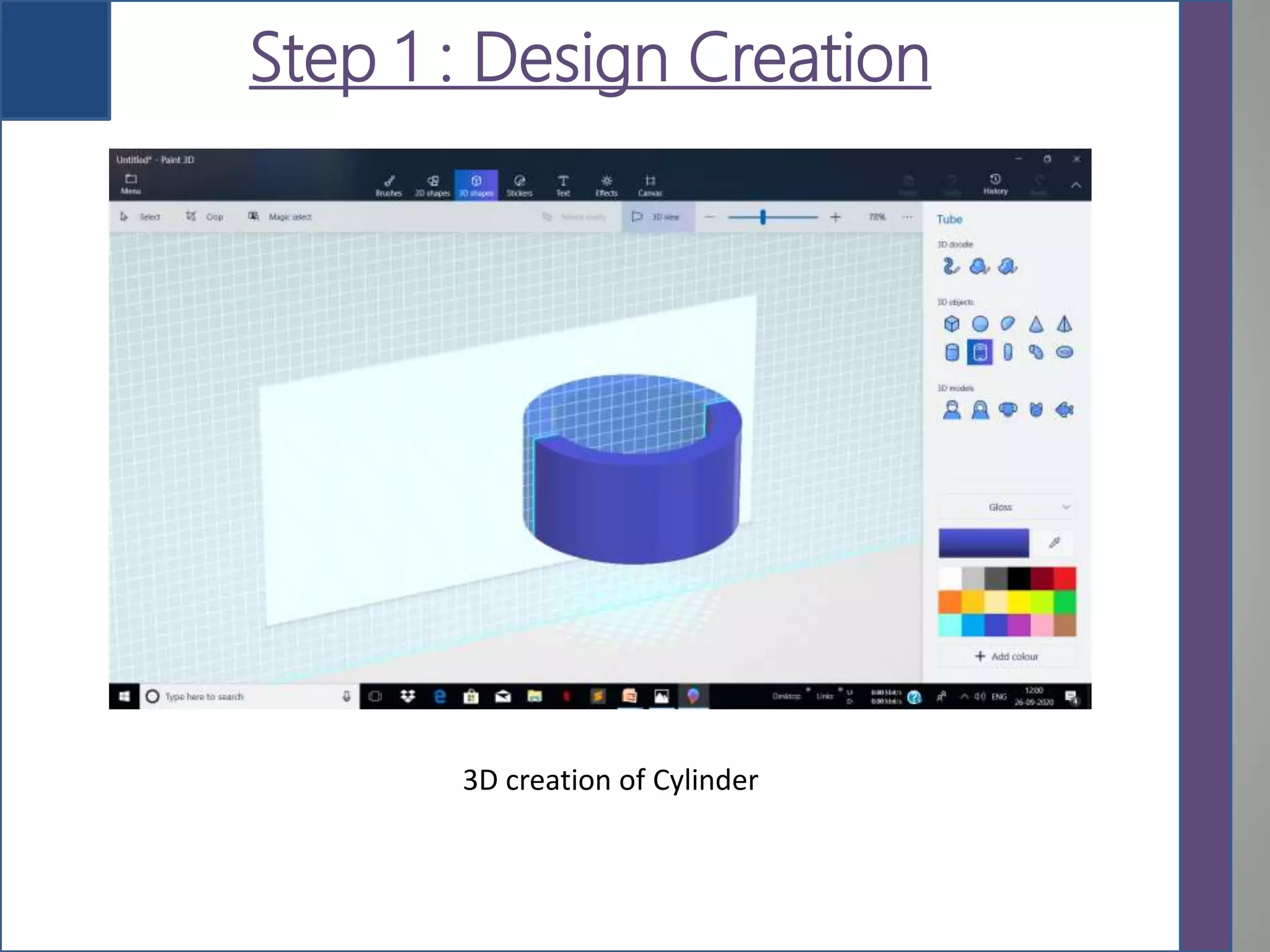
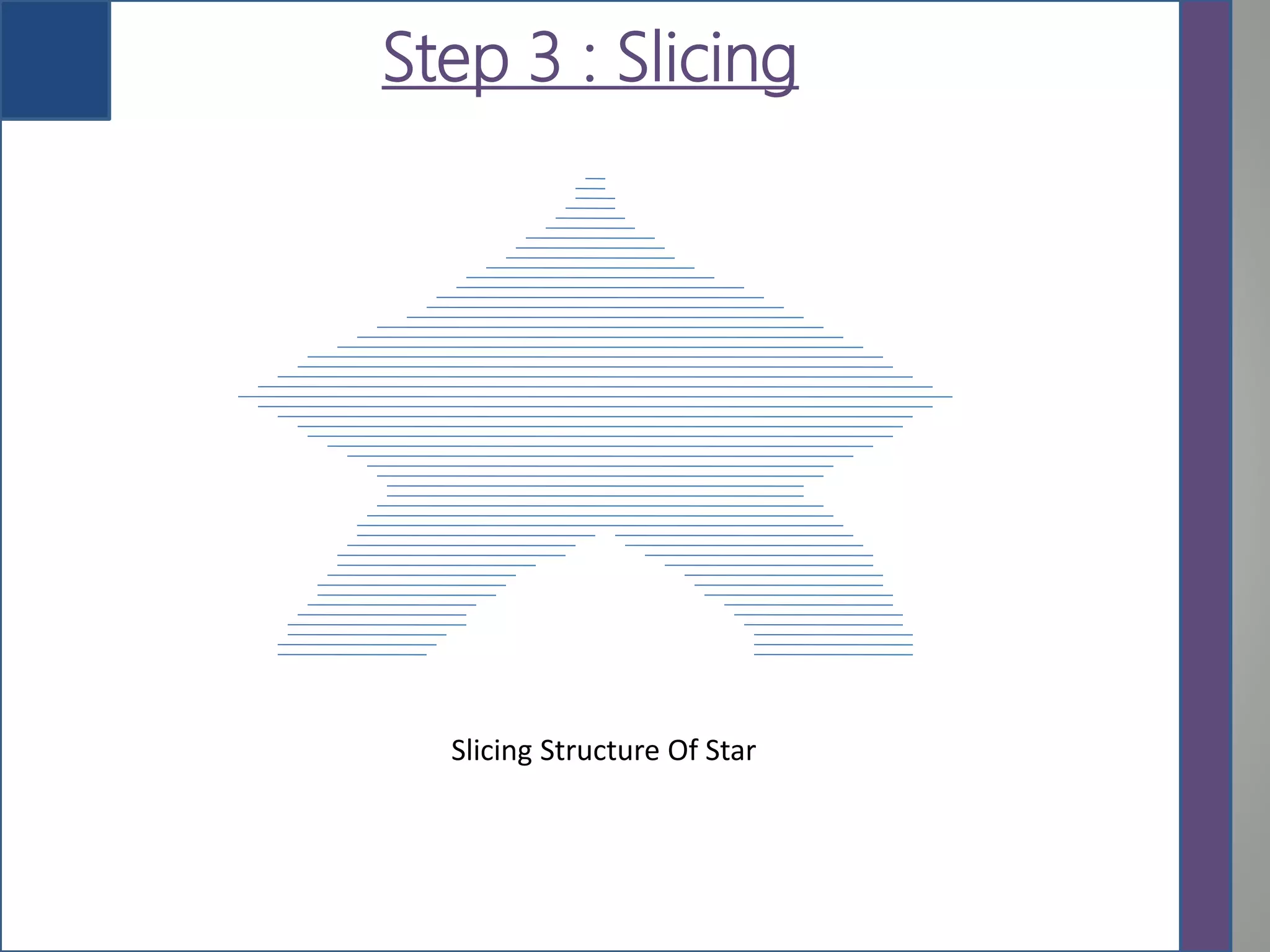
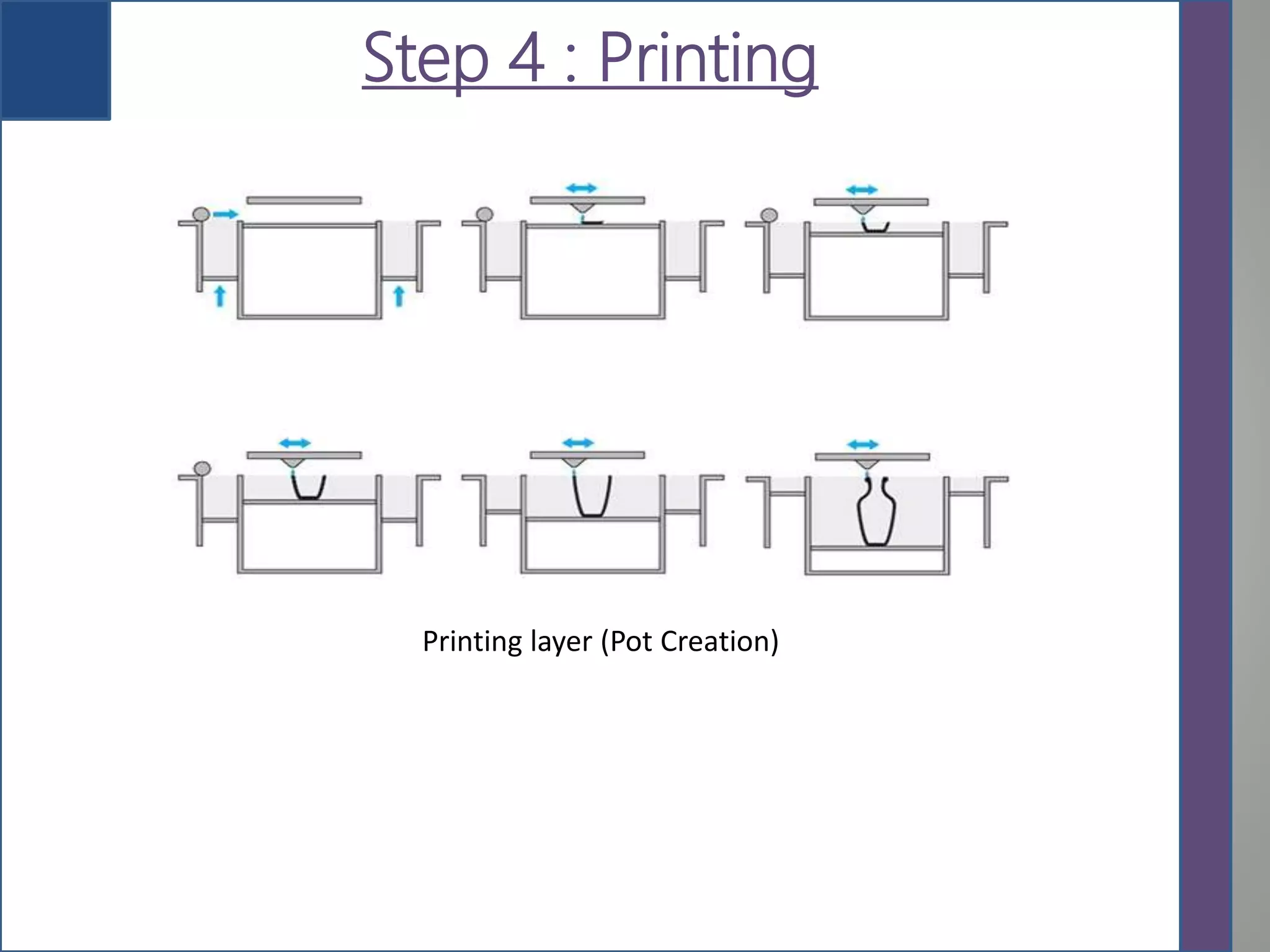
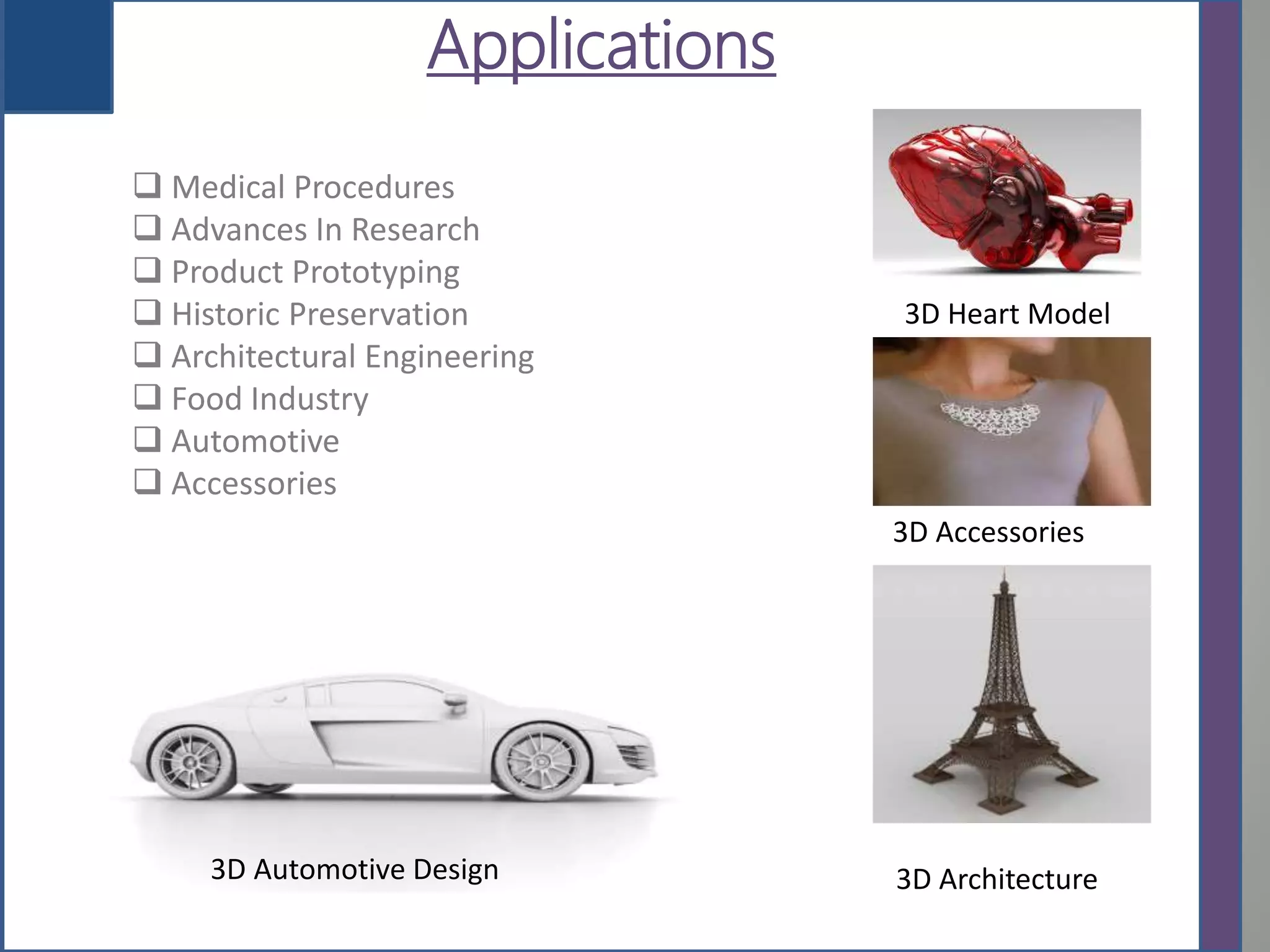
This document provides an overview of 3D printing, detailing its history, types of scanners, components, materials used, working process, software requirements, advantages, limitations, applications, and future scope. It highlights the evolution of 3D printing technology from its inception in the 1980s to its contemporary applications in various industries. The conclusion notes the ongoing challenges in adopting 3D printing for large-scale construction projects.