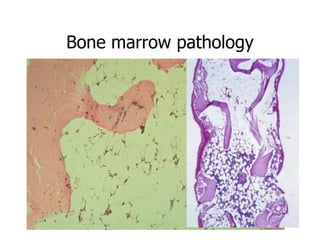
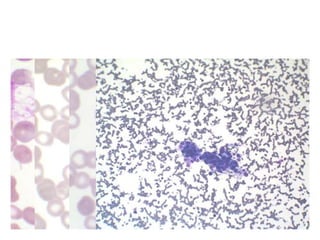
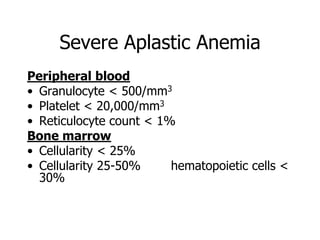
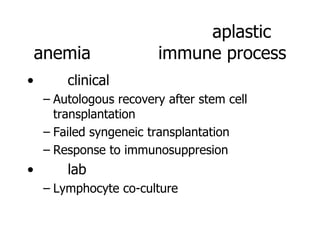
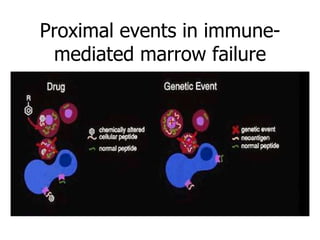
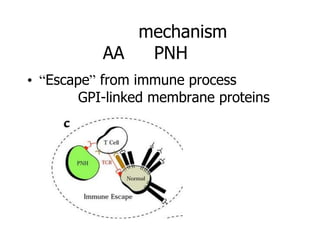
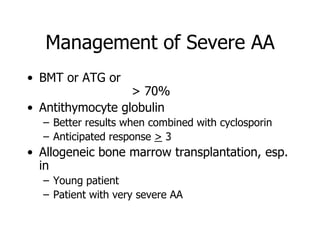
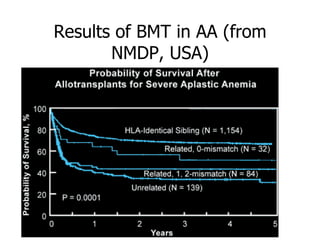
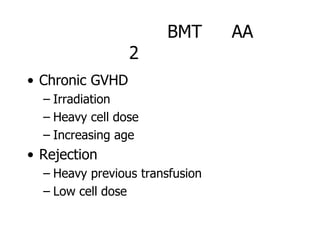
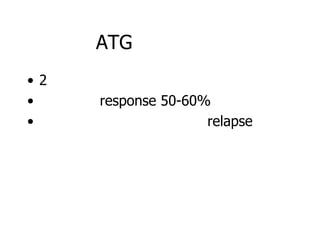
Aplastic anemia is a bone marrow failure syndrome characterized by pancytopenia and a hypocellular bone marrow. It is diagnosed through a bone marrow biopsy showing fewer than 25% of normal hematopoietic cells. The causes of aplastic anemia include exposure to toxins, certain drugs, viruses, and an immune-mediated process destroying hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow. Treatment involves immunosuppressive therapy with antithymocyte globulin and cyclosporine, or allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for severe cases. Long term management focuses on supportive care through blood product transfusions and monitoring for complications.