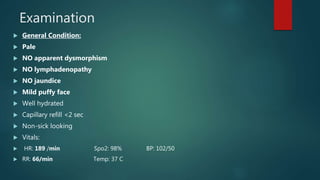
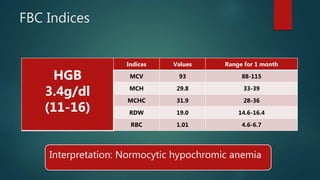
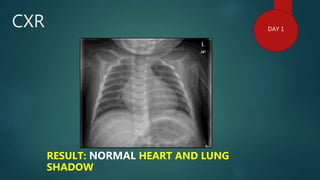
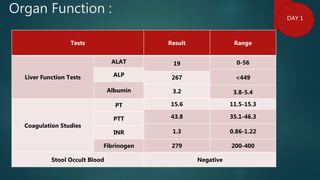
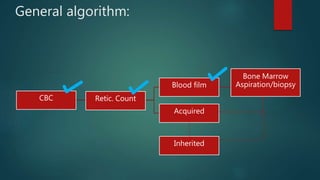
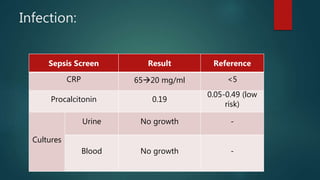
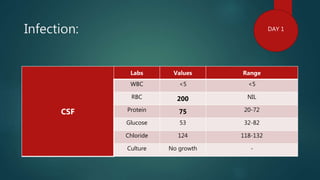
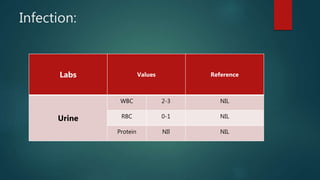
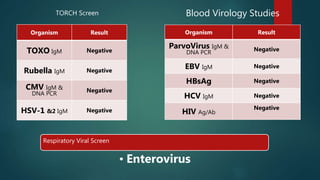
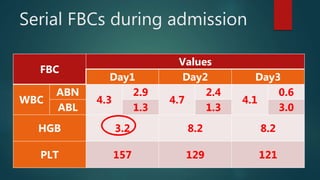
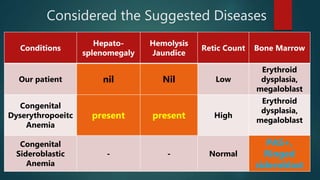
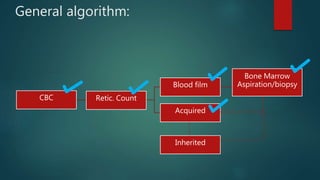
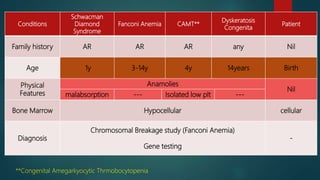
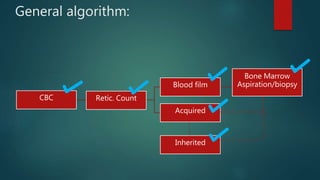
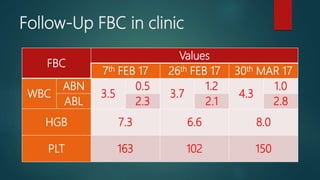
1) A 1.5 month boy presented with fever and pancytopenia. Examination found pallor. Blood tests found normocytic anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia.
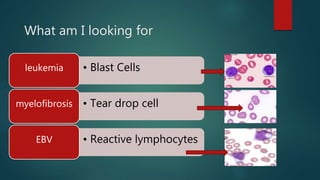
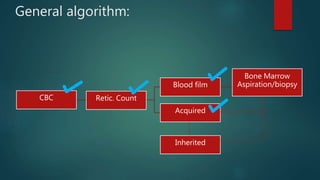
2) Bone marrow aspiration found erythroid dysplasia and megaloblastosis. Chromosomal breakage study and karyotyping were normal.
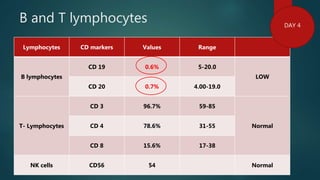
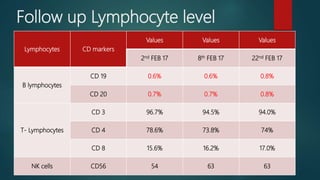
3) Flow cytometry found B cell immune deficiency. The pancytopenia and symptoms improved with supportive care.
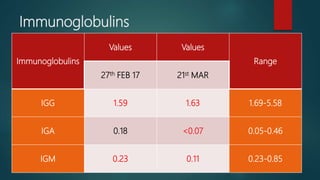
4) Genetic testing in Germany found a MYSM1 mutation, which has been associated with bone marrow failure and immunodeficiency. The patient will require long term supportive care including transfusions, immunoglobulins and G