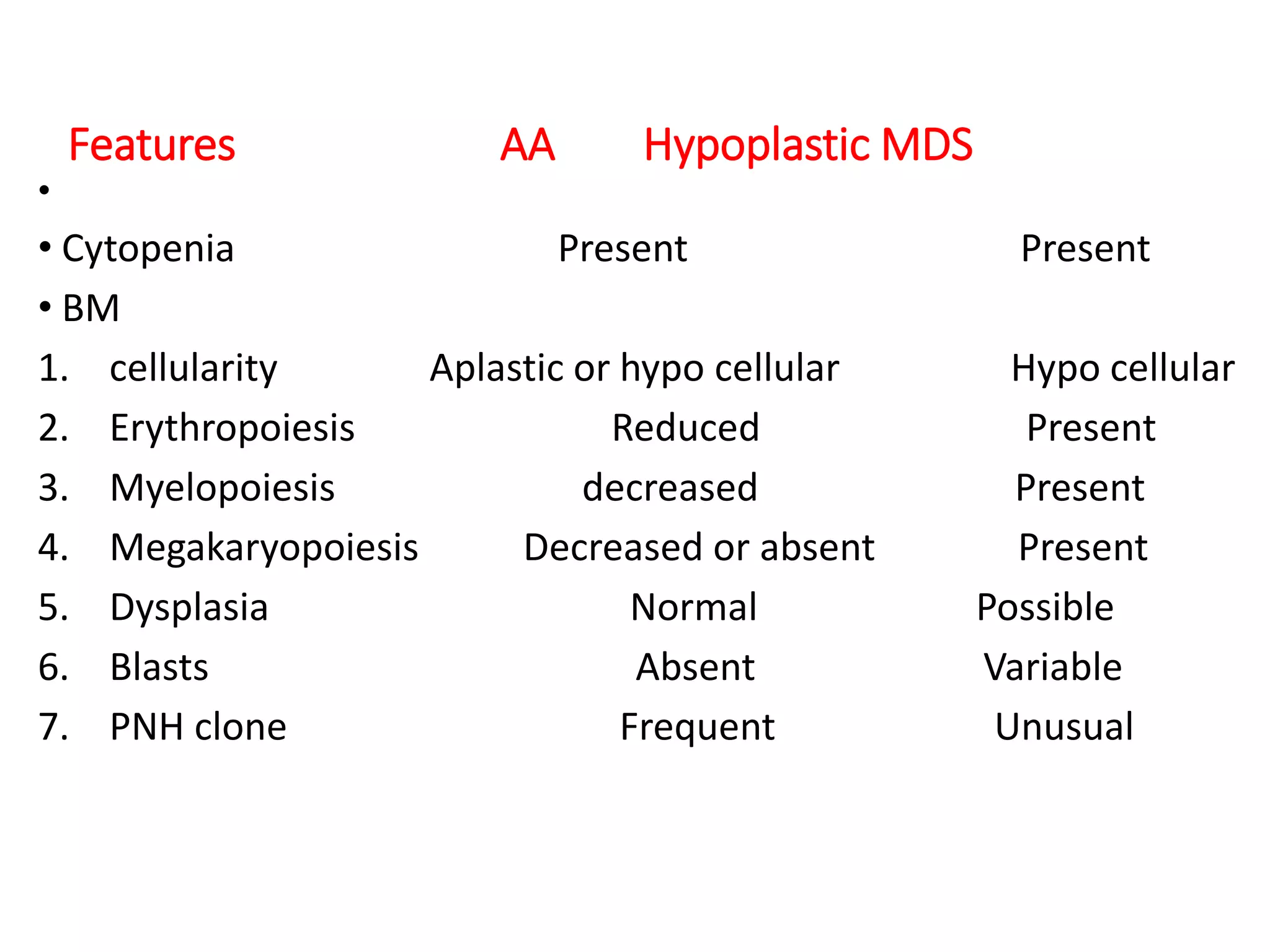
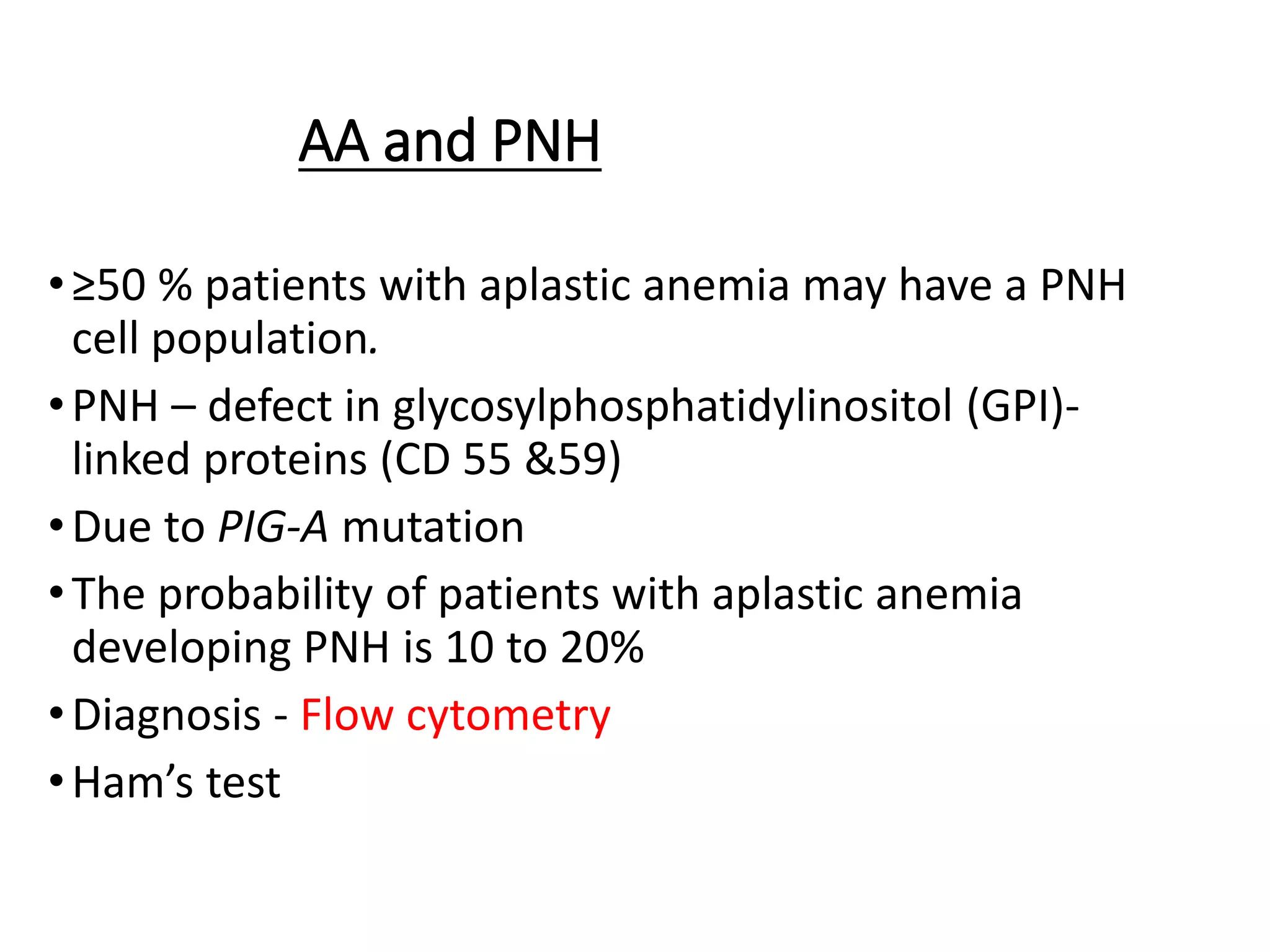
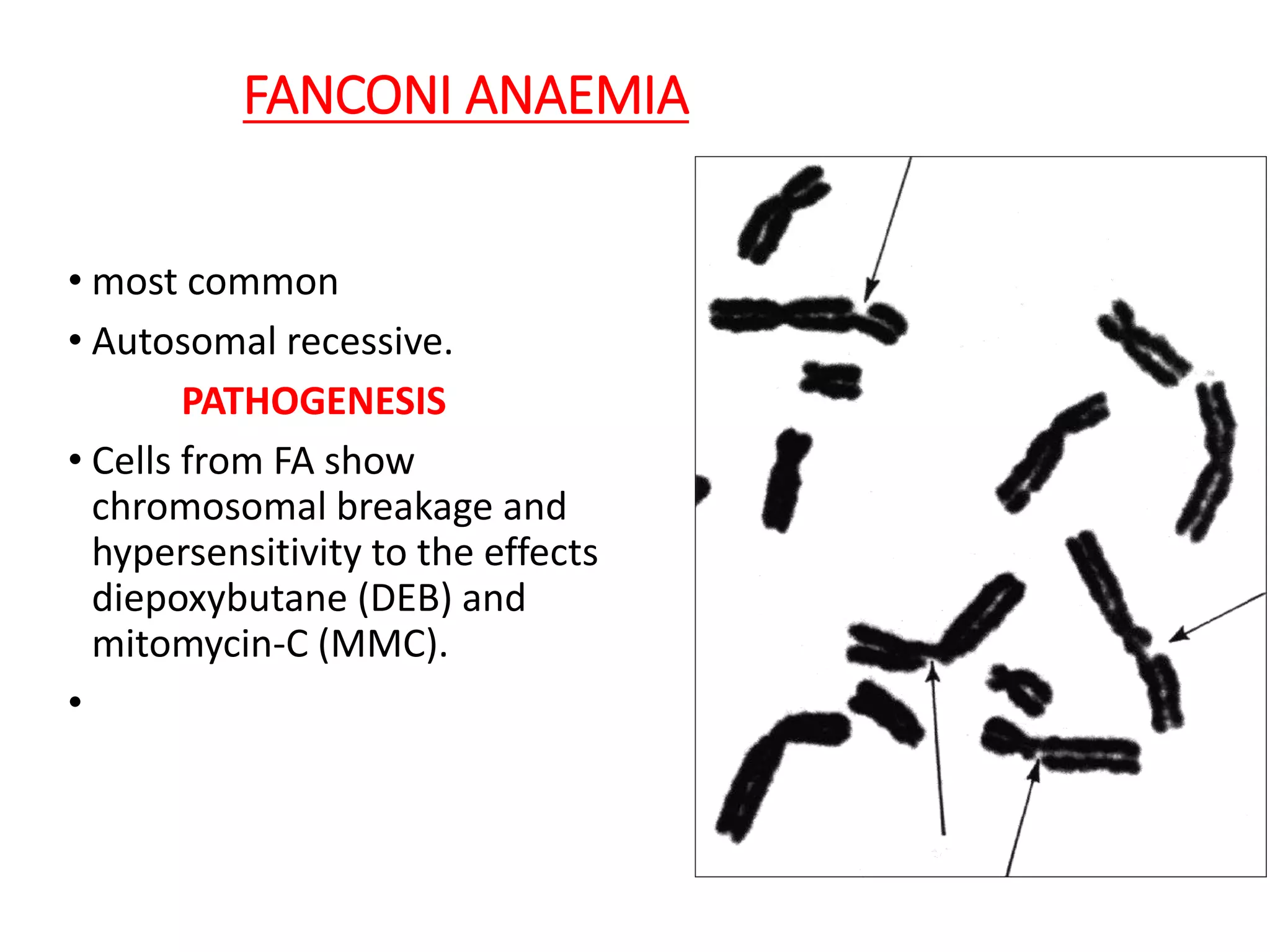
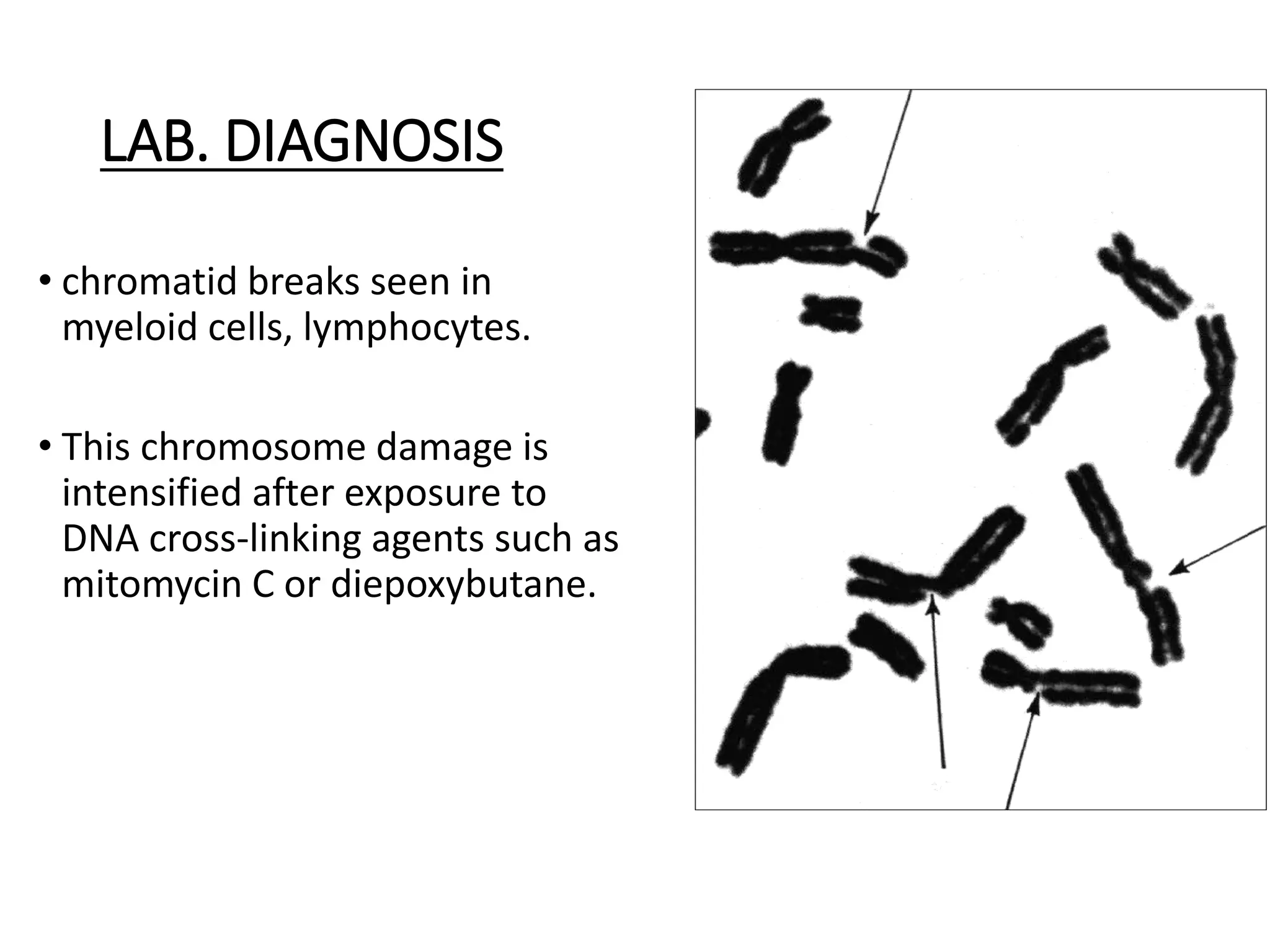
This document summarizes laboratory diagnosis of aplastic anemia. It describes how aplastic anemia is defined by pancytopenia, hypocellular bone marrow, and absence of abnormal cells. Laboratory evaluation includes complete blood count, reticulocyte count, bone marrow examination, and tests to identify causes. Bone marrow aspiration looks at cellularity and morphology while trephine biopsy assesses cellularity, infiltrative disease, fibrosis, and granulomas. Inherited forms of aplastic anemia include Fanconi anemia, dyskeratosis congenita, and Shwachman-Diamond syndrome. Laboratory diagnosis of these inherited types involves identifying characteristic features and genetic testing.