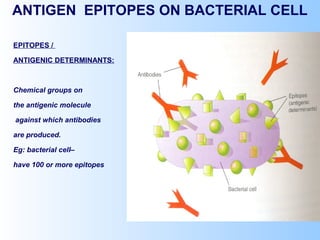
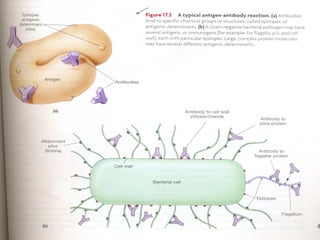
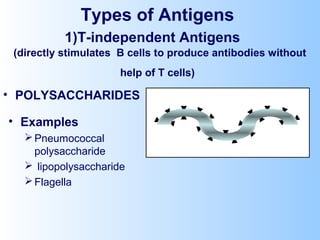
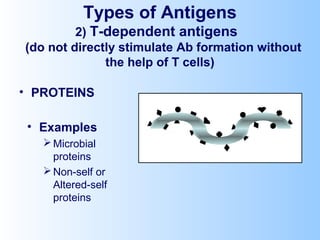
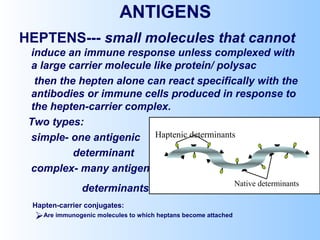
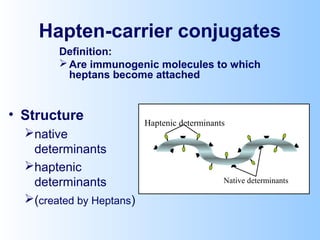
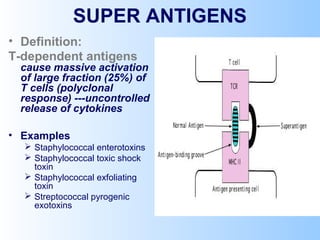
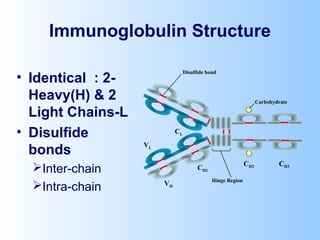
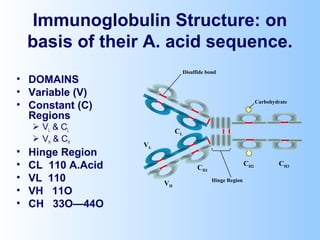
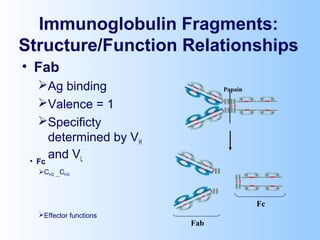
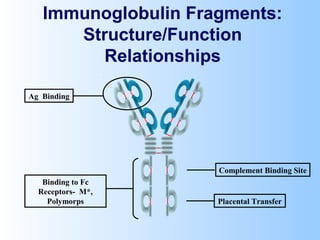
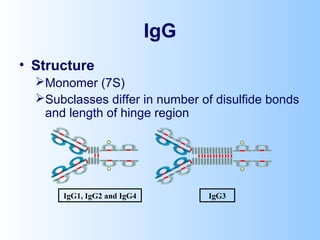
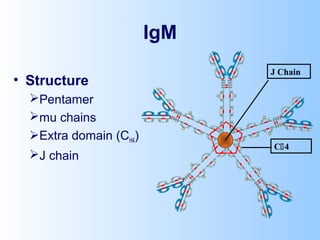
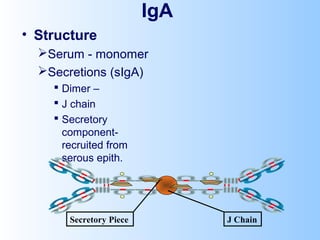
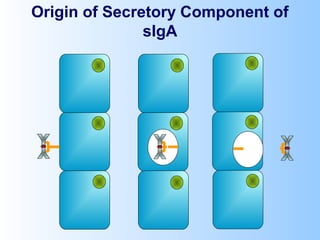
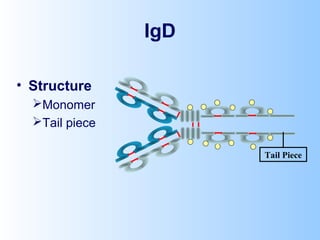
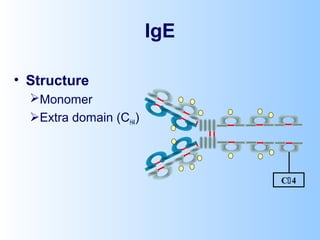
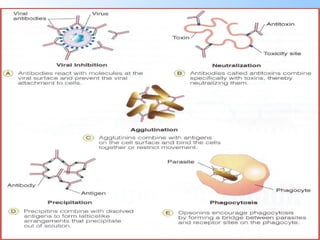
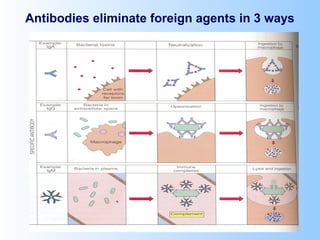
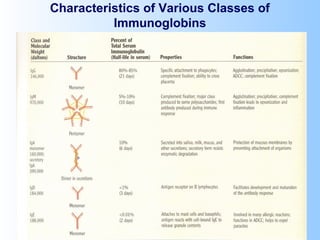
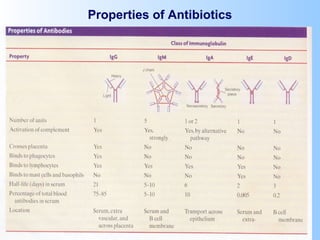
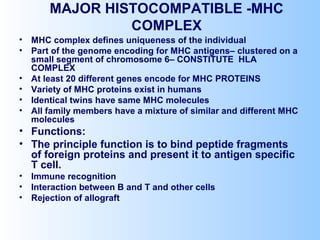
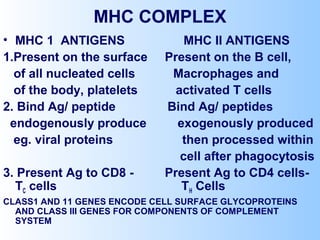
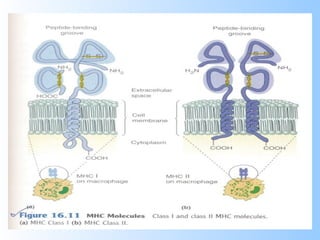
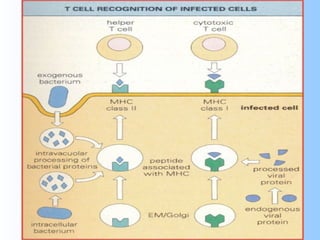
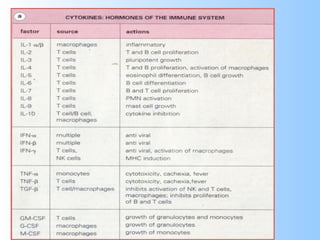
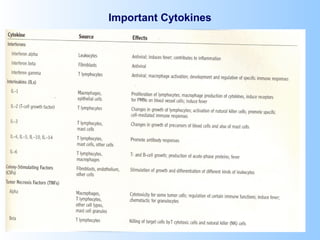
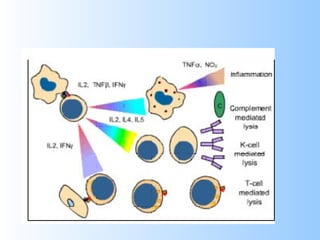
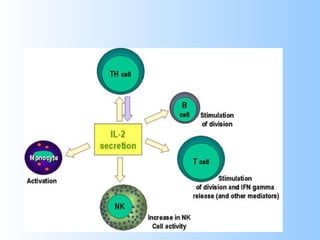
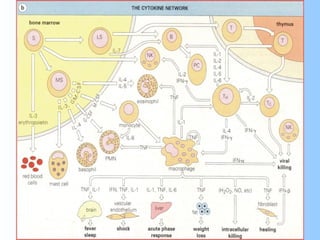
Antigens are substances that induce an immune response when introduced to a host. They have two key characteristics - immunogenicity, which is the ability to stimulate an immune response, and antigenicity, which is the ability to react with antibodies or sensitized T cells. Antigens can be classified as foreign, auto, iso, or hetero antigens depending on their source. Important antigen types include haptens, epitopes, and superantigens. The immune system responds to antigens through antibodies and T cell activation.