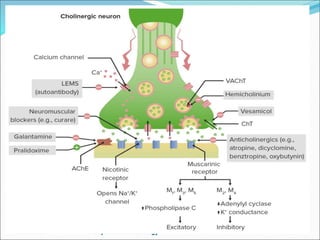
Dr. Manoj Kumar presented on anticholinergic drugs. He discussed how they block the action of acetylcholine through muscarinic receptor antagonism. Atropine was highlighted as the prototypical anticholinergic, being a tertiary amine that competitively blocks muscarinic receptors. Its widespread effects include drying secretions, pupil dilation, tachycardia, urinary retention, and relief of Parkinson's symptoms. Adverse effects include dry mouth, blurred vision, fever, and delirium at high doses.