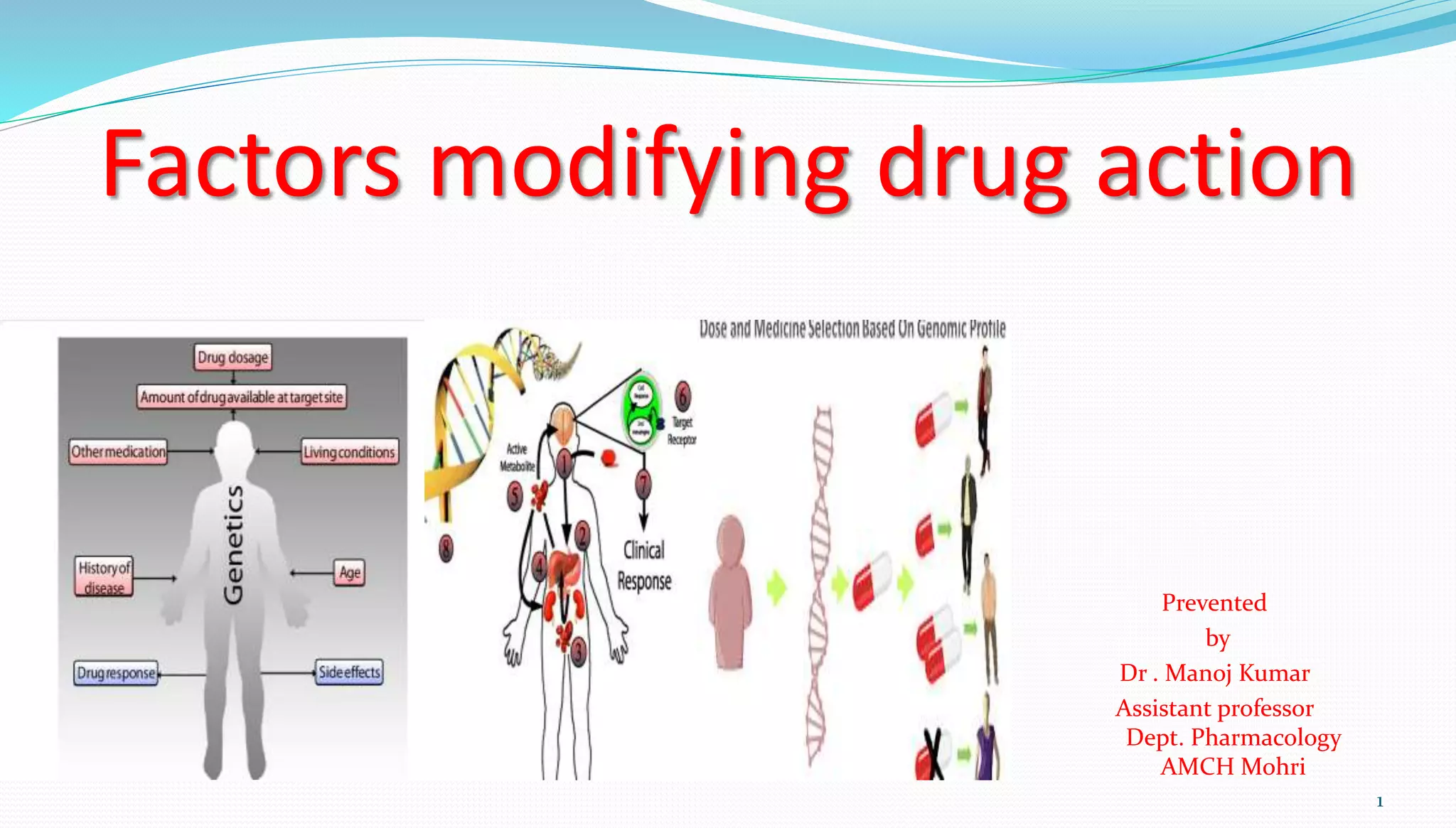
This document discusses many factors that can modify a drug's effects, including physiological, pathological, genetic, environmental, and psychological factors. It provides examples of how factors like age, gender, pregnancy, disease states, genetics, route of administration, and food can impact drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. It also covers concepts like tolerance, tachyphylaxis, teratogenicity, and drug-drug interactions that can alter a drug's effects.