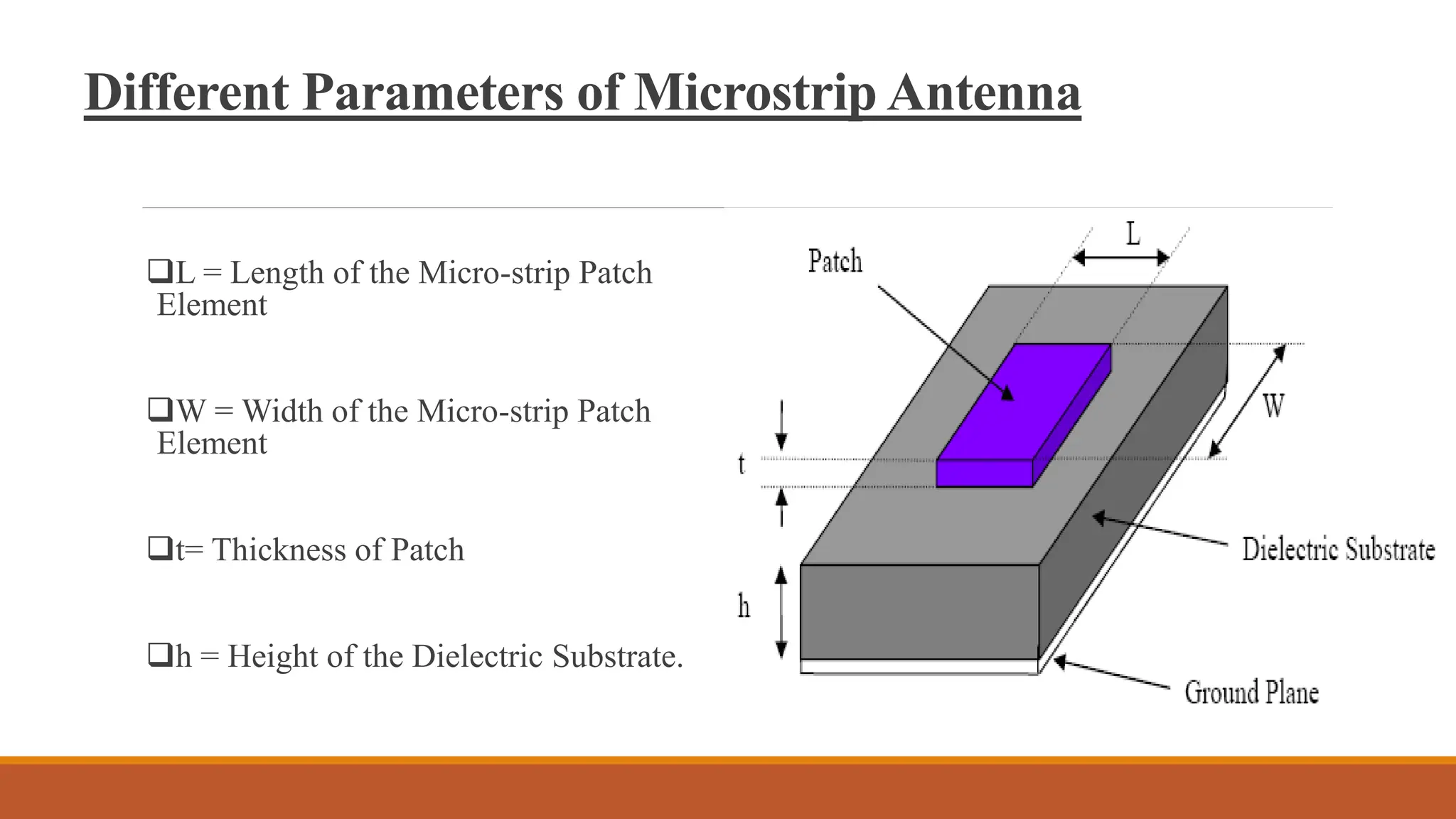
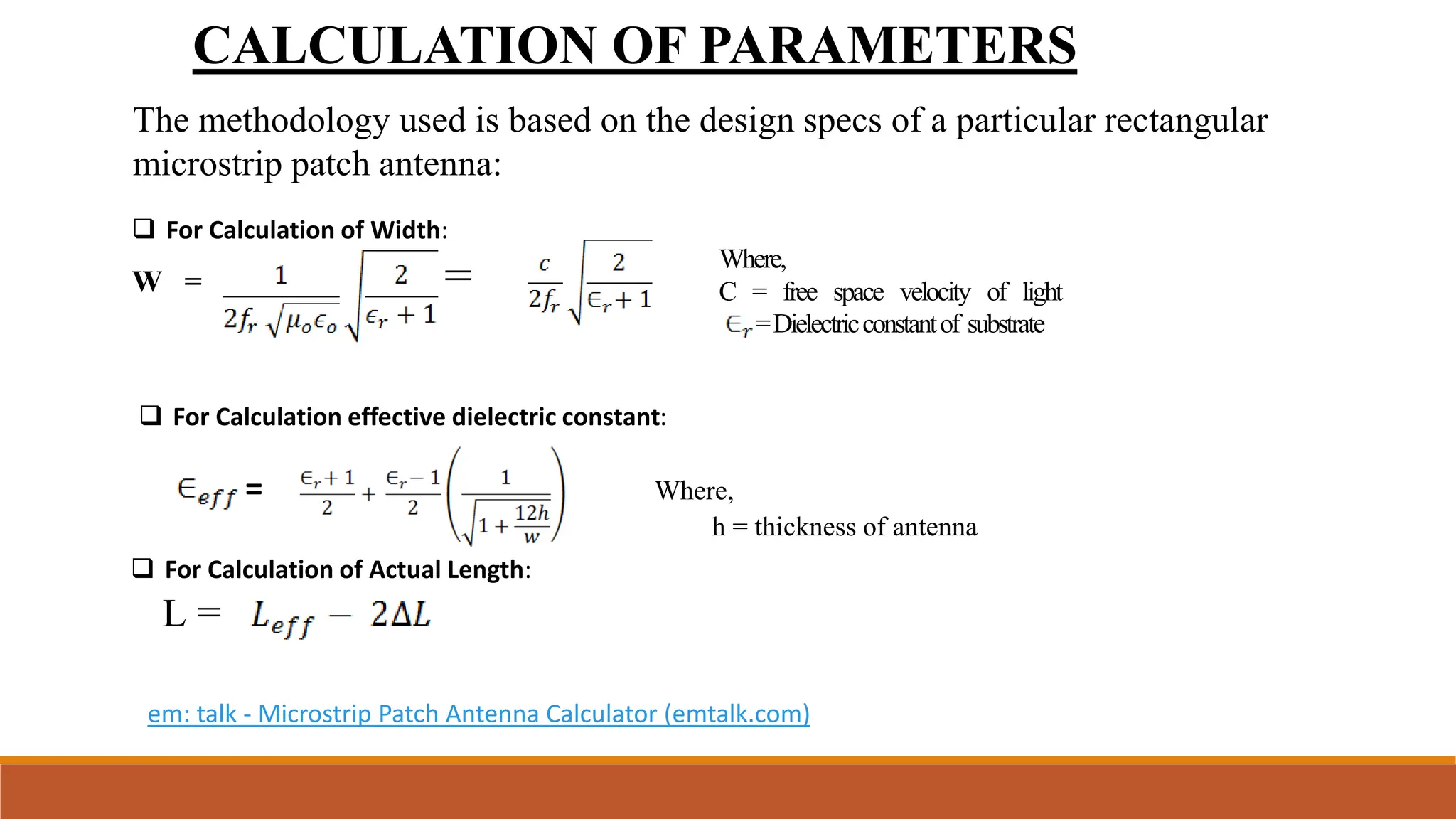
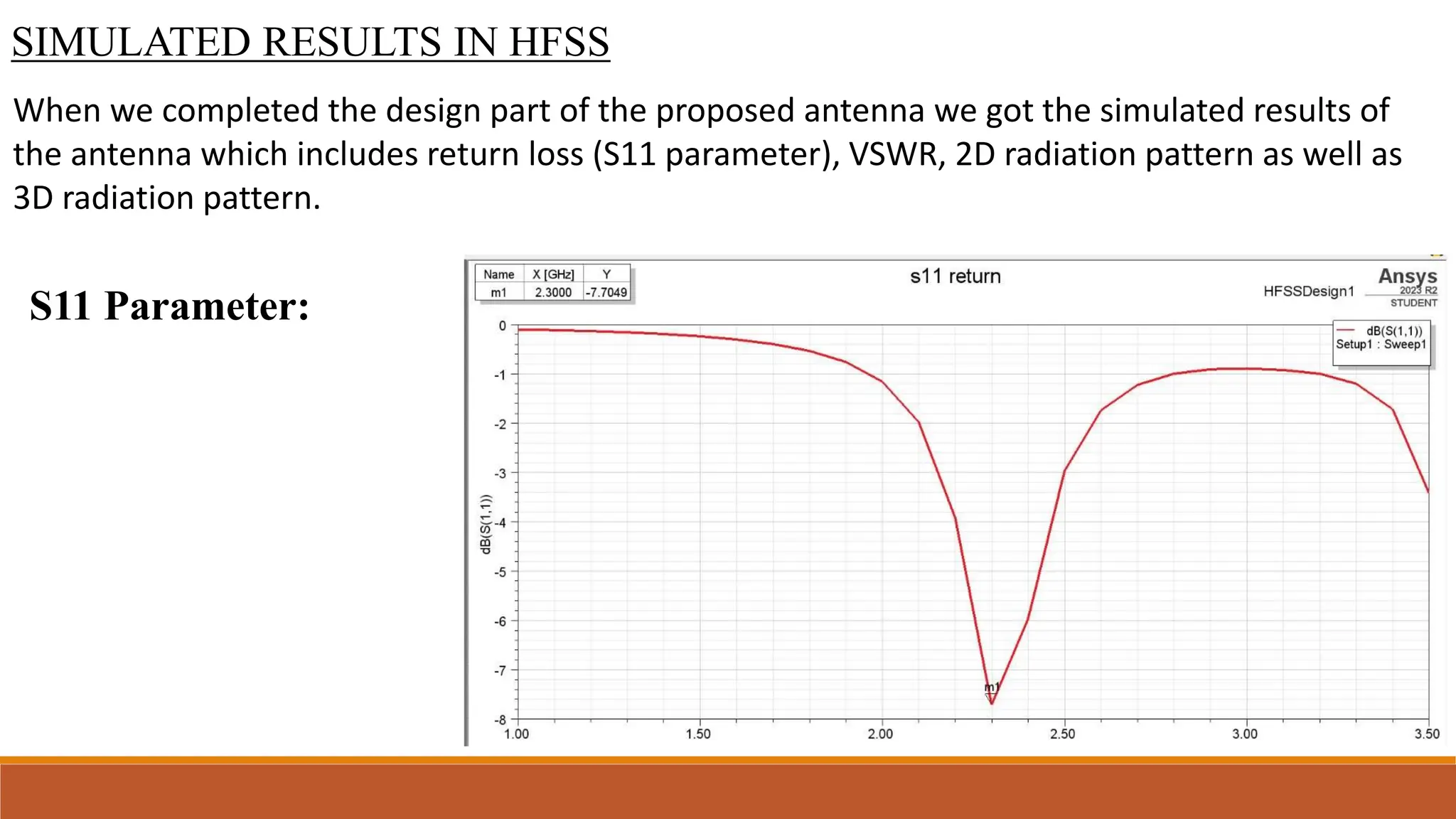
This document describes the design and simulation of a microstrip patch antenna using ANSYS HFSS. It begins with introductions to antennas and how they work. It then discusses microstrip patch antennas specifically, including their basic structure and common shapes. It covers the key parameters in designing microstrip patch antennas and how to calculate them. The document explains the basic operating principles and various feeding techniques. It lists the advantages and disadvantages of microstrip patch antennas and describes some of their applications. Finally, it discusses the results from simulating a rectangular patch antenna in HFSS, including return loss, VSWR, and radiation patterns.