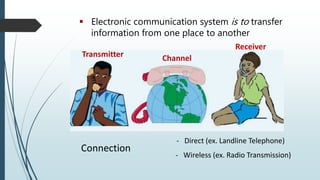
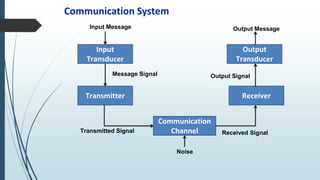
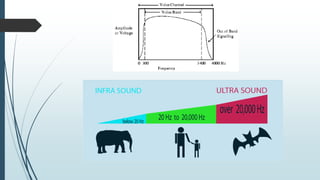
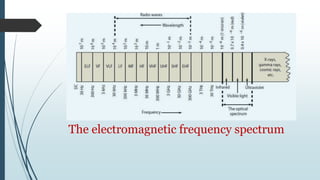
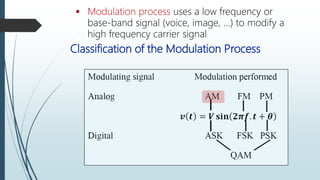
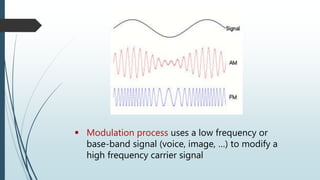
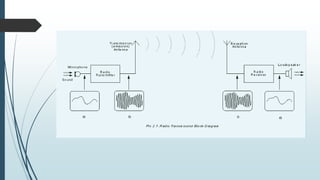
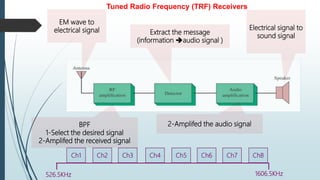
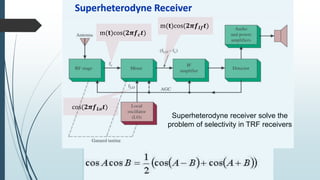
This document discusses AM radio transmission and reception. It describes how AM radio works by taking an input signal like audio and modulating a carrier wave to transmit it through the air. It explains that modulation involves modifying a high frequency carrier signal with a low frequency audio signal. It also discusses how early radio receivers worked by tuning different radio frequency channels, but that modern radios use the superheterodyne principle to convert signals to a fixed intermediate frequency for better selectivity.