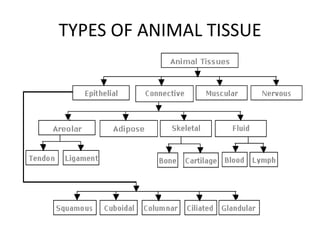
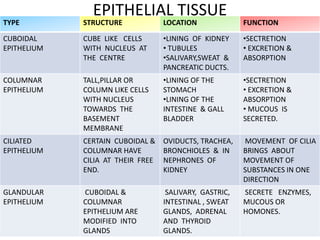
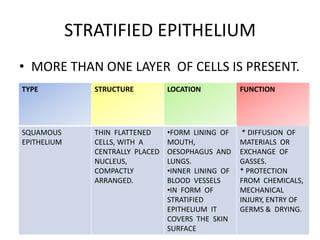
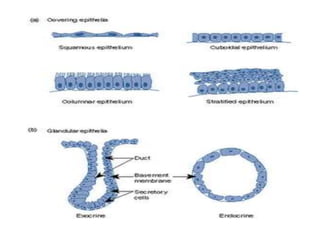
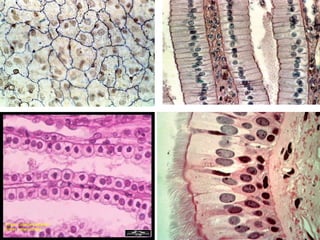
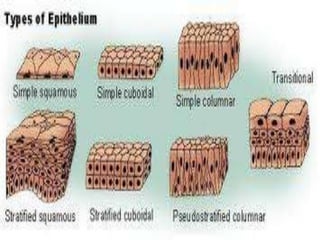
Animal tissues are divided into four main types - epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. Epithelial tissue covers the internal and external surfaces of the body and its main functions include secretion, absorption, protection, and filtration. It is made up of cells that are arranged in one or more layers. Connective tissues are found throughout the body and function to bind, support, and connect other tissues. They contain fibers and ground substances along with loosely arranged cells. The major liquid connective tissue in the body is blood, which contains plasma and three main types of corpuscles - red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.


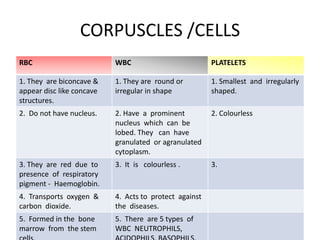
![Liquid connective tissue
• Our body contains two liquid connective
tissues:
1) blood
2) lymph
Blood is the major liquid connective tissue. It’s
constituents are divided into two types
Liquid : plasma
Solid : corpuscles [ cells]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/animaltissues9cbse-130227083409-phpapp01/85/Animal-tissues-9-cbse-9-320.jpg)