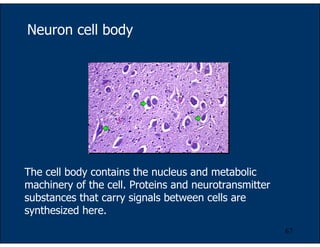
Animal tissues are organized into four main types - epithelial, connective, muscular and nervous. Epithelial tissues cover external and internal surfaces and line organs. They form protective barriers and enable fluid/gas exchange. Connective tissues include bone, cartilage, blood and loose connective tissues that support and connect other tissues. They are made of cells within an extracellular matrix. Muscular tissues contain specialized contractile cells that generate force and motion. Nervous tissues transmit electrical signals in the brain, spinal cord and nerves to coordinate body functions.