The document discusses hypertension including its definition, classification, risk factors, symptoms, complications, diagnosis, and management. It provides details on lifestyle modifications and drug therapies used to treat hypertension as well as the management of hypertensive crises. The document is intended to serve as an educational reference for healthcare providers on the topic of hypertension.






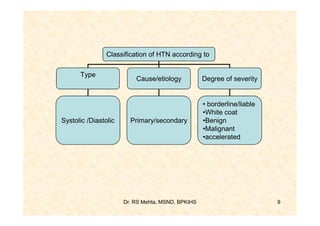
![Classification of HIN
1. Systolic HTN / Diastolic HTN
- Systolic BP > 140/ Diastolic BP > 90
2. Primary [essential] HTN/Secondary HTN
- Majority idiopathic cause/cause known
3. White coat HTN: Normotensive otherwise
4. Malignant HTN: DBP > 120 mg, Retinal
hemorrhage, papilledema, ARF, Rapid
vascular deterioration
Dr. RS Mehta, MSND, BPKIHS 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hypertension-130217203719-phpapp02/85/Hypertension-8-320.jpg)