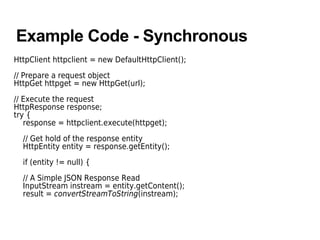
The document discusses Android web services using the HttpClient API. It describes invocation styles in HttpClient as synchronous and asynchronous. It provides examples of sending HTTP requests using HttpGet and HttpPost, and receiving HTTP responses using HttpResponse and ResponseHandler interfaces. Common response formats like XML, JSON, RSS and Atom are mentioned and examples of parsing JSON responses using the JSONObject class are given.