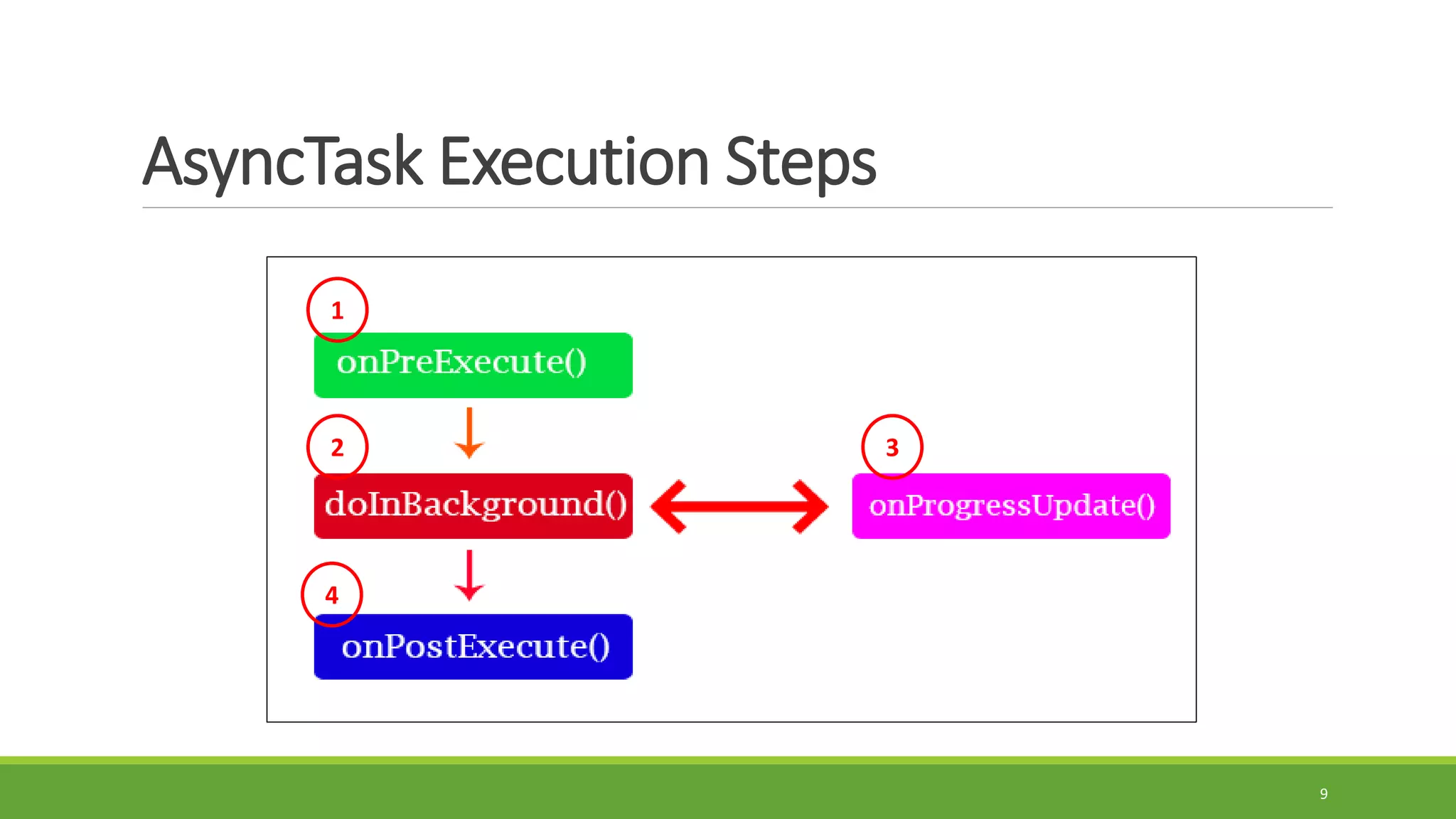
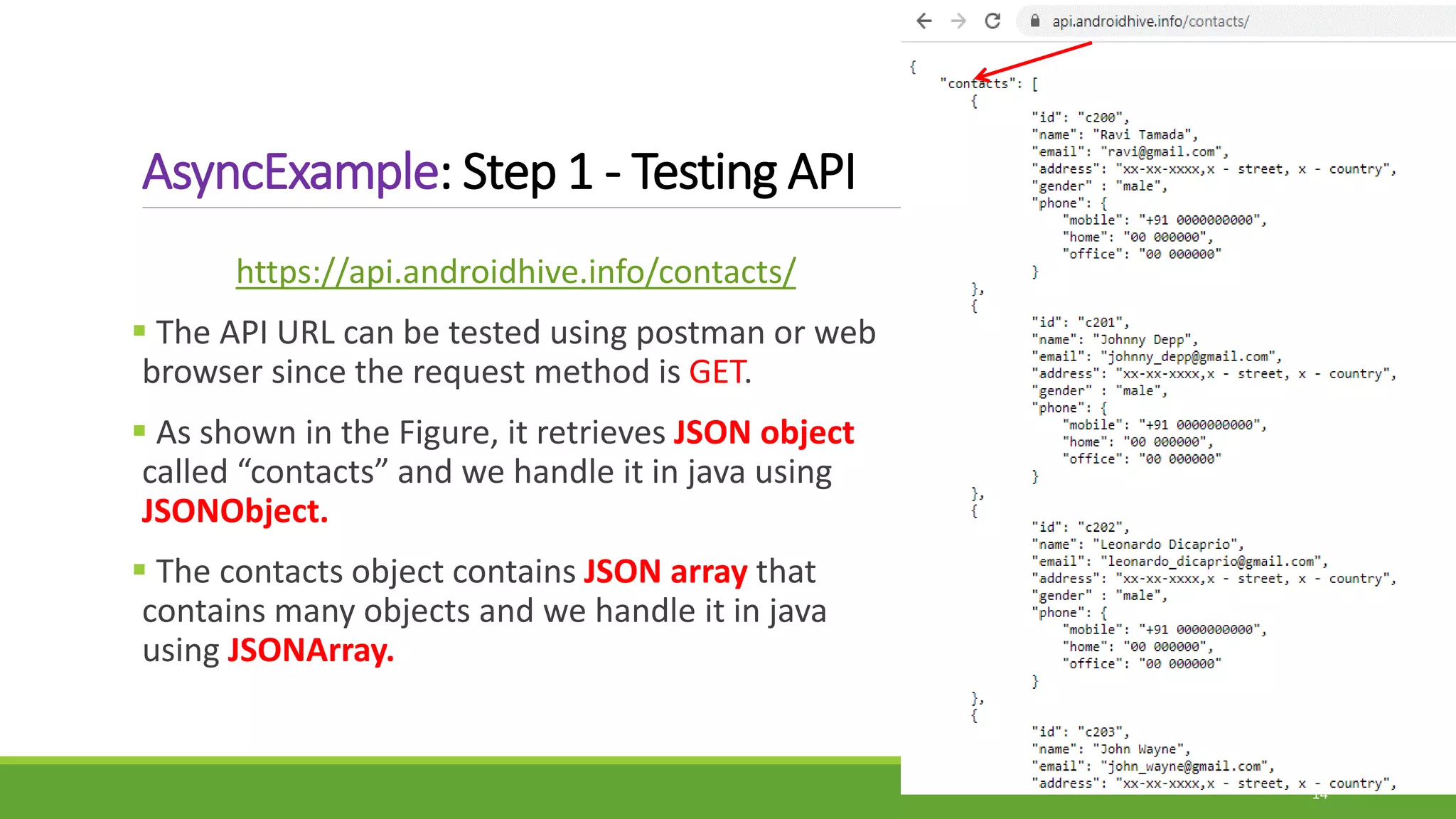
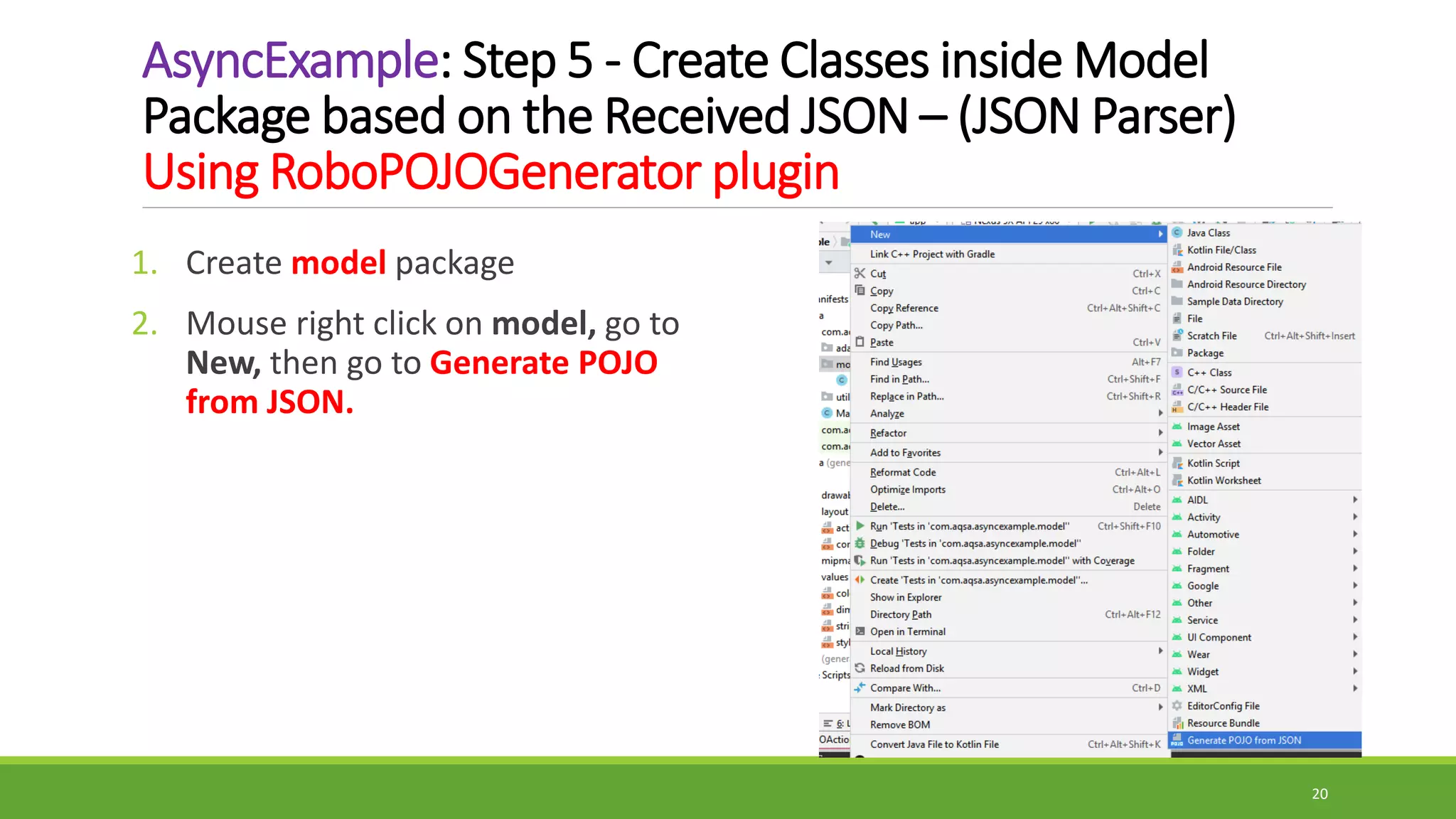
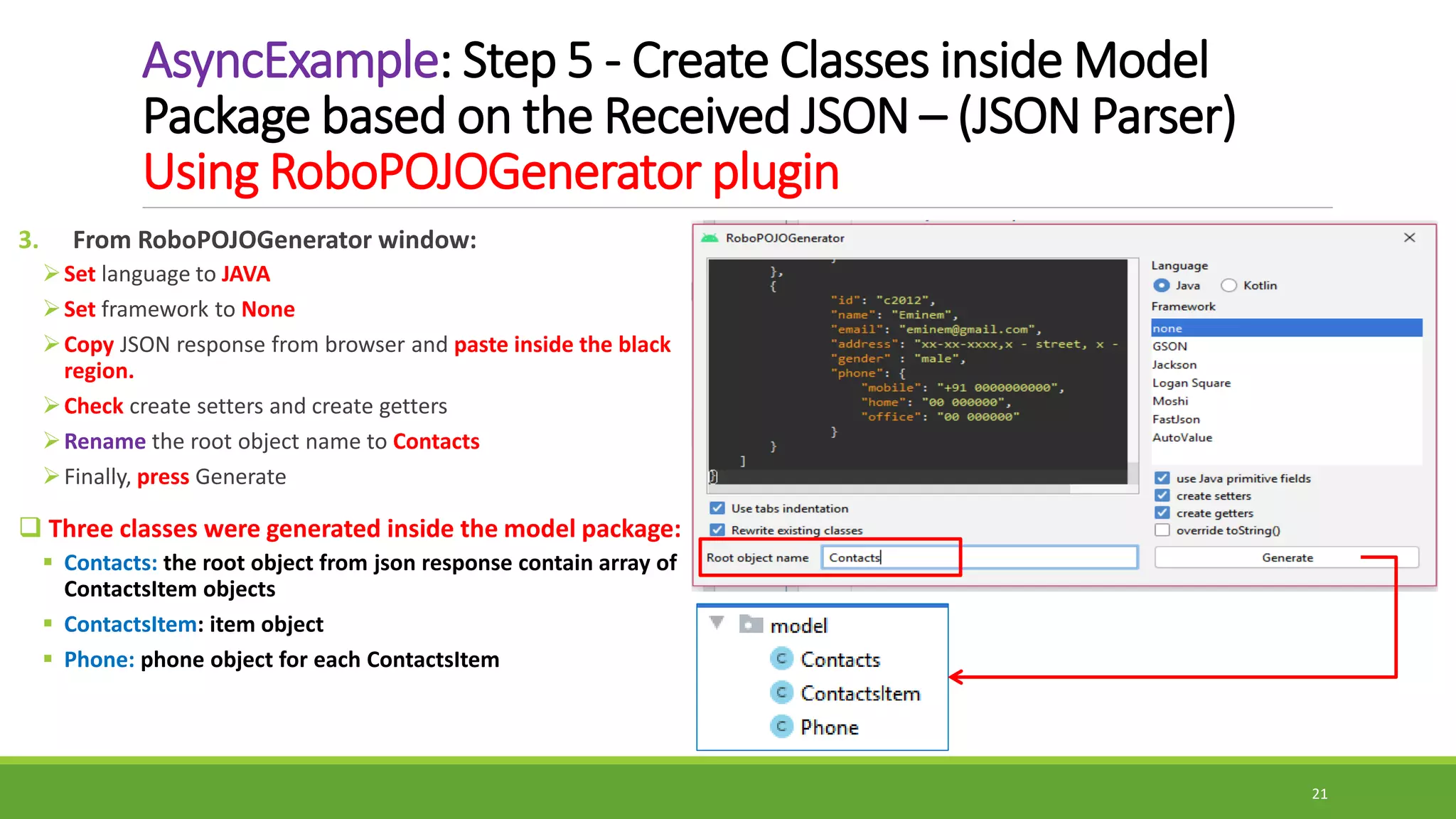
The document provides information on handling API requests in Android using AsyncTask. It discusses the different ways to handle API in Android including AsyncTask, Volley, and Retrofit. It then focuses specifically on AsyncTask, explaining what it is, its generic types, methods like doInBackground(), onPreExecute(), onPostExecute(), onProgressUpdate(). It outlines the execution steps of an AsyncTask and provides an example of handling API requests using AsyncTask to fetch contact data from a URL. The example discusses adding internet permission, creating an HTTPHandler class to make the request, parsing the JSON response using model classes, and displaying the data in a recycler view.