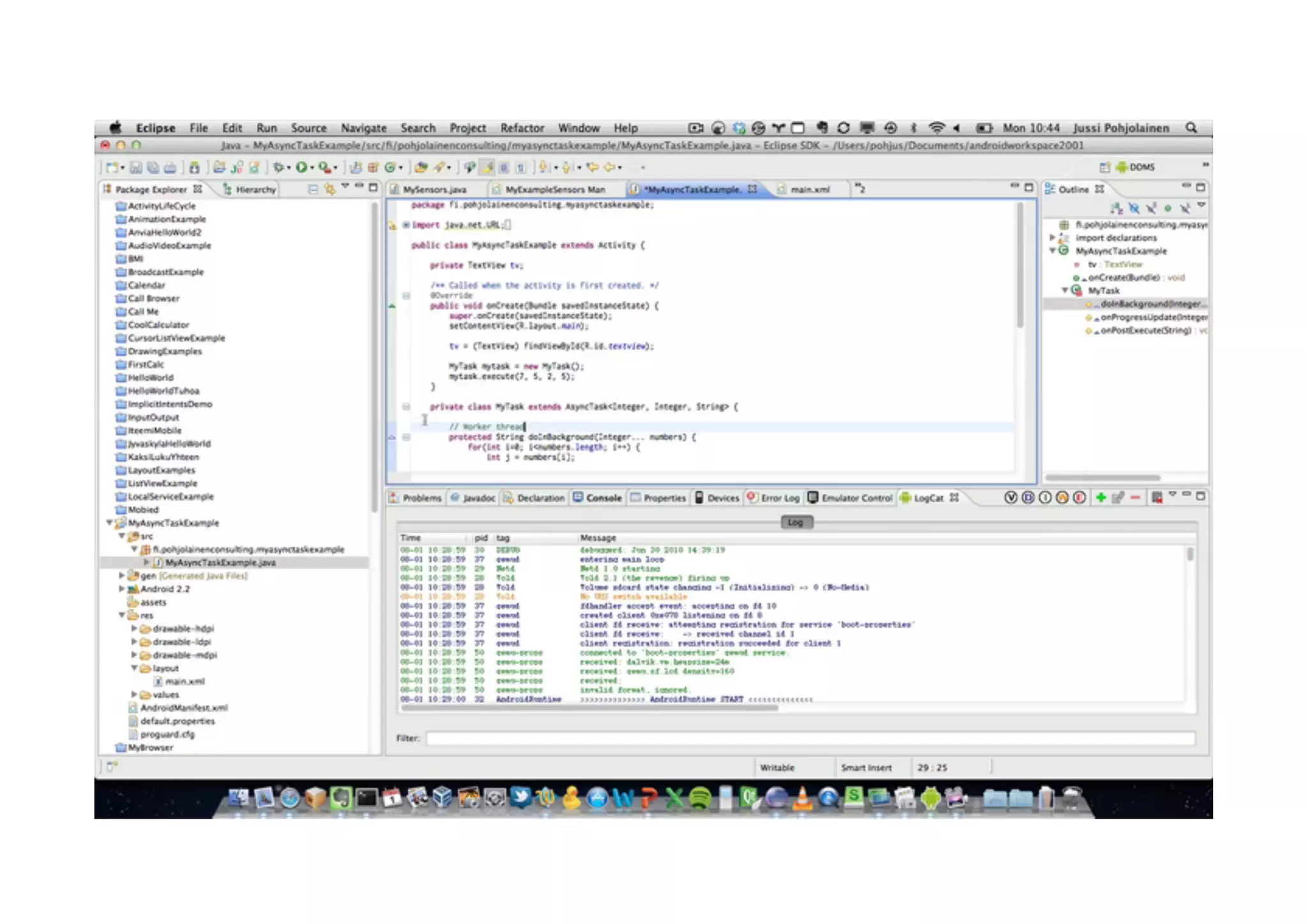
The document discusses Android networking and XML parsing using SAX. It describes how to make HTTP requests using URLConnection in Android, including opening a connection, preparing and sending requests, reading responses, and disconnecting. It also covers performing network requests asynchronously using AsyncTask to avoid blocking the UI thread. Finally, it provides an overview of XML parsing with SAX in Android.