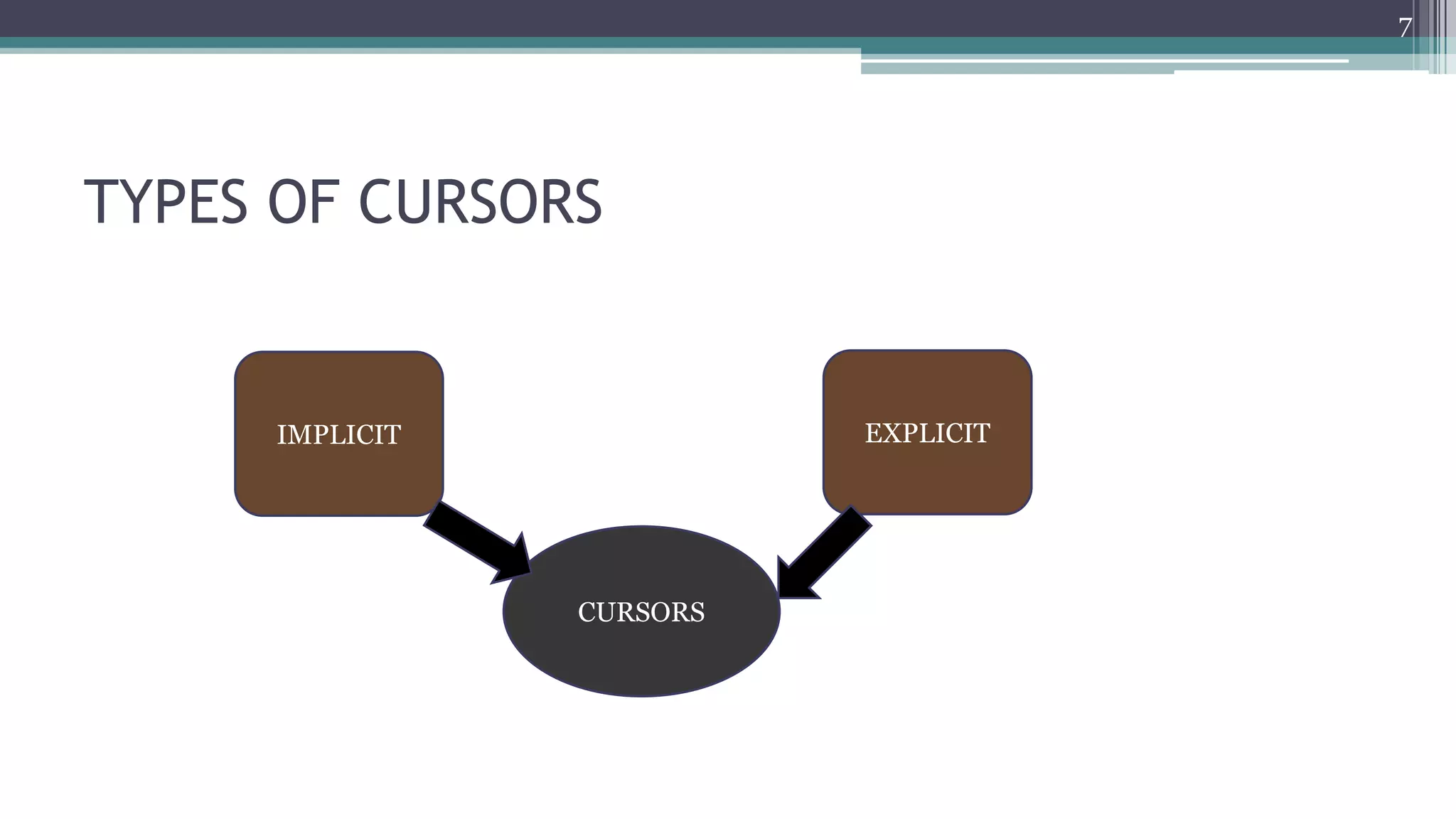
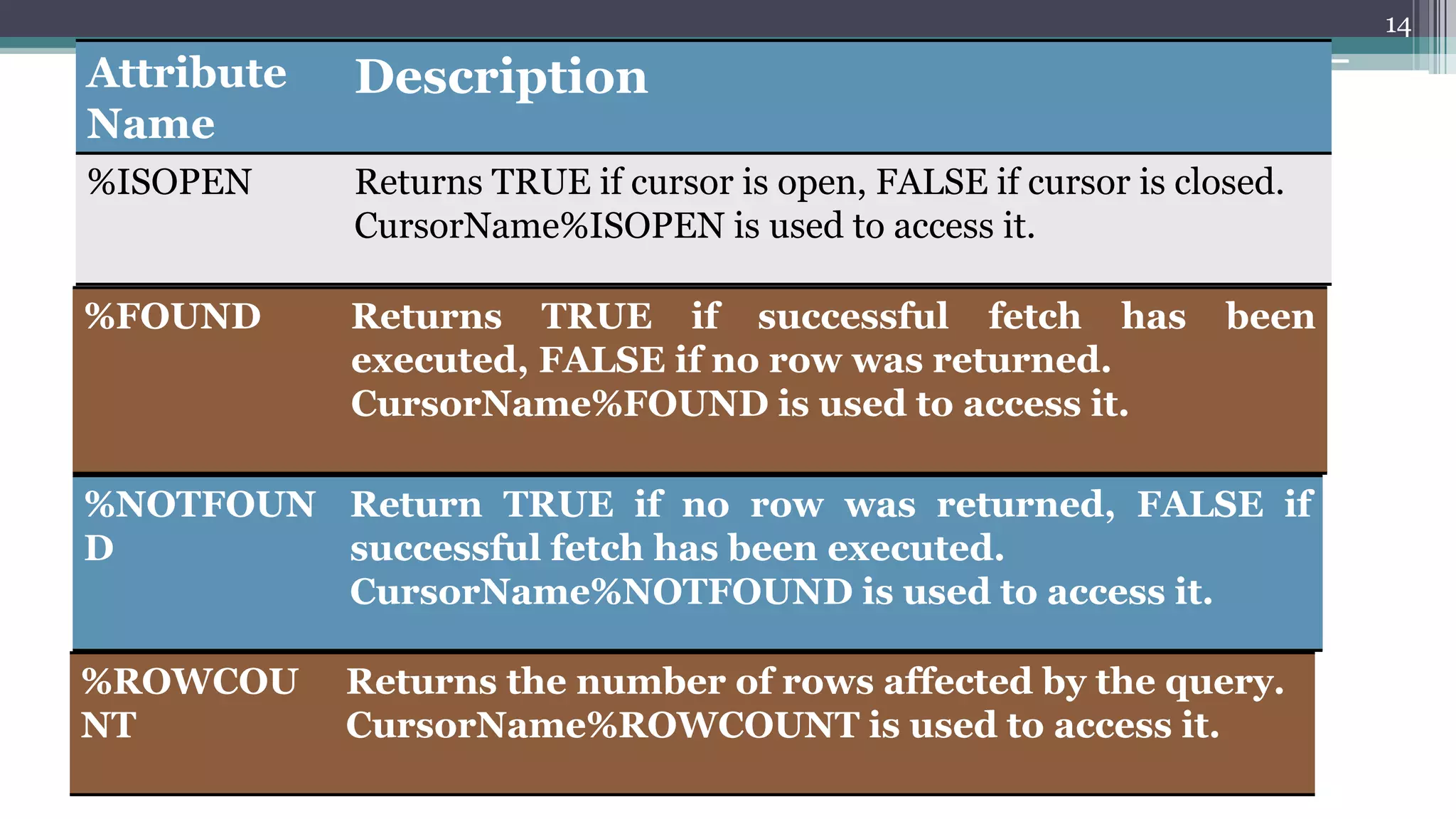
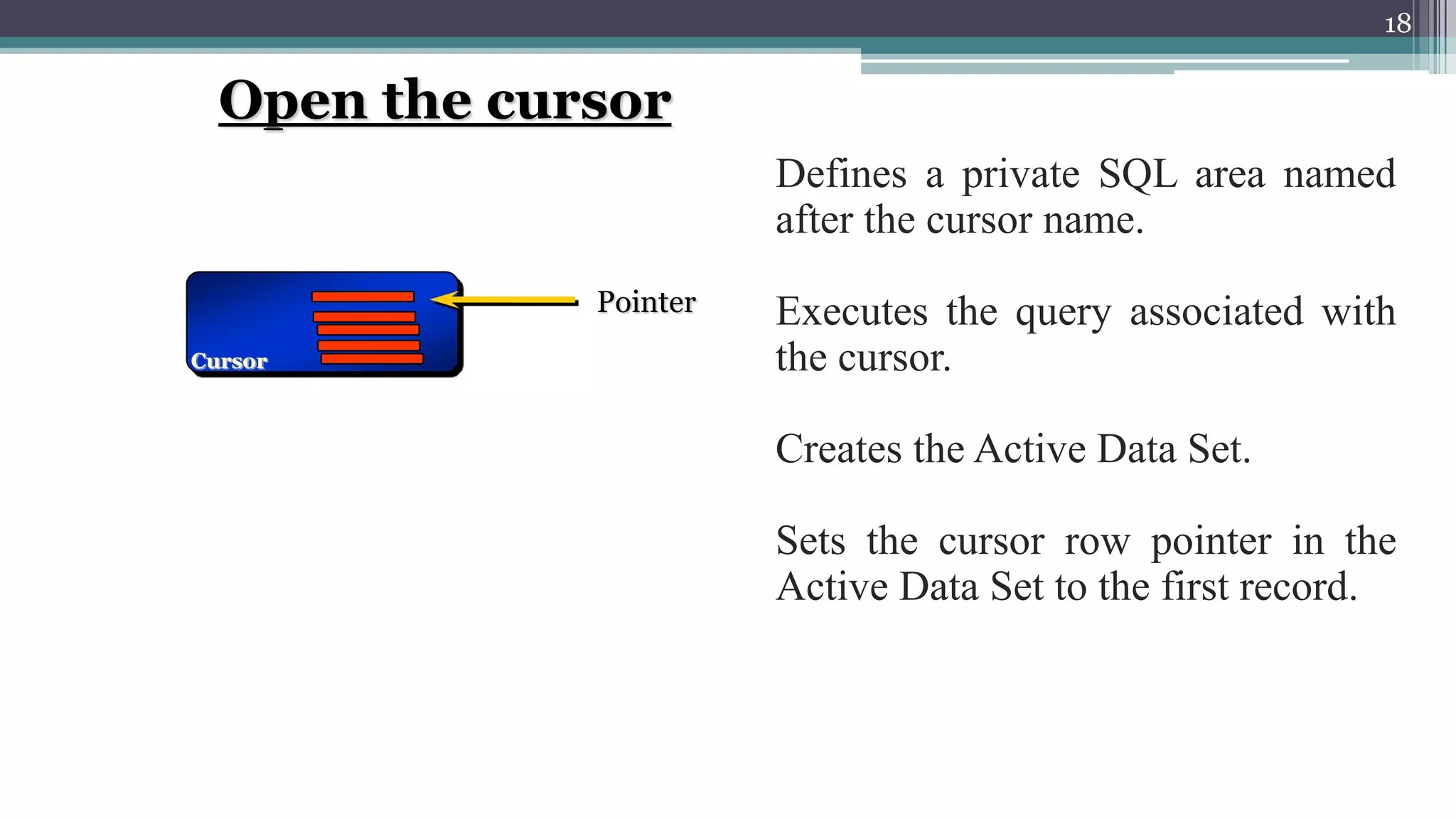
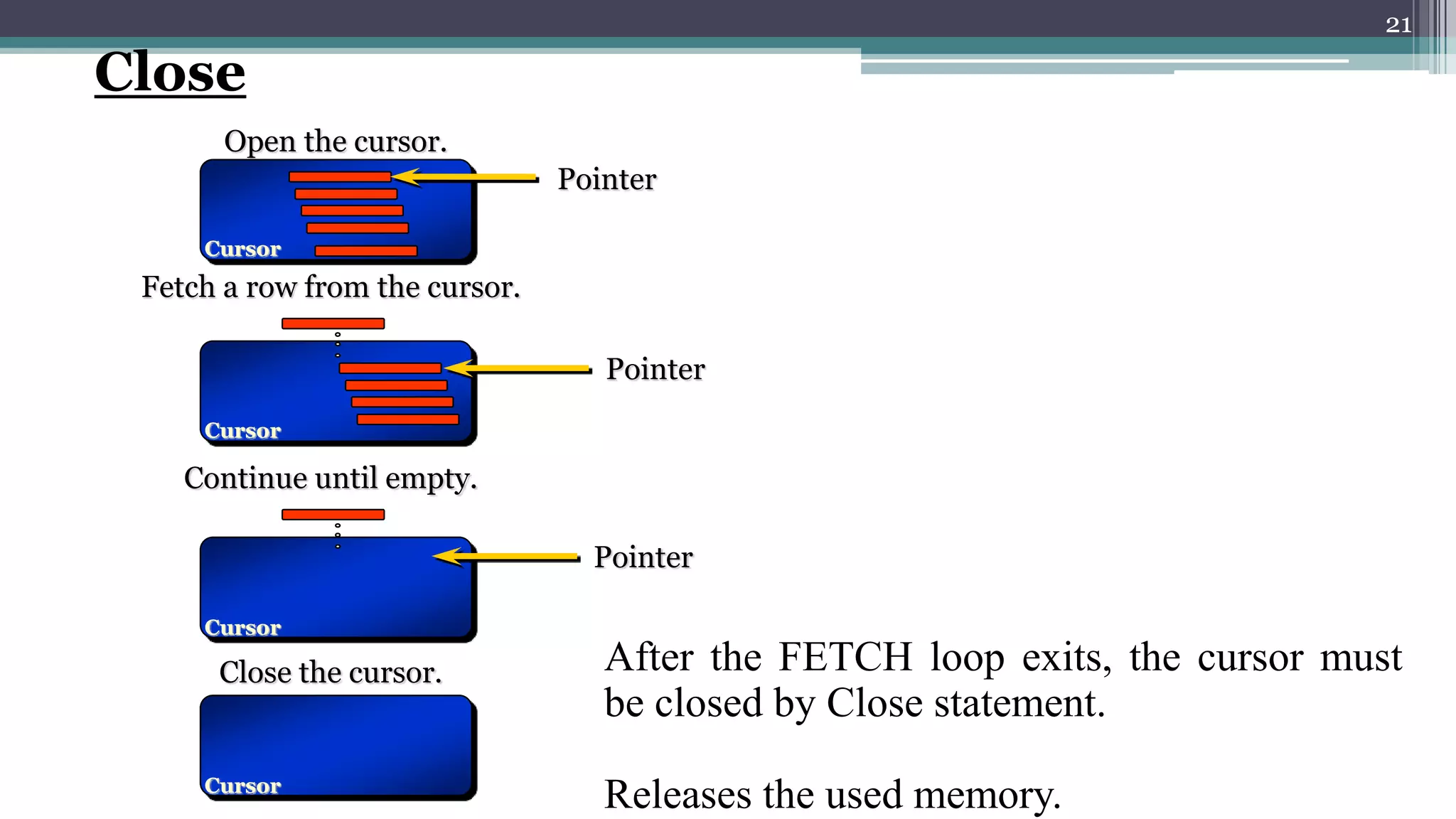
The document discusses cursors in Oracle databases. It defines cursors as temporary work areas for processing query results row by row. There are two main types of cursors - implicit and explicit. Explicit cursors provide more control and involve declaring, opening, fetching from, and closing the cursor. Examples demonstrate using explicit cursors to retrieve and process multiple rows in a PL/SQL block. The document also covers cursor attributes, cursor for loops, parameterized cursors, and comparisons of implicit and explicit cursors.