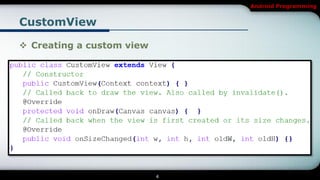
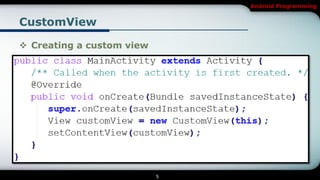
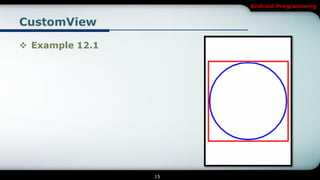
This document covers Android programming focusing on 2D graphics, specifically creating custom views and using SurfaceView. Key topics include overriding the onDraw() method, optimizing drawing objects, managing layout events, and the differences between View and SurfaceView for rendering. The content also includes examples and exercises related to these concepts.