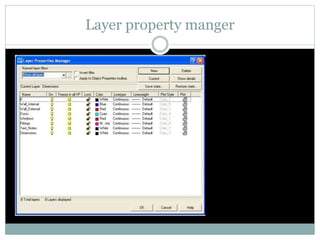
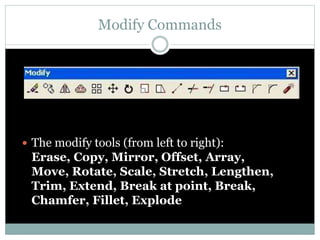
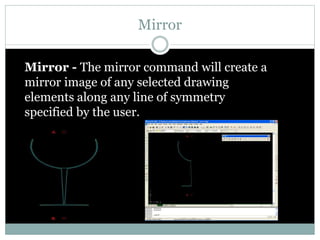
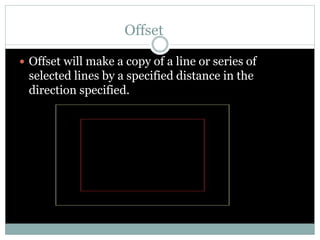
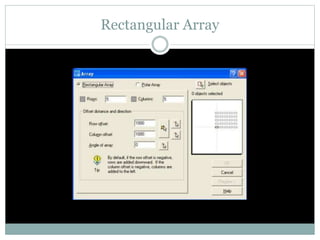
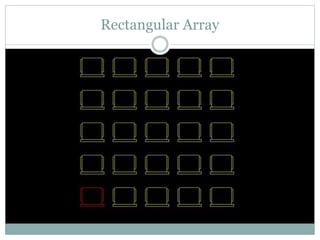
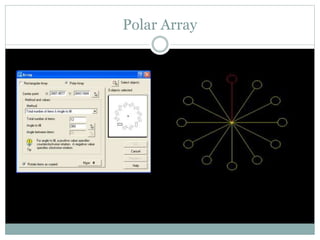
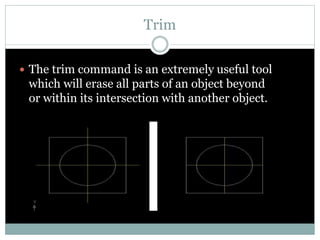
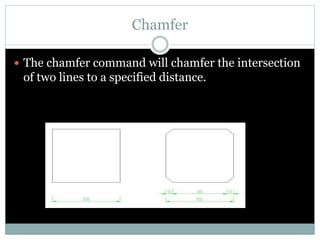
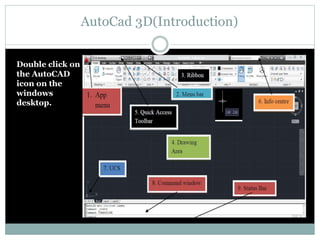
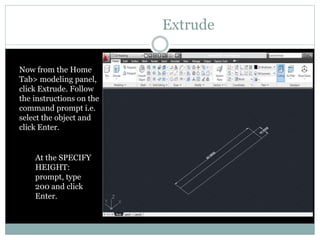
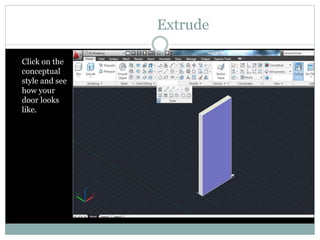
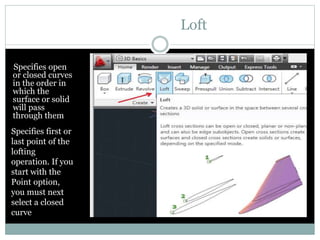
The document discusses AutoCAD and its features. It describes AutoCAD as CAD software for 2D and 3D design. It outlines various commands like toolbars, key commands, and key sequences. It also discusses layers, drafting settings, modify commands, and 3D modeling tools like extrude, revolve, sweep, and loft. Layers allow organizing a drawing by turning parts on and off. Commands like copy, move, and array duplicate or rearrange objects. 3D tools extrude, revolve, sweep, and loft create 3D geometry from 2D profiles.