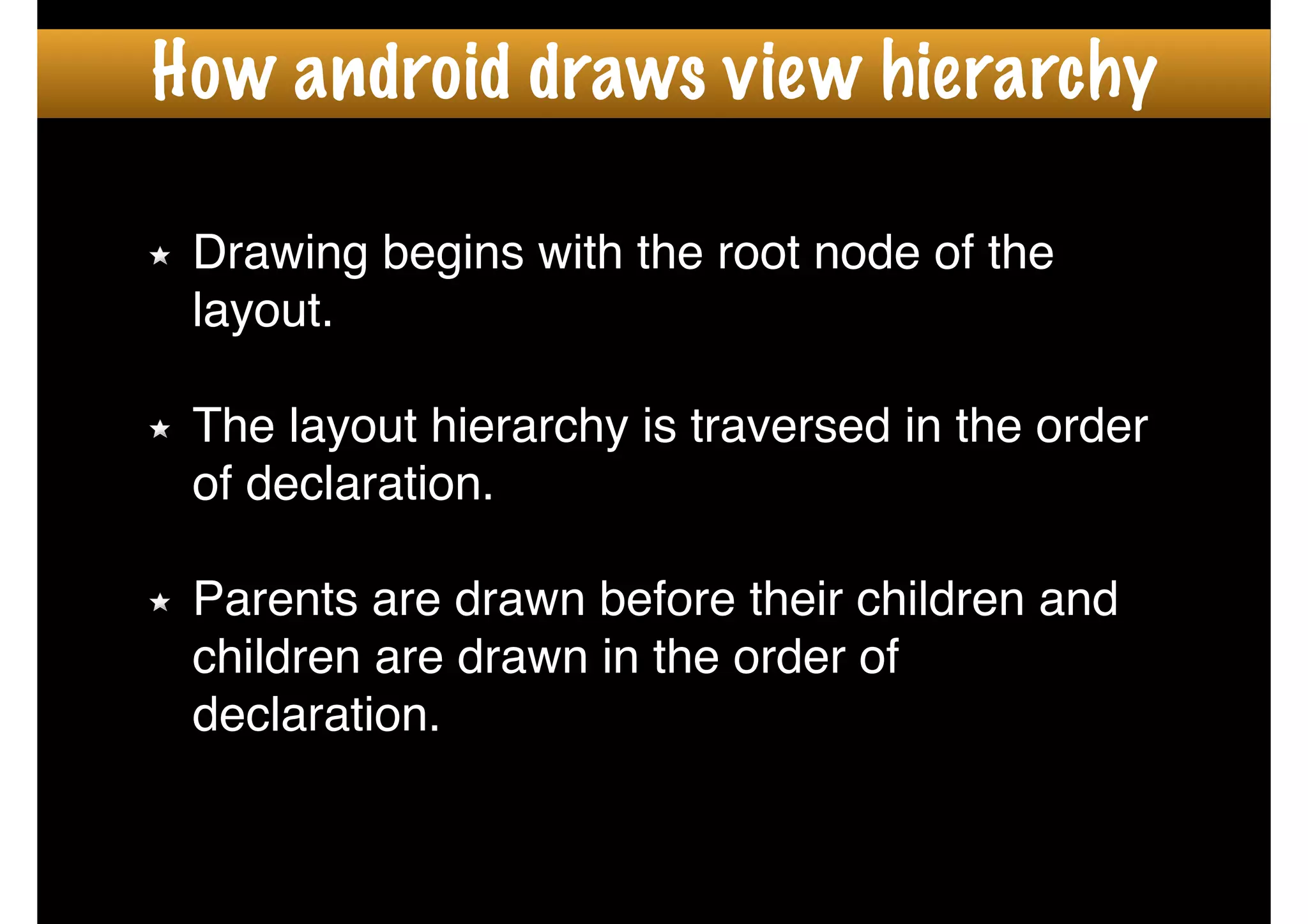
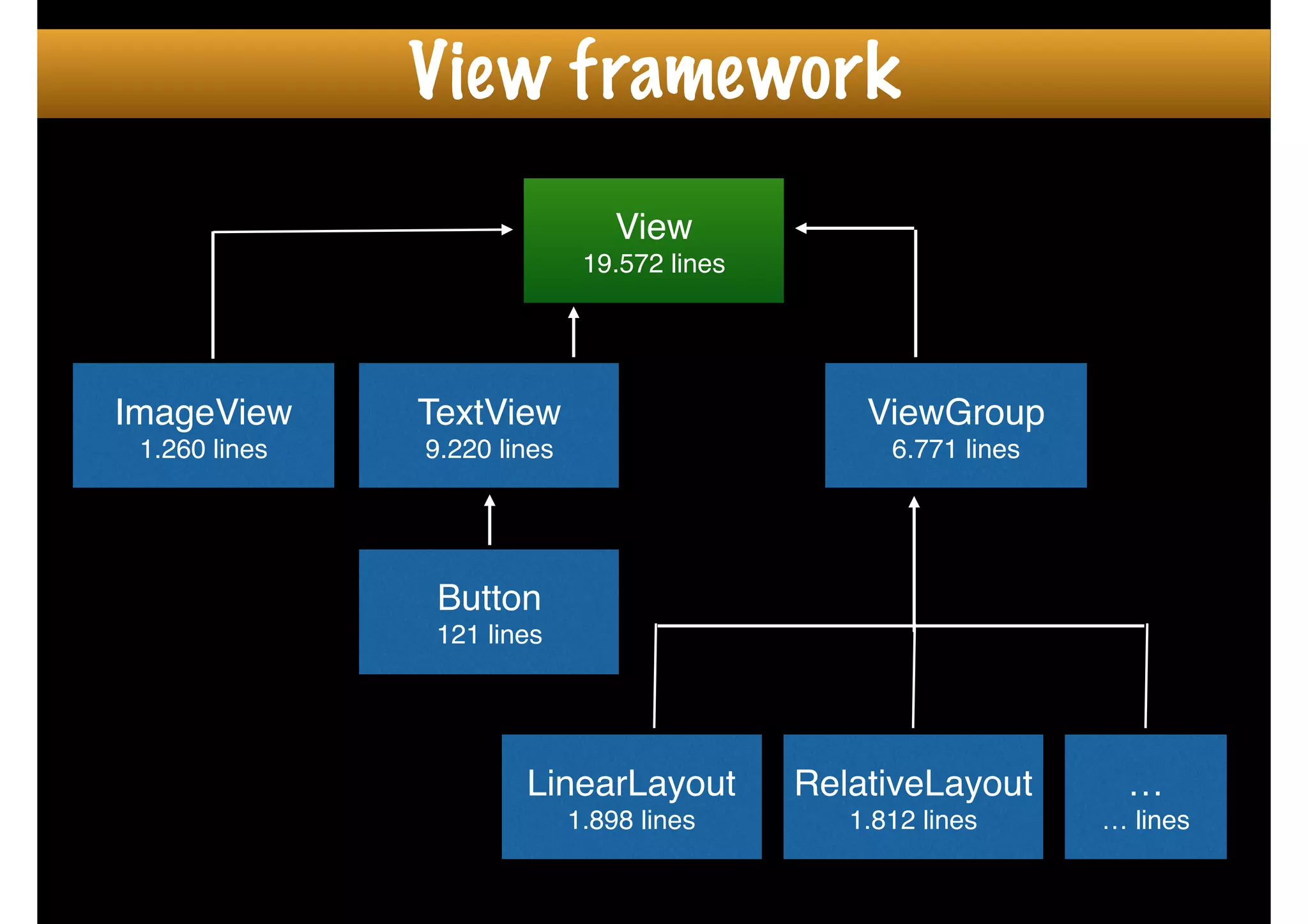
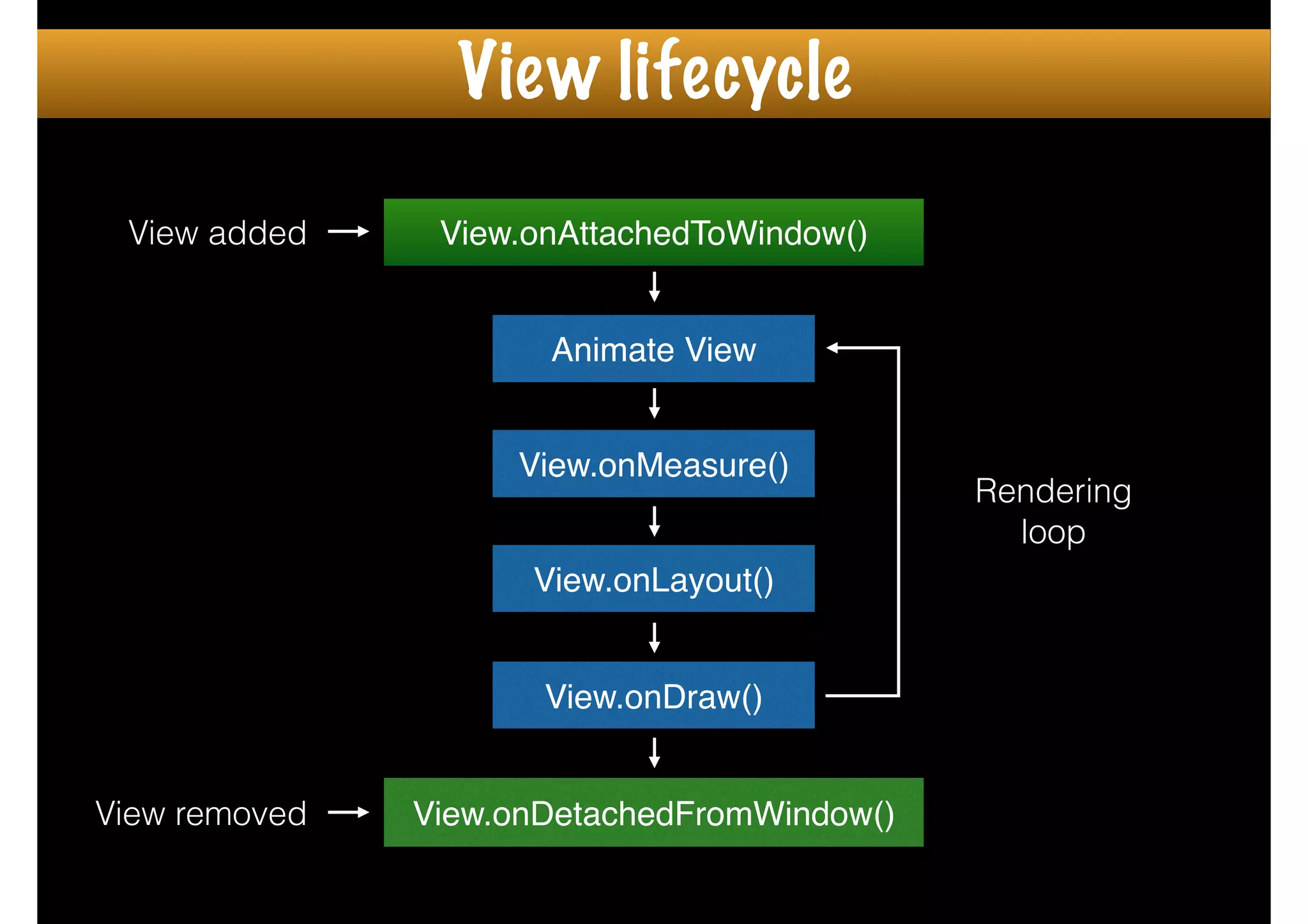
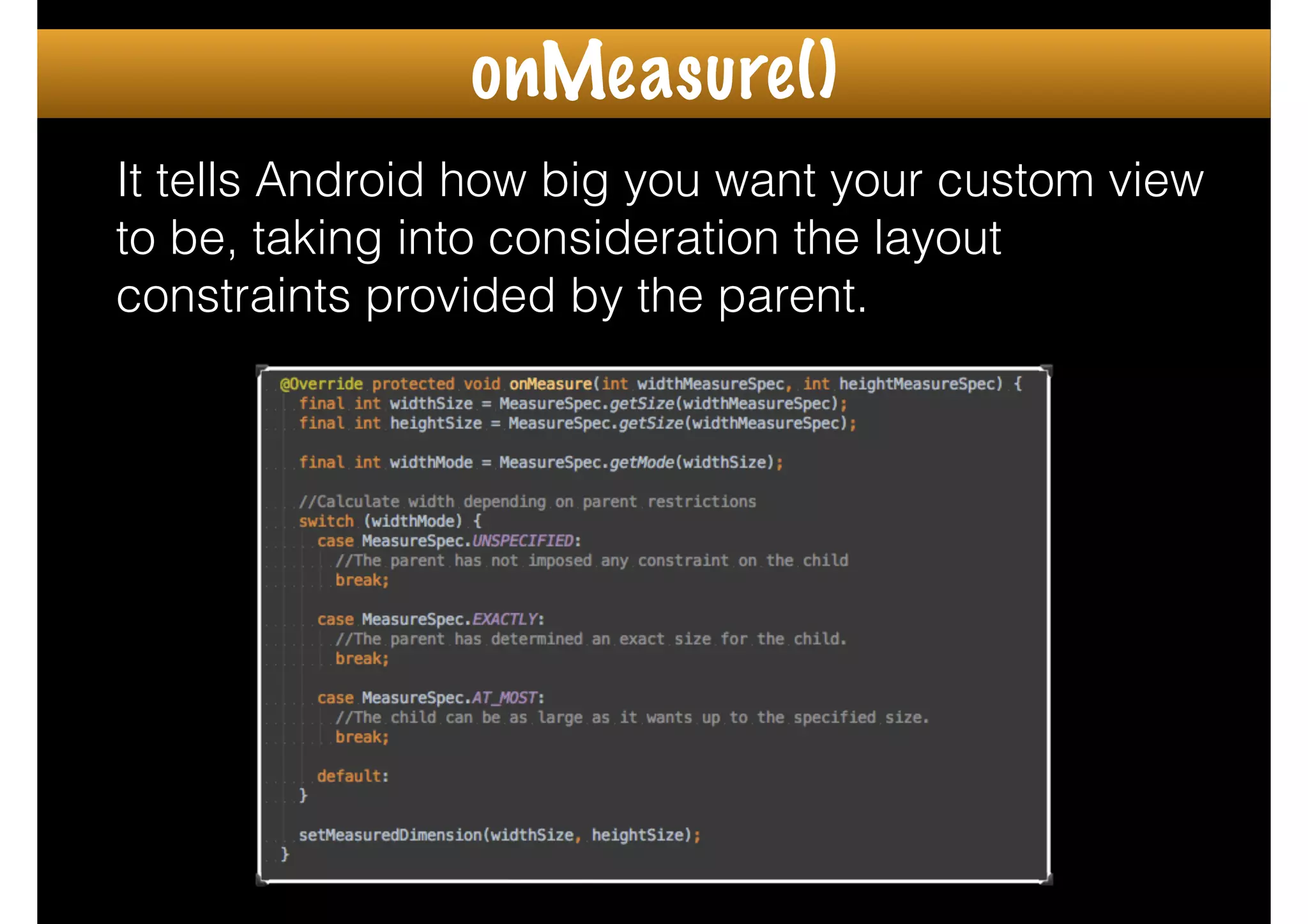
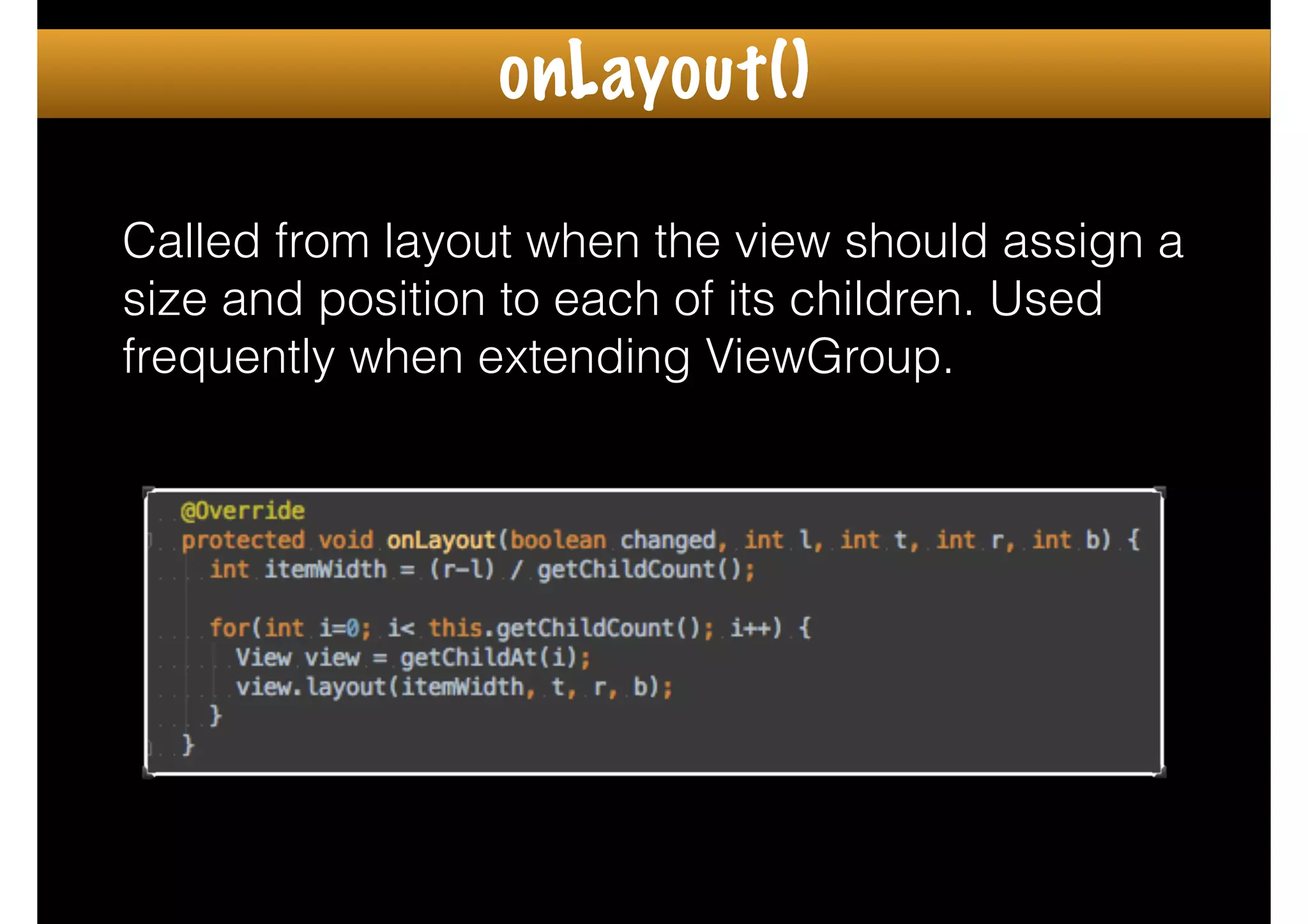
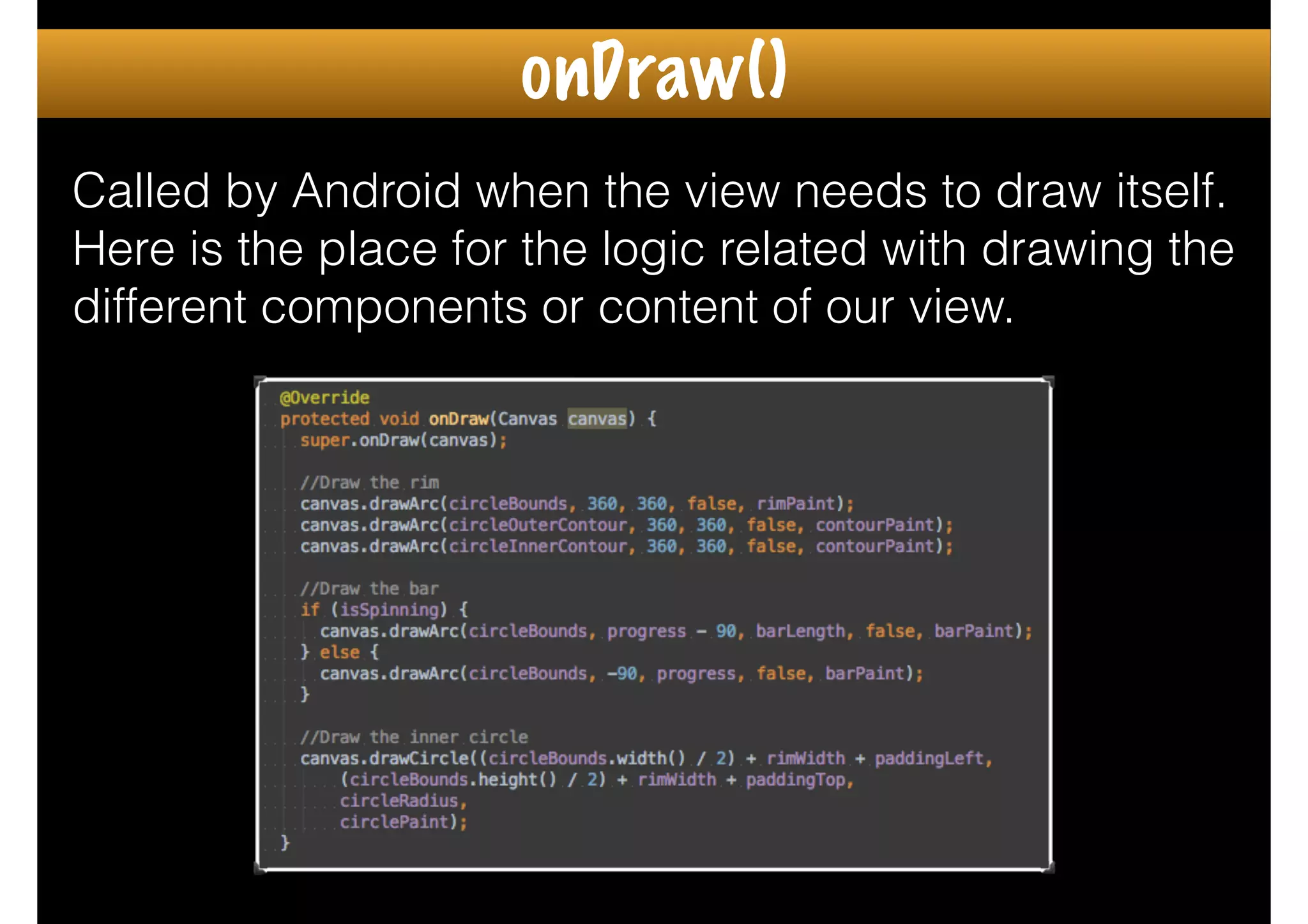
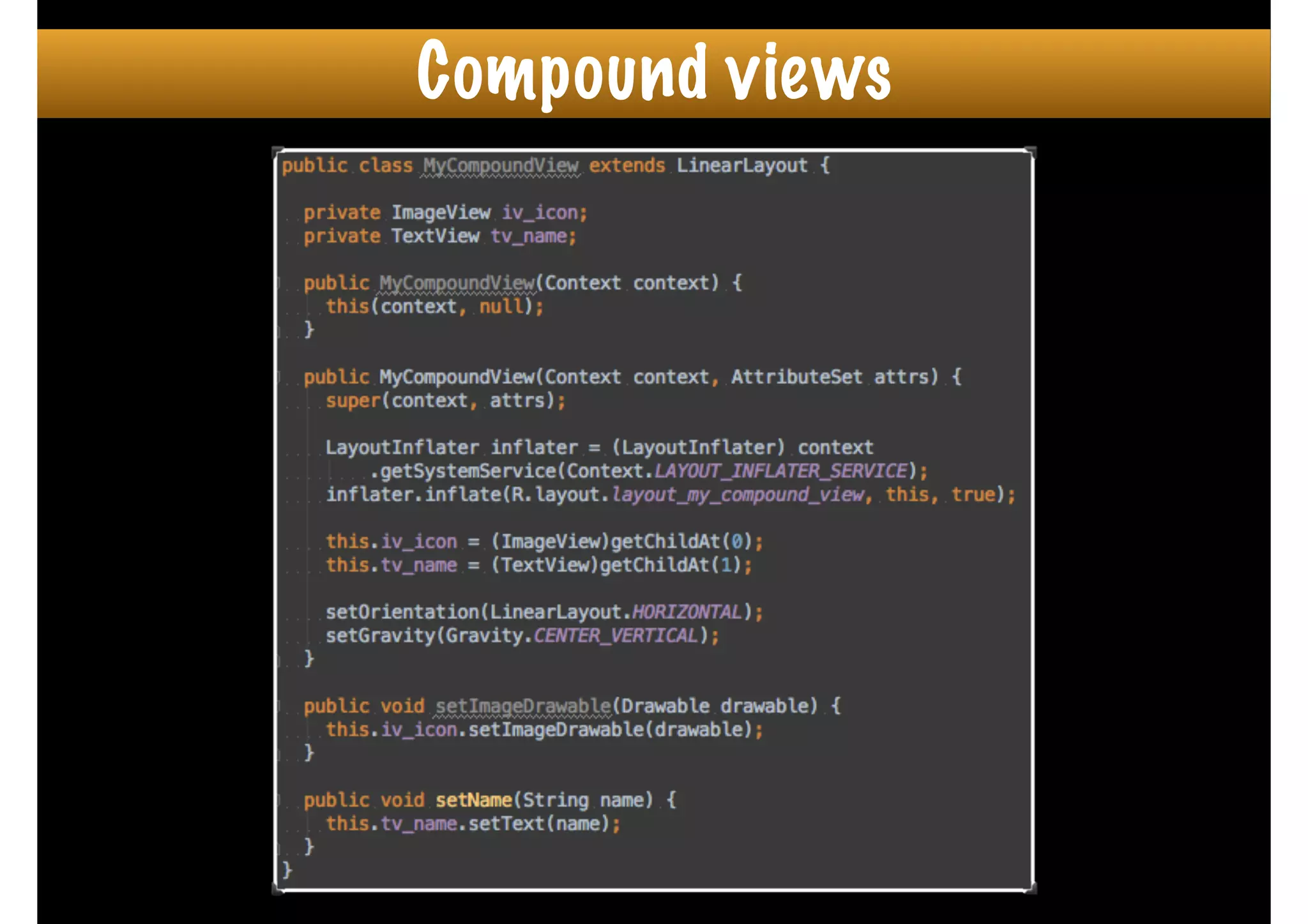
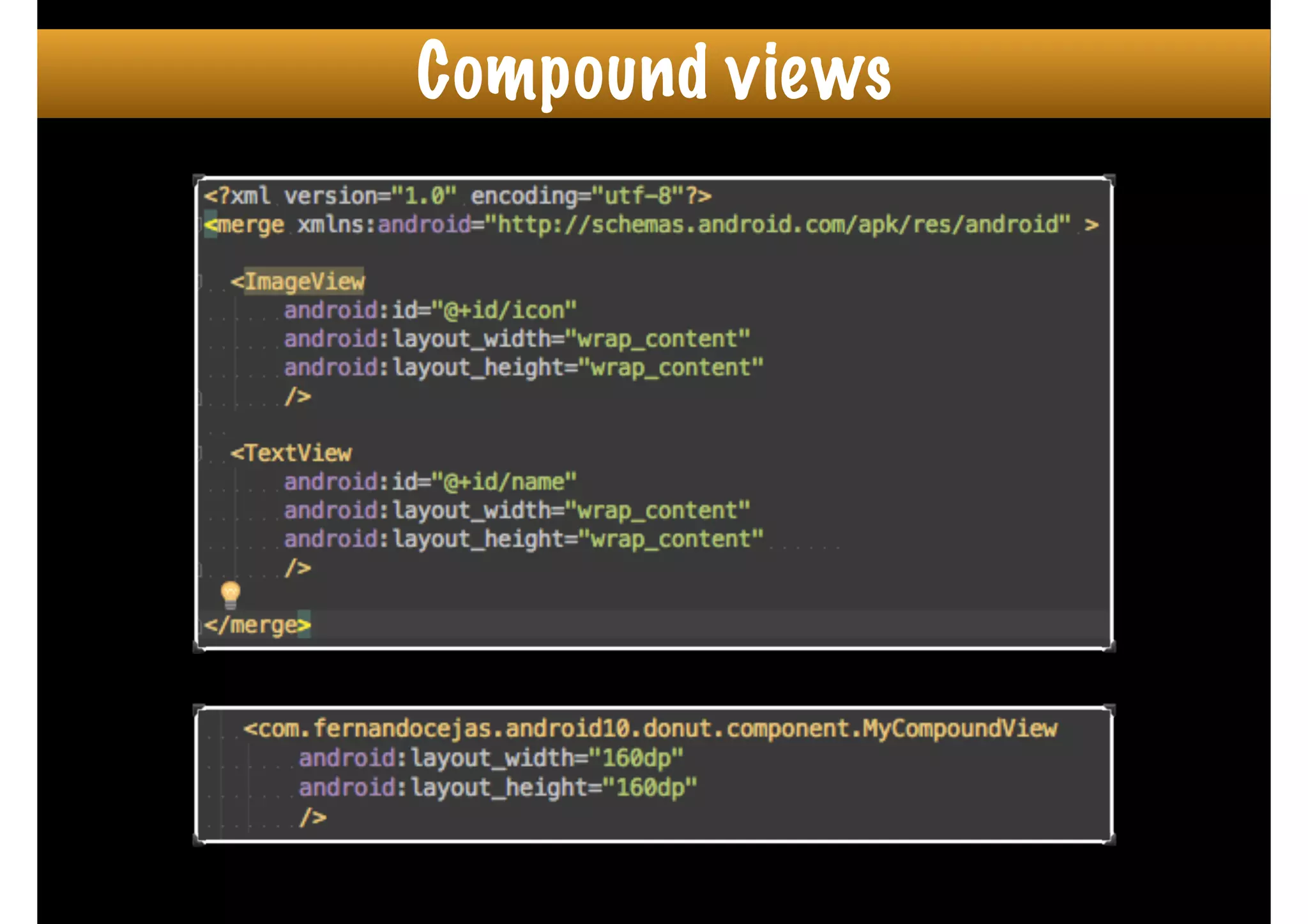
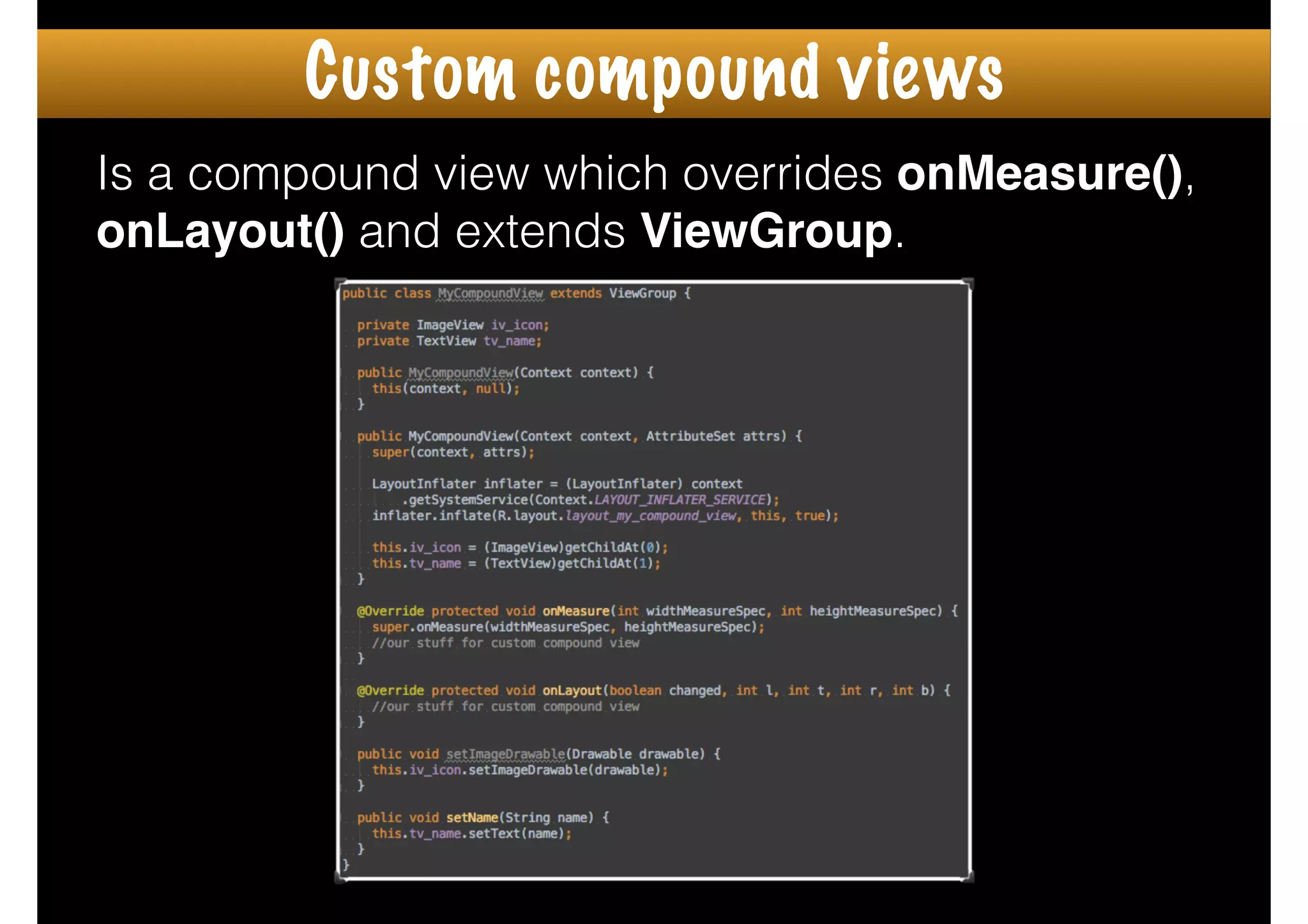
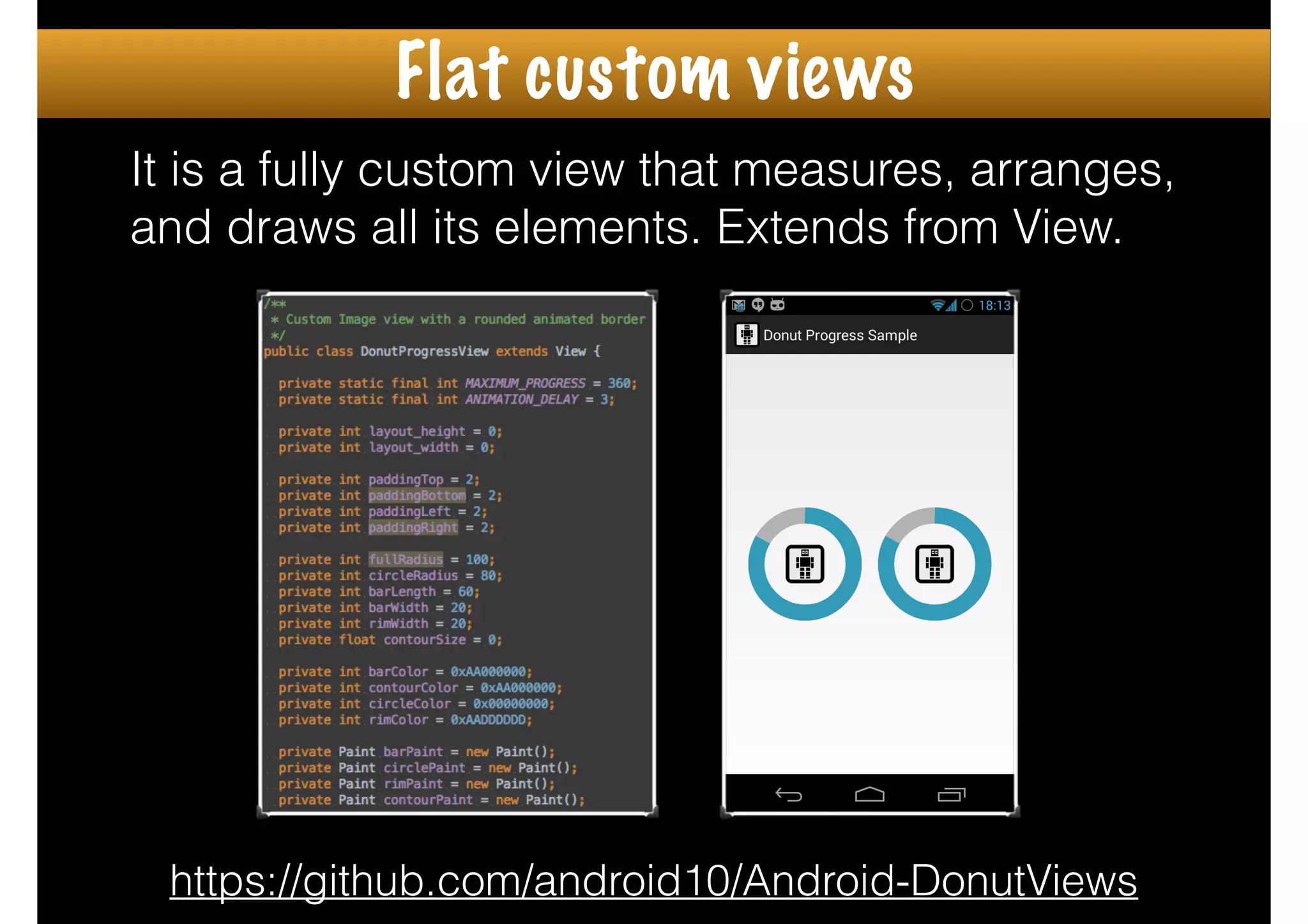
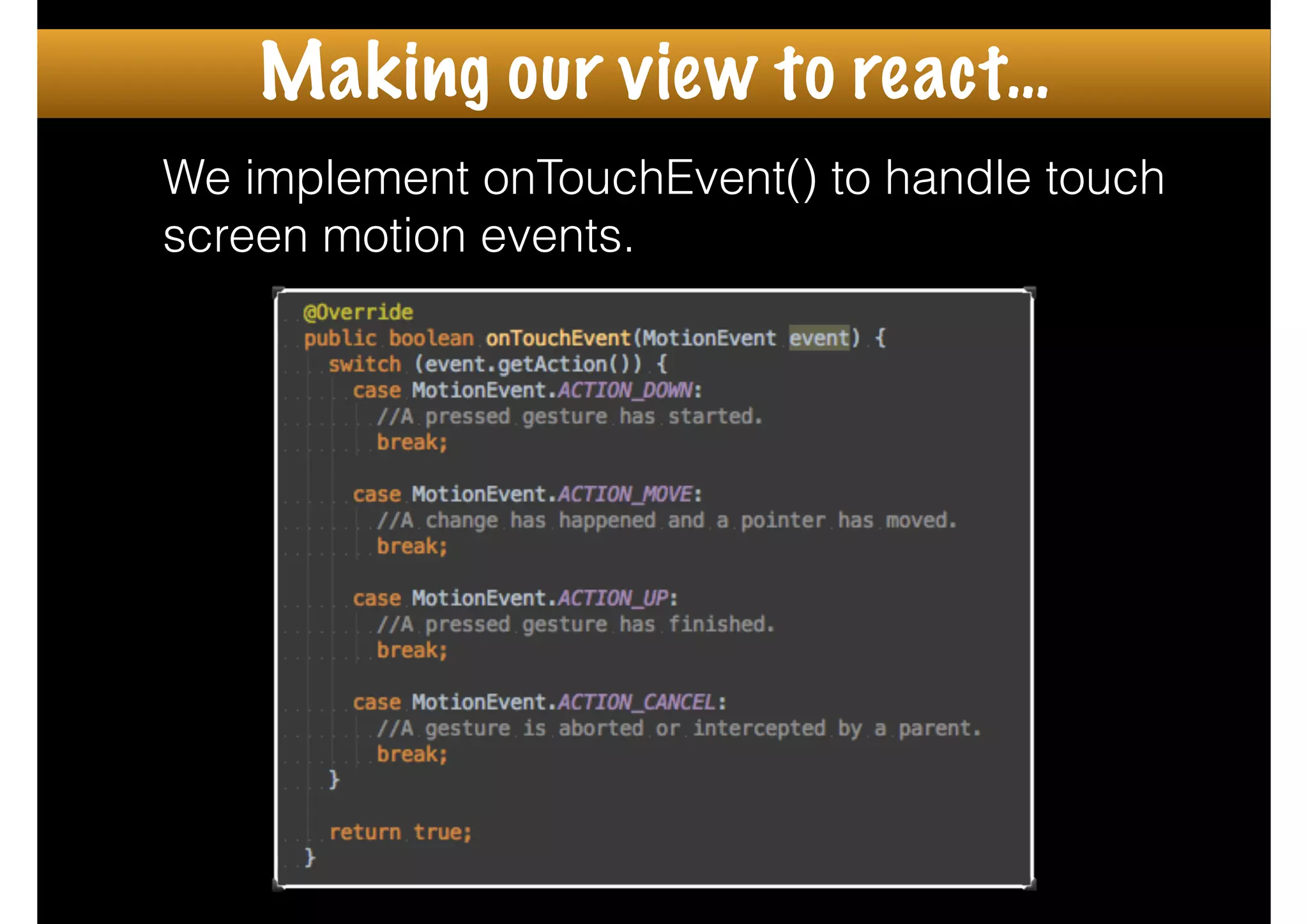
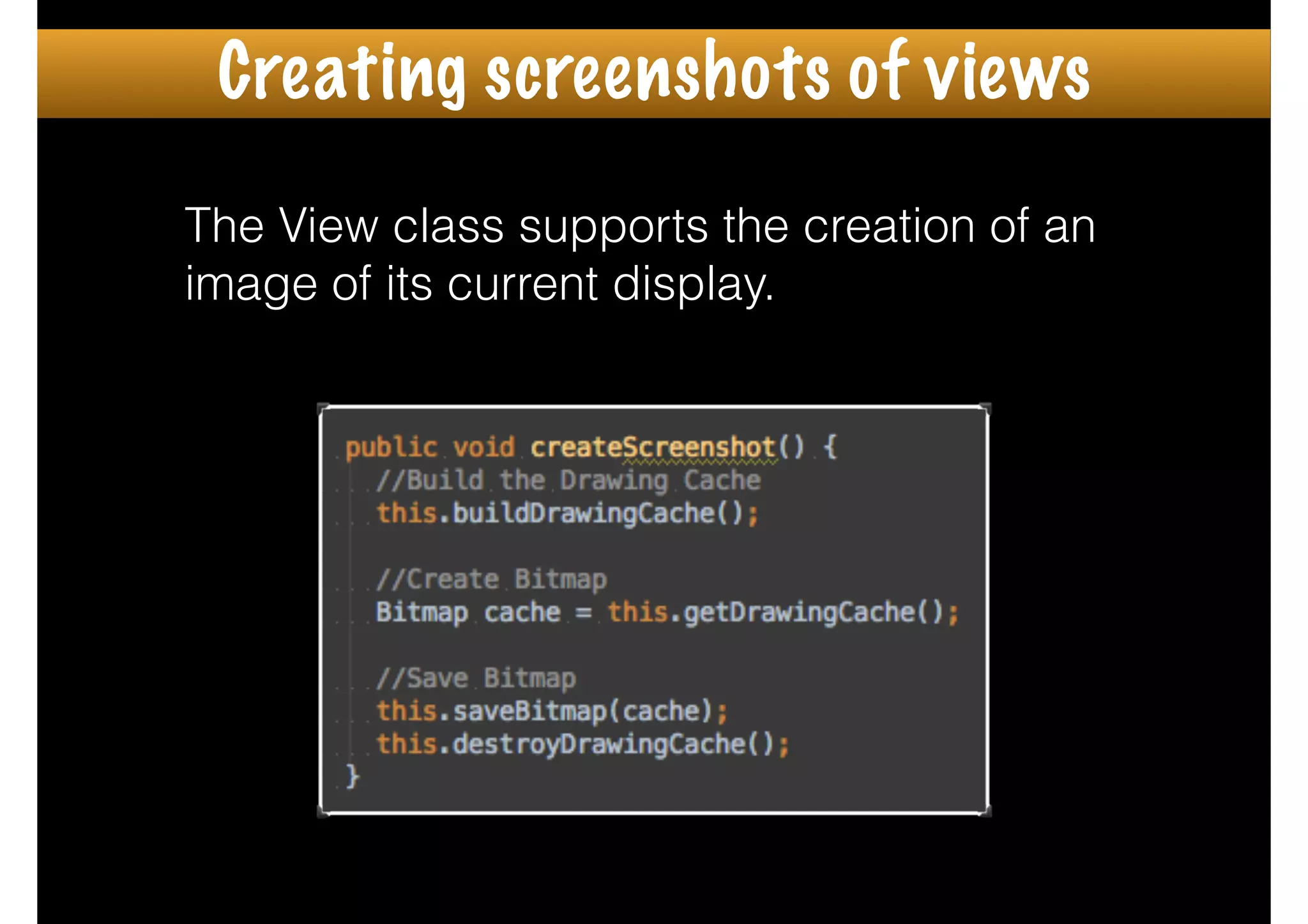
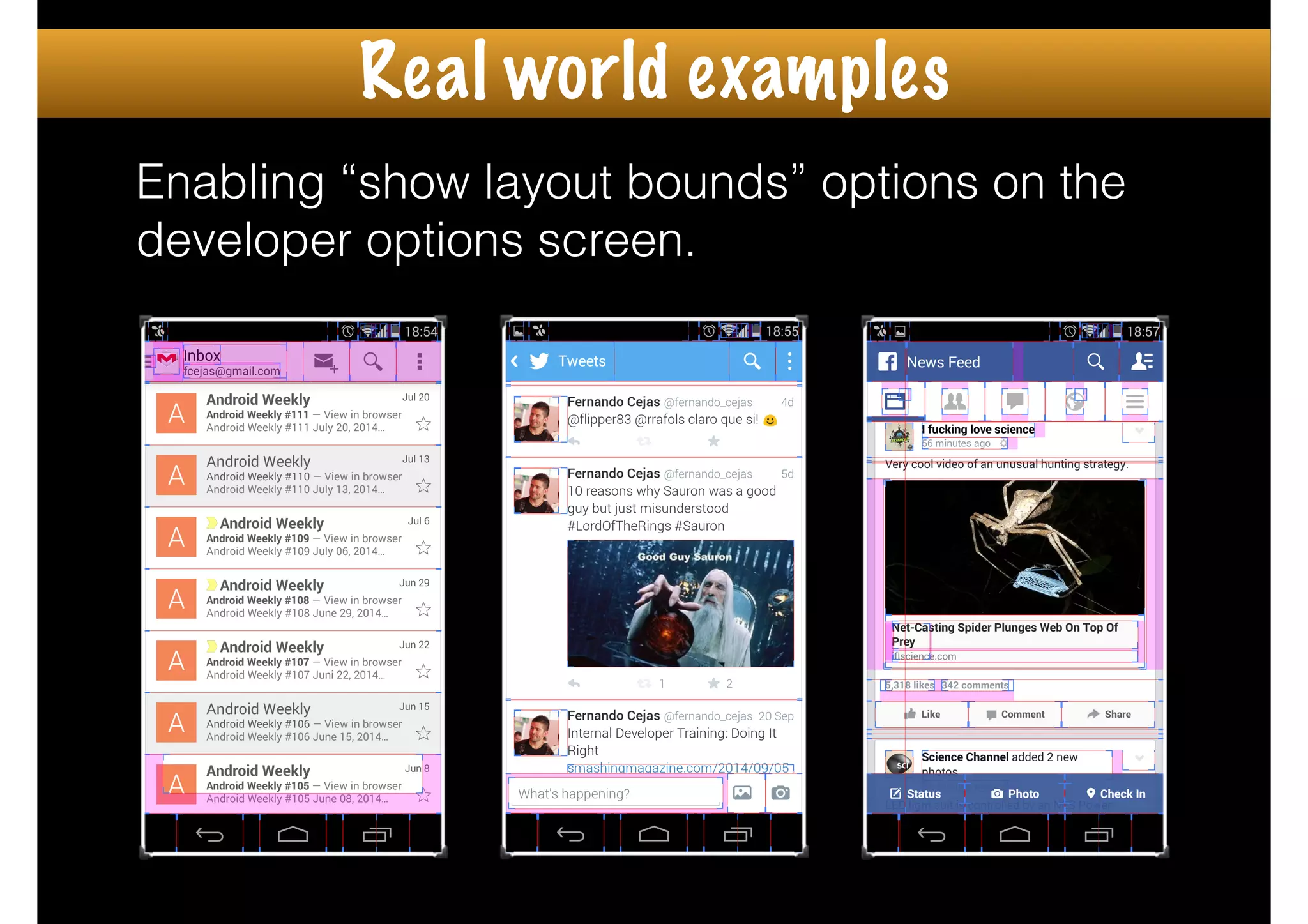
The document outlines how to create custom views in Android, emphasizing the importance of the view hierarchy, the measurement, layout, and drawing processes. It discusses the responsibilities of views and provides guidelines for creating compound and flat custom views, as well as tips for performance optimization. It also highlights best practices for handling view attributes, state saving, and when to avoid using custom views.