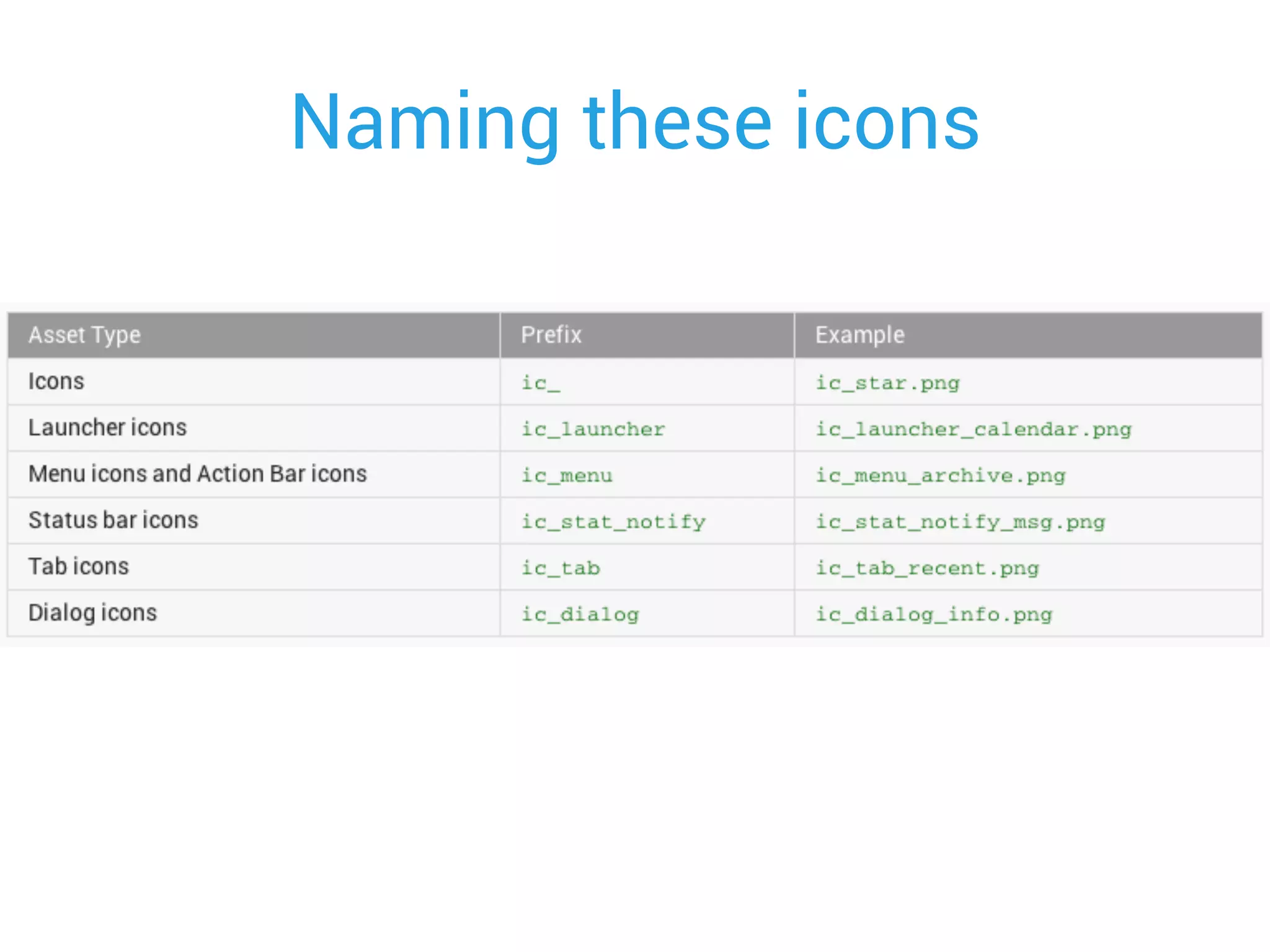
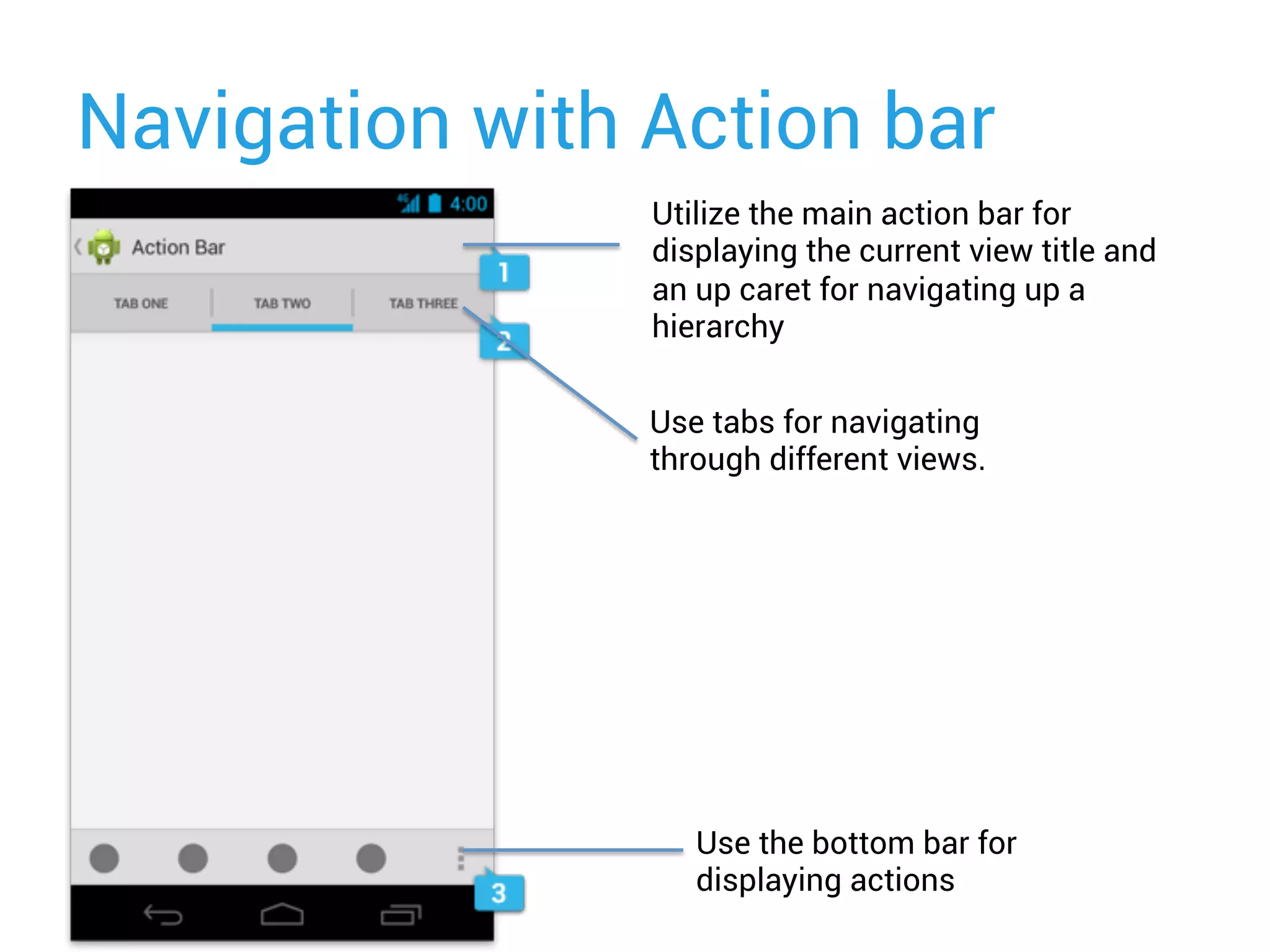
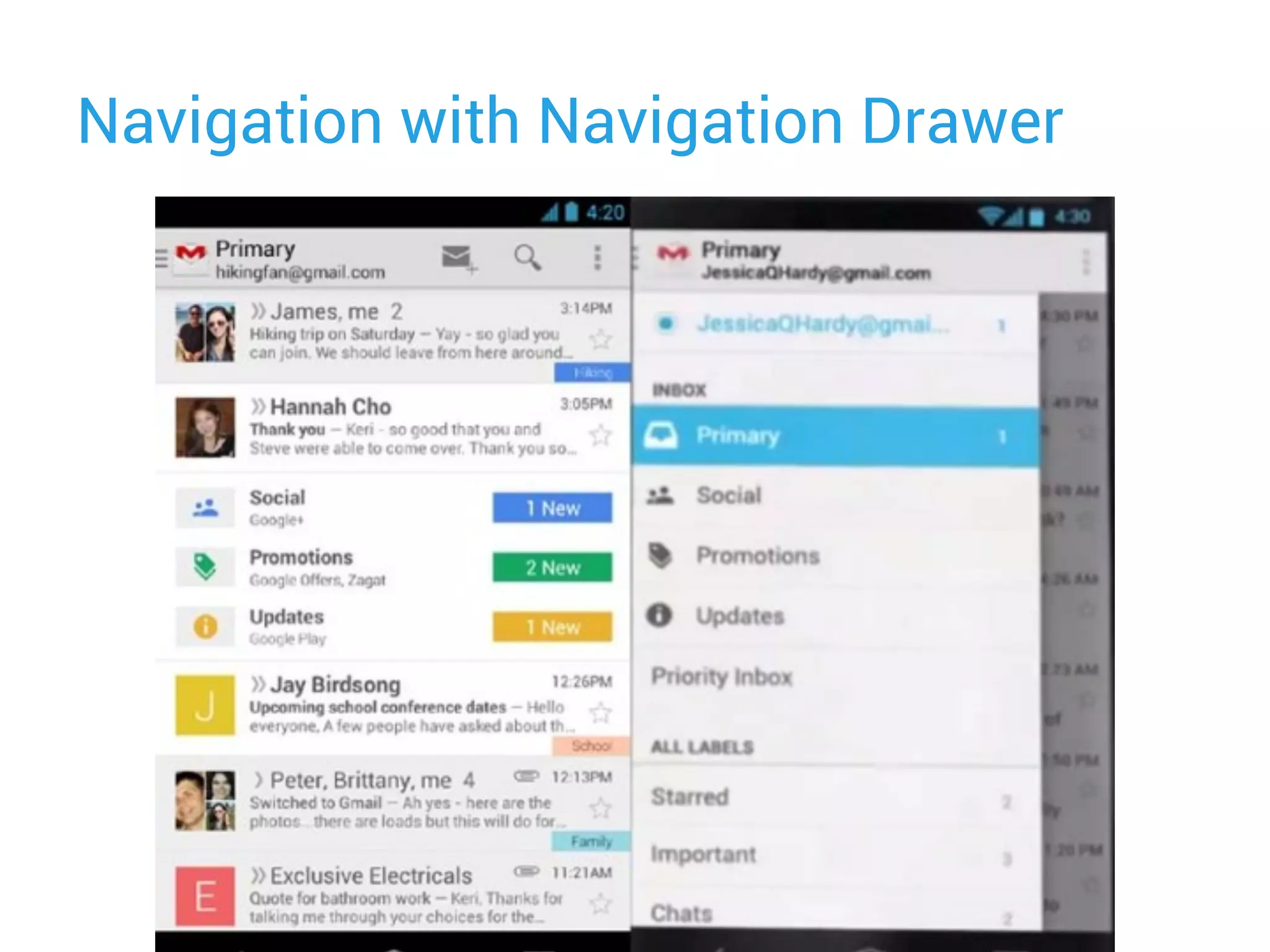
This document provides an overview of designing user interfaces for Android apps. It discusses:
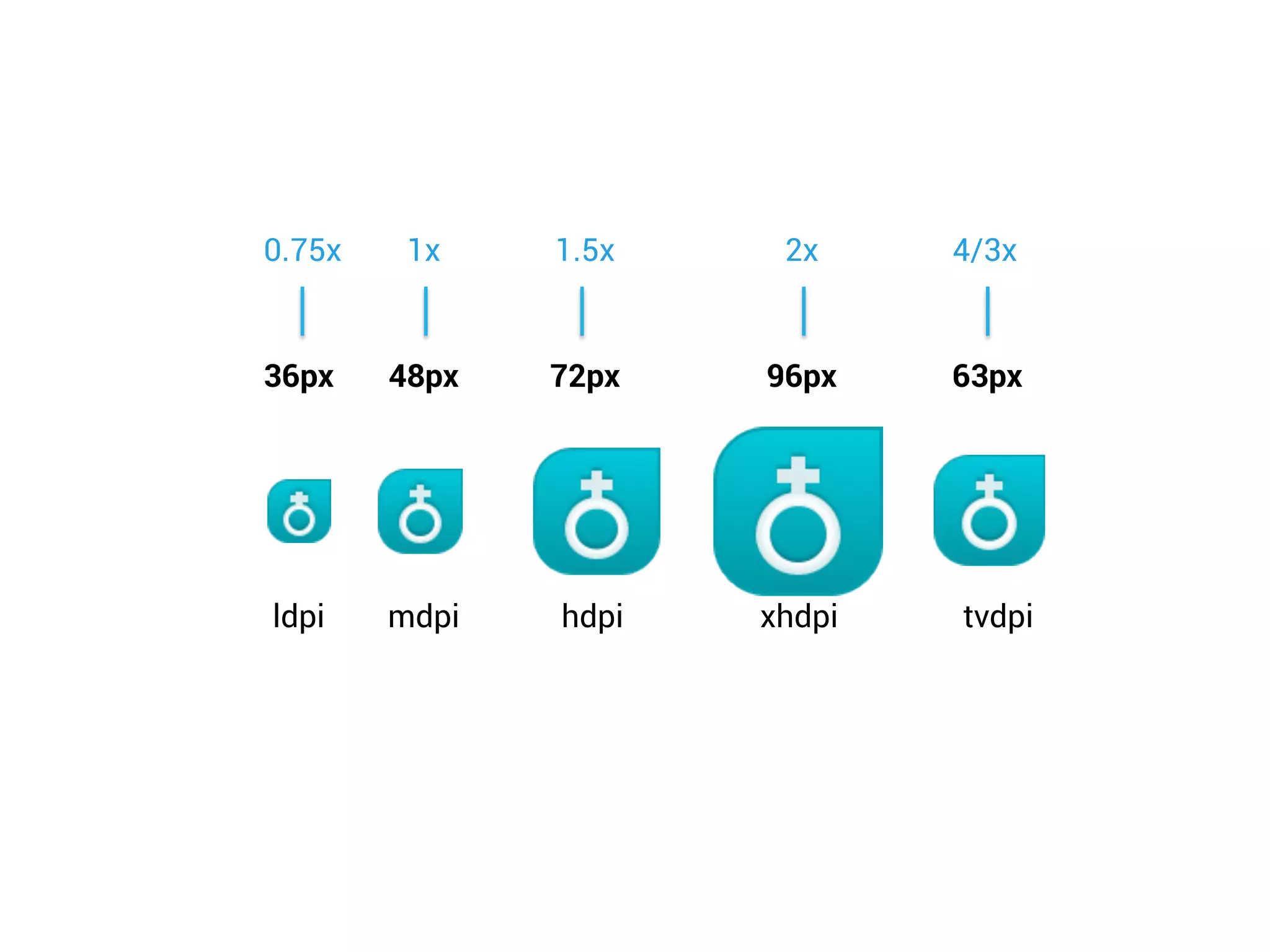
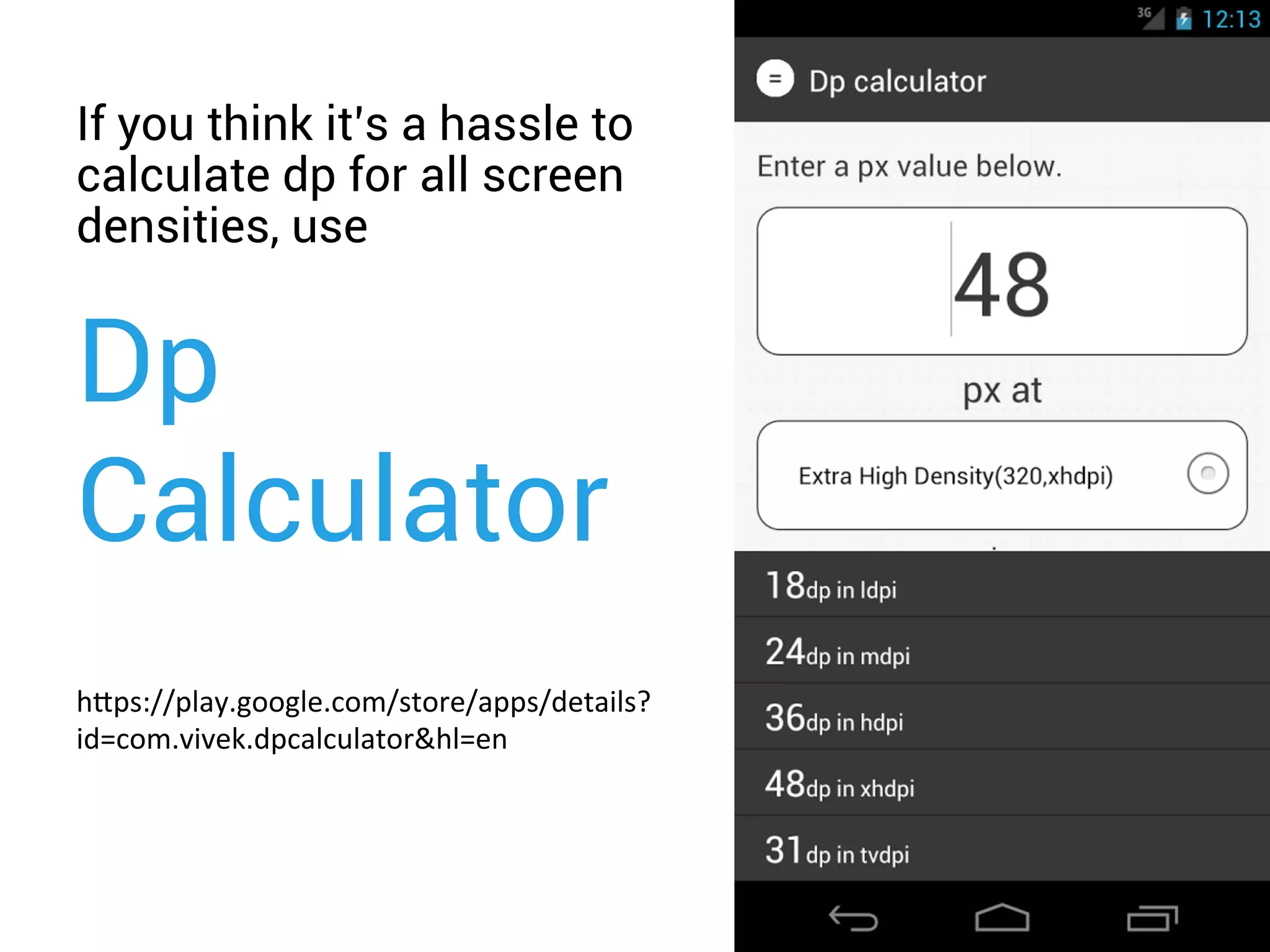
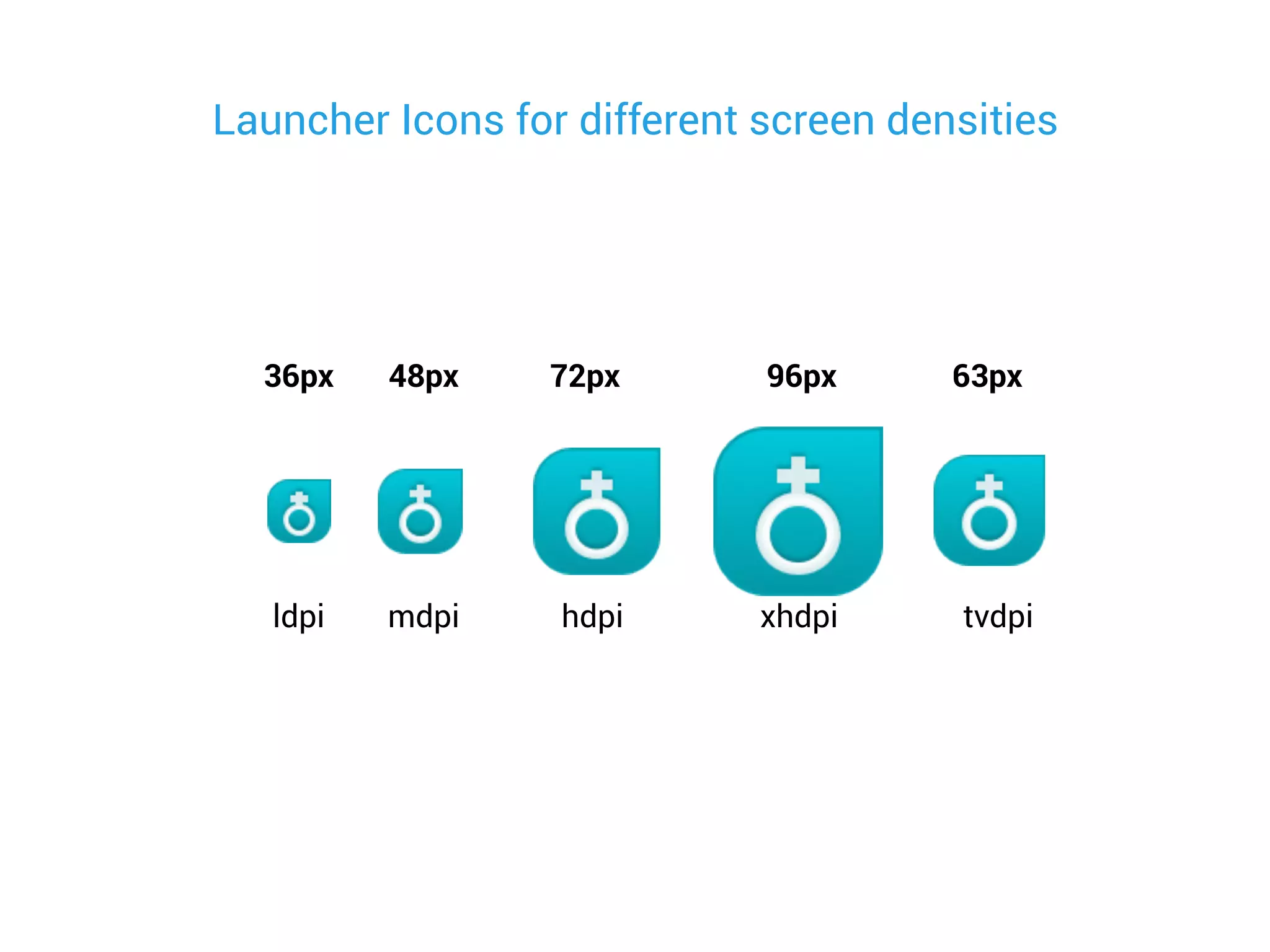
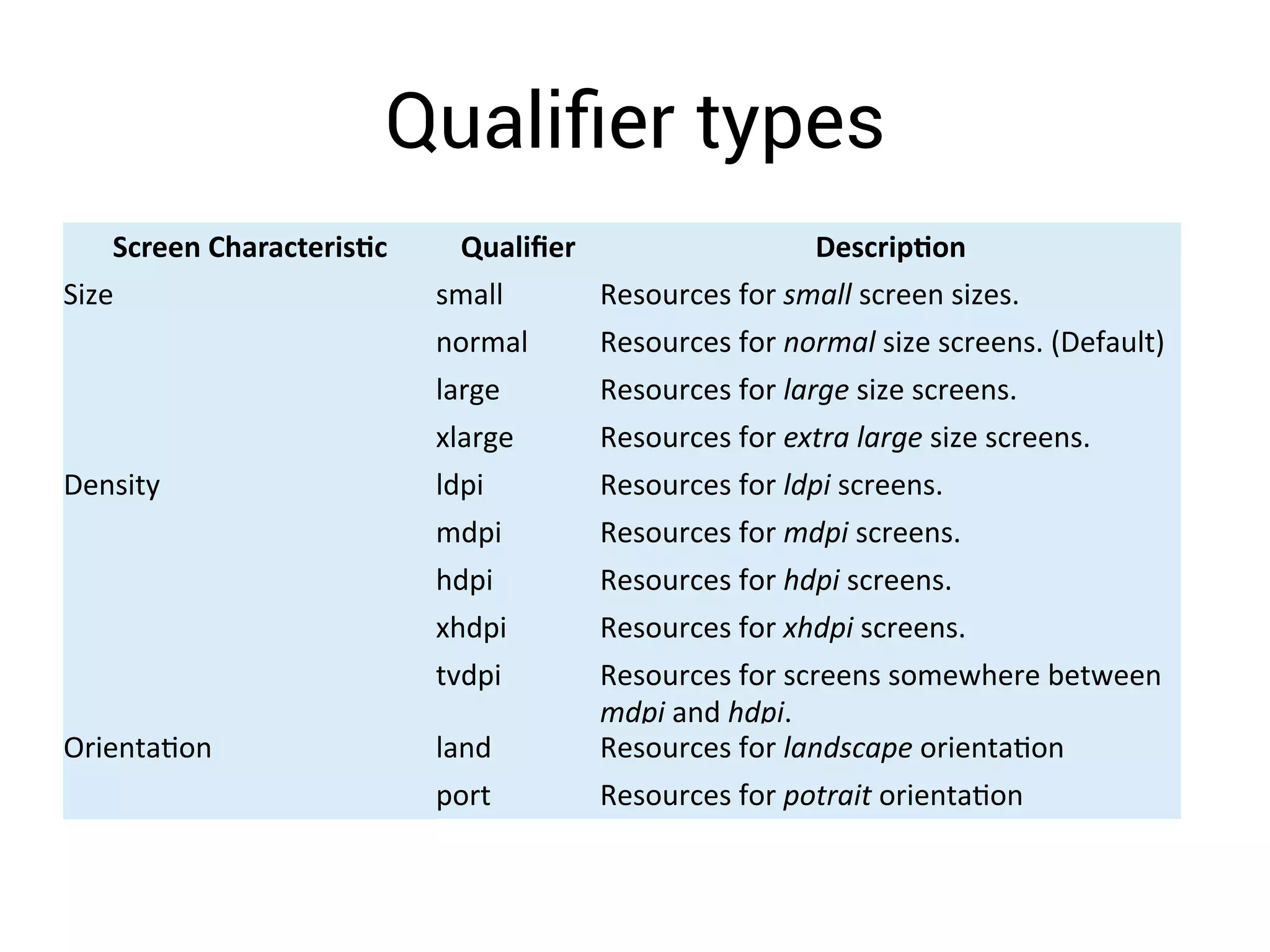
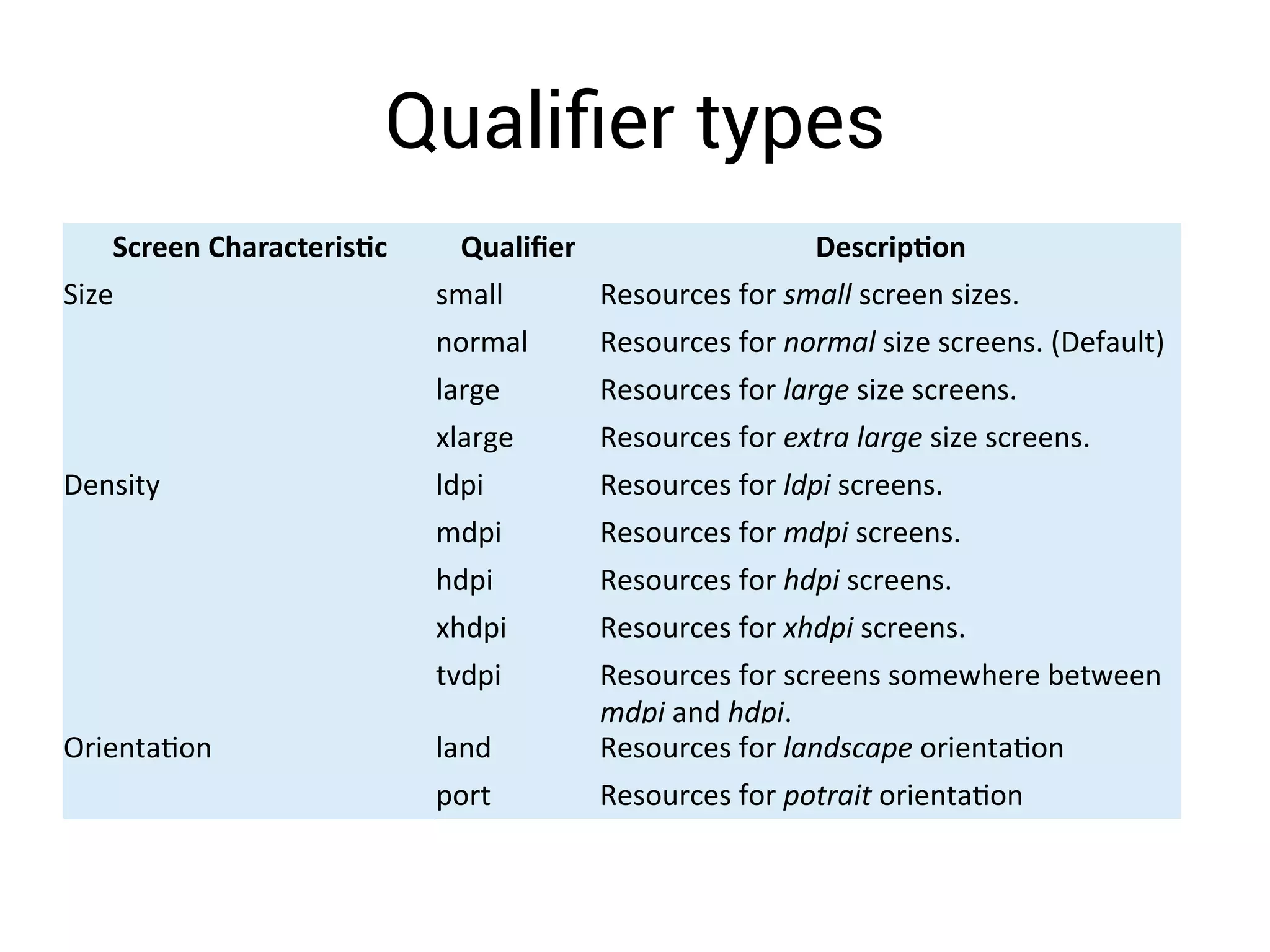
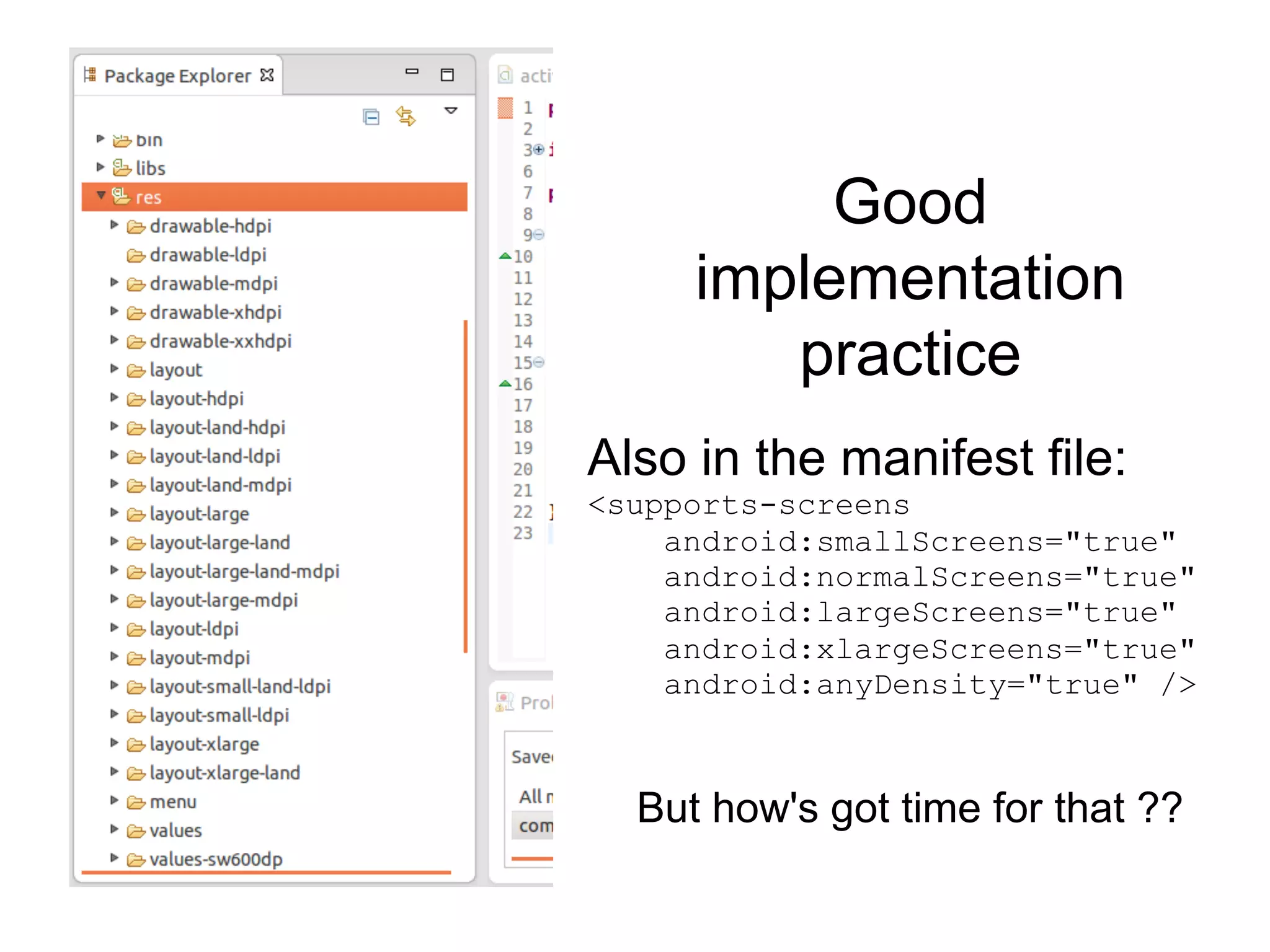
- Using layout qualifiers to provide resources for different screen densities and sizes, such as -mdpi or -large.
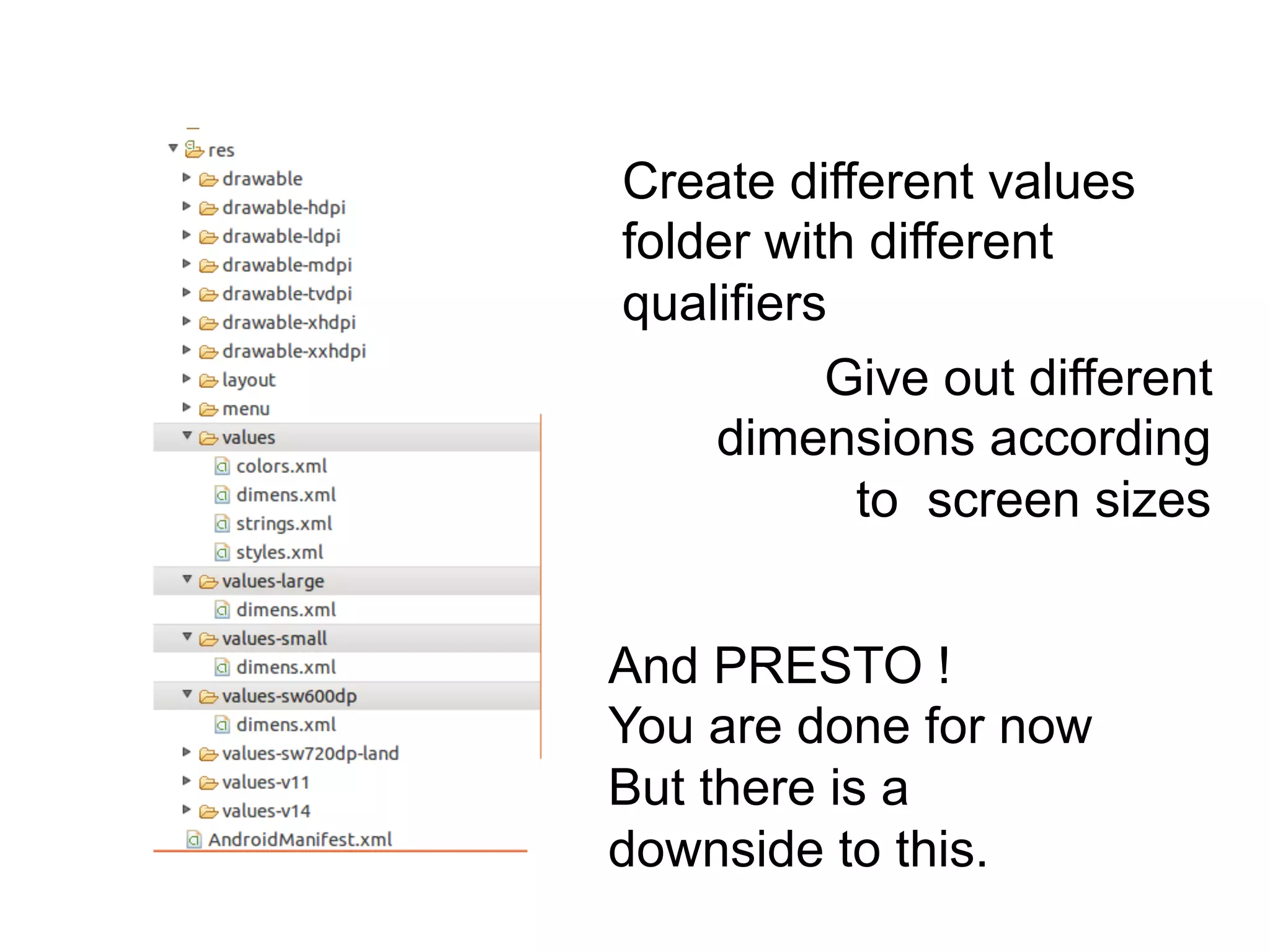
- Implementing qualifiers by placing resources like layouts and bitmaps in folders like res/layout-small and res/drawable-hdpi.
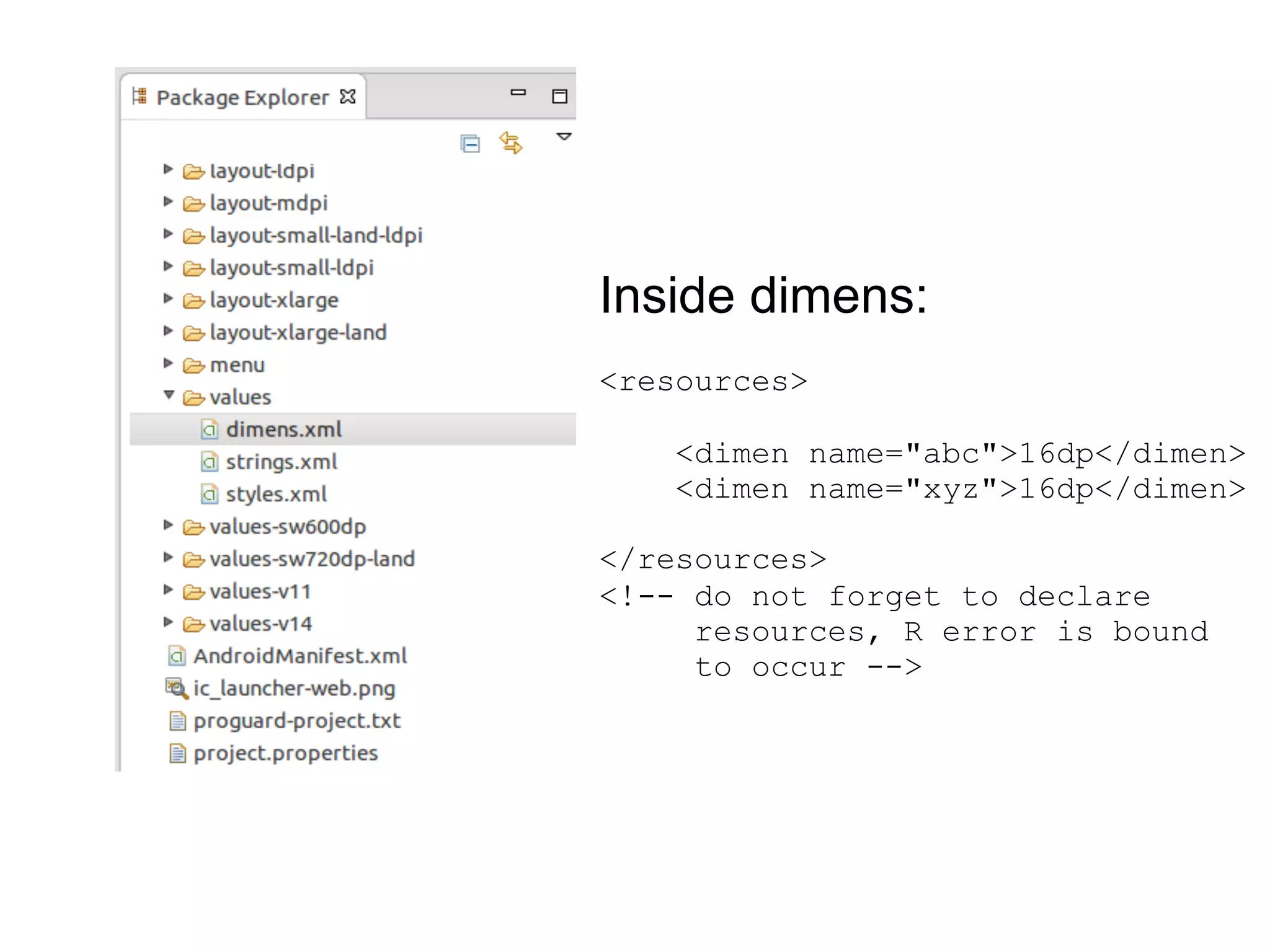
- A hack to use dimensions defined in dimens.xml to set view widths and heights flexibly across screen densities without needing multiple layout files.
- The benefits of using this approach are that it reduces the need to create multiple layout files, but it has downsides like not being as precise as unique layout files.