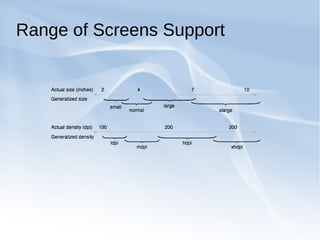
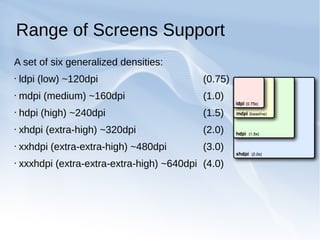
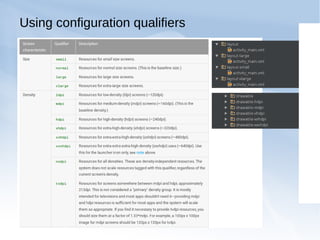
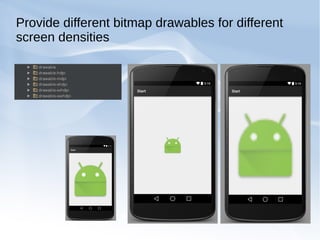
The document discusses supporting multiple screen sizes in Android applications. It explains that Android supports a variety of screen sizes and densities, and provides developers with tools to adjust their user interfaces accordingly. The key methods for supporting multiple screens involve declaring supported screen sizes in the manifest, using configuration qualifiers for resources, providing alternative layouts and drawables, and programmatically scaling UI elements. The best approach is to follow Android's built-in support for multiple screens by using these configuration techniques together rather than relying on any single method.