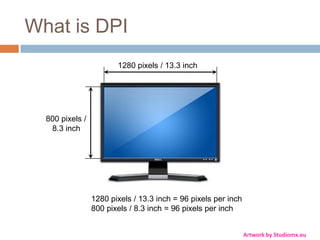
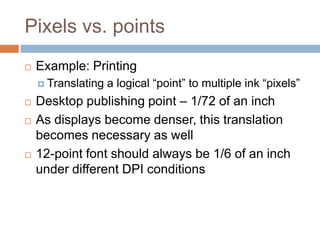
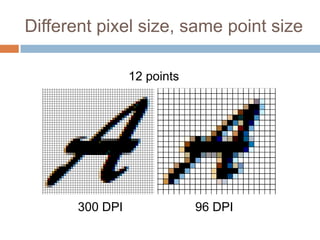
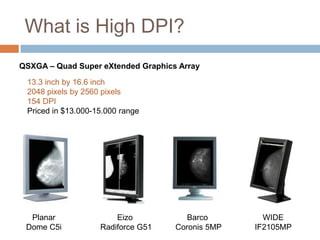
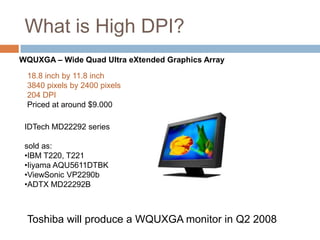
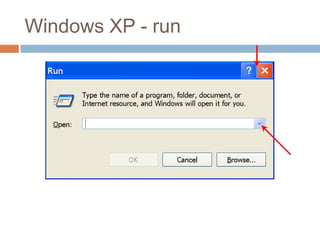
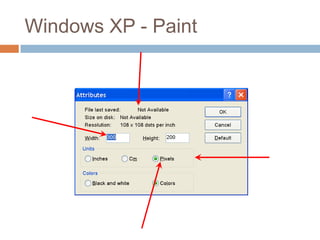
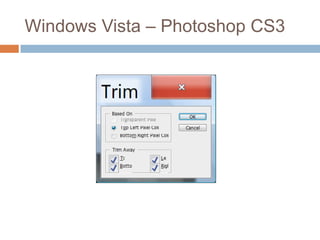
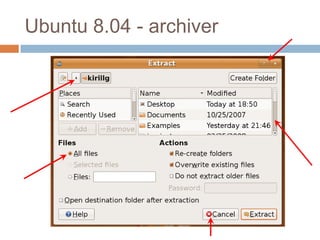
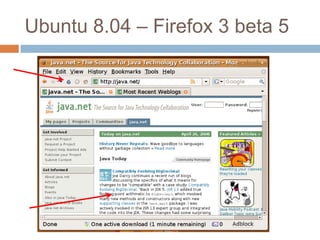
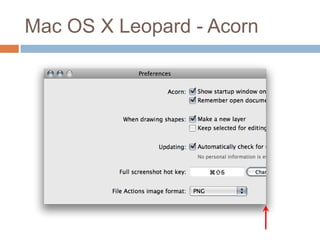
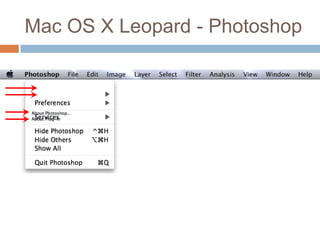
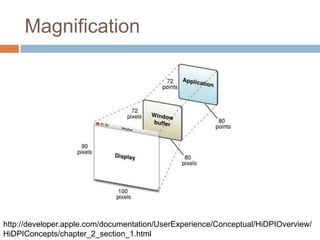
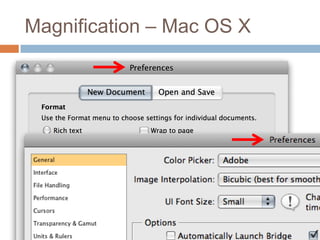
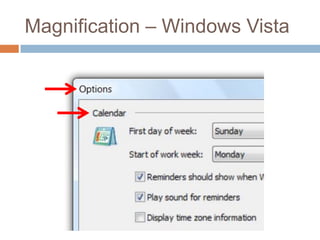
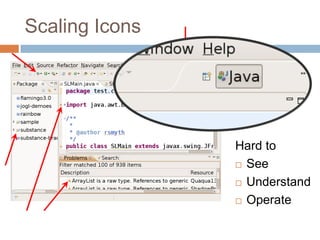
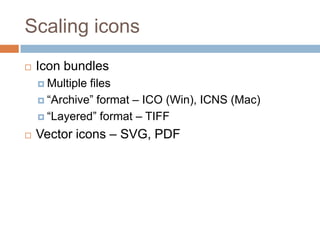
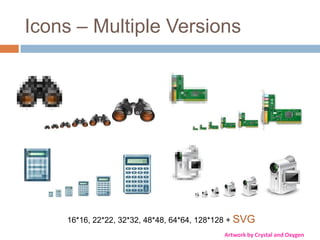
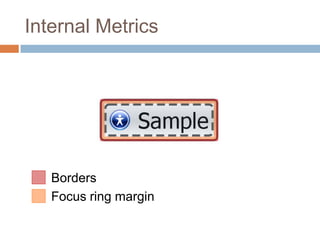
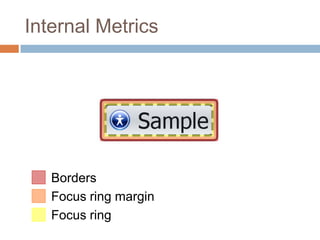
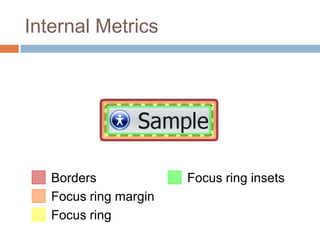
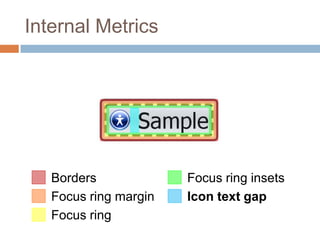
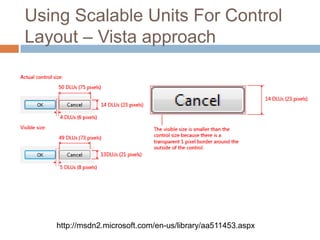
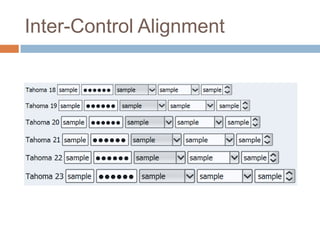
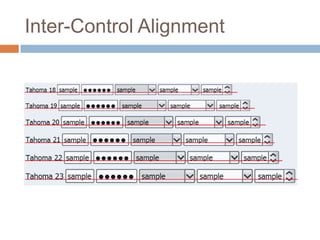
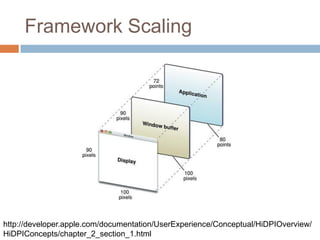
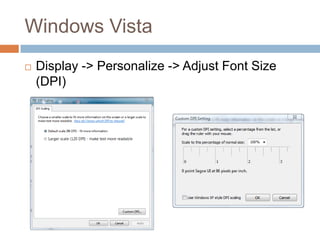
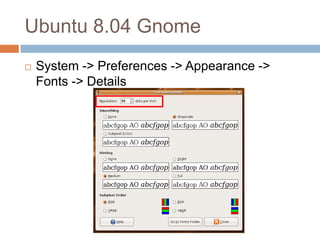
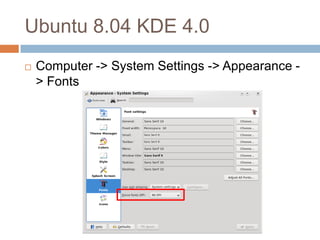
This document discusses high-resolution monitors and how to make user interfaces scale properly with increasing screen resolutions. It begins with an introduction and agenda, then covers key concepts like DPI, pixels vs. points, and what constitutes a high DPI display. Several examples of broken applications at higher resolutions are shown. The document discusses different scaling modes including magnification, application scaling, and framework scaling. It provides tips for testing apps at different resolutions and recommendations for tools like Swing to design apps that scale properly. Related sessions at the conference are also listed.