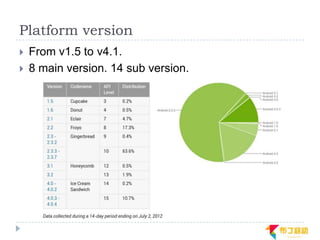
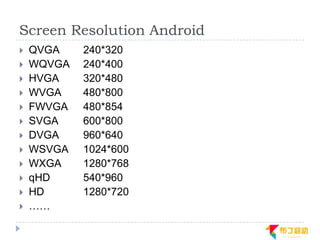
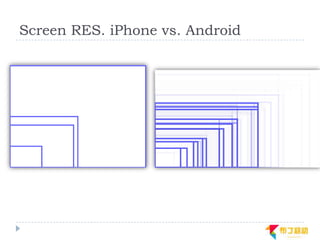
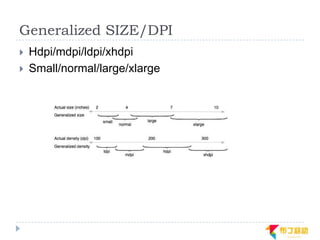
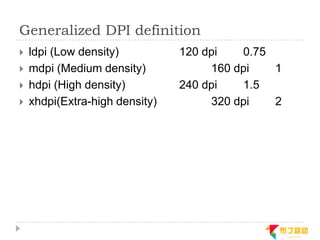
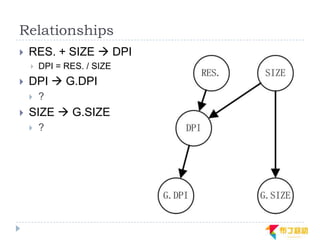
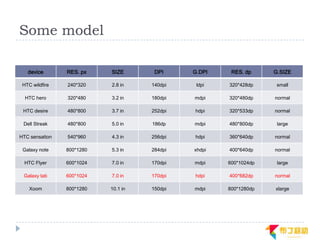
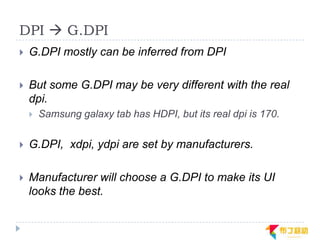
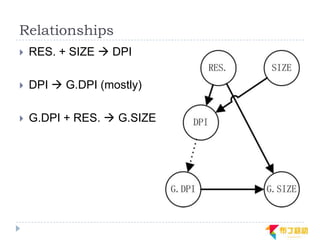
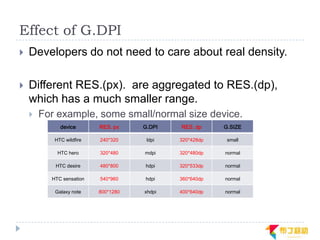
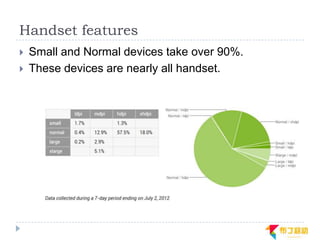
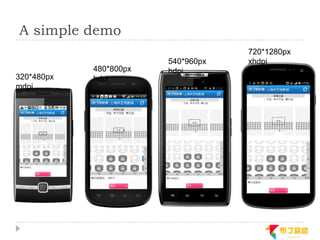
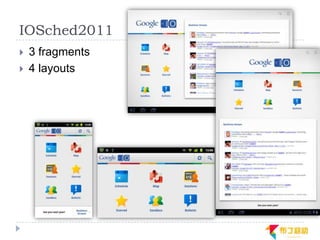
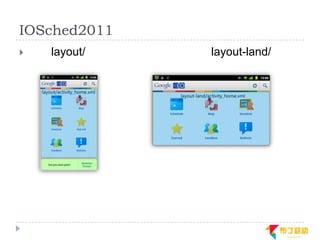
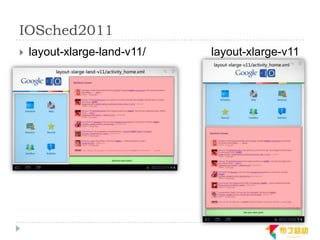
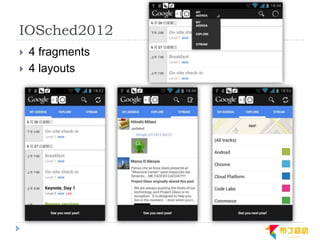
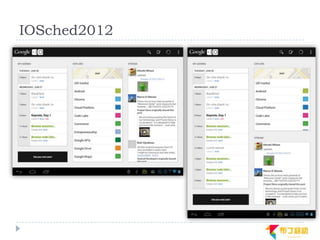
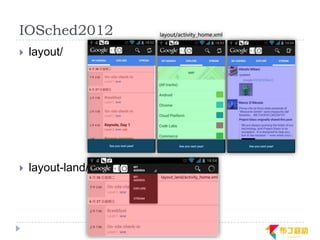
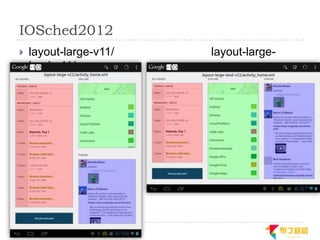
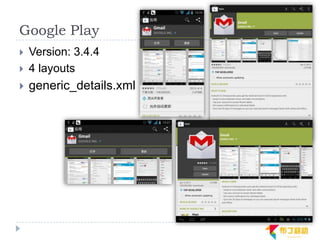
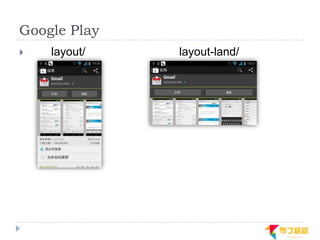
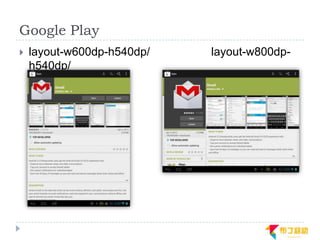
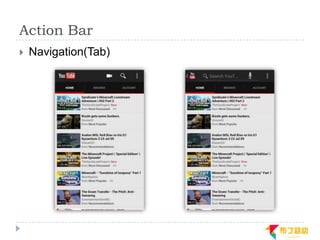
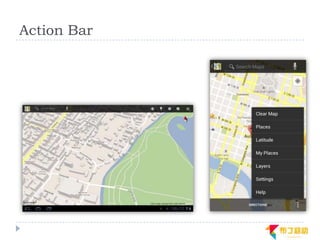
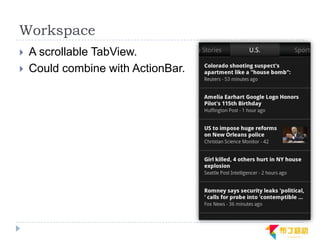
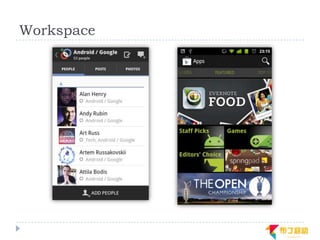
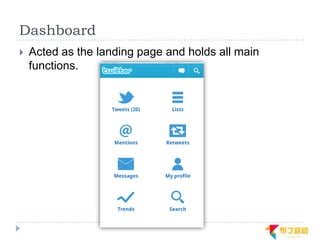
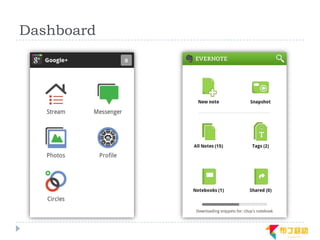
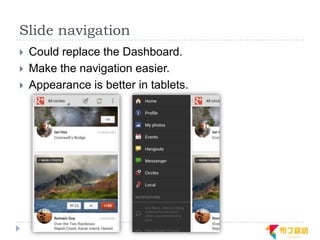
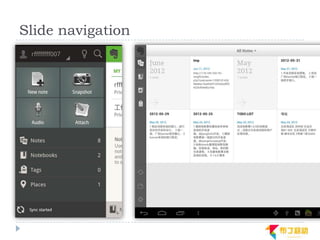
This document discusses supporting multiple screens in Android. It begins by outlining the fragmentation challenges posed by the wide variety of Android devices, platforms, screen sizes, and resolutions. It then explains how Android addresses this through generalized screen size qualifiers, density-independent pixels, and scaling resources based on density. The document recommends developing flexible layouts using a responsive design approach similar to web design. It provides examples of effectively supporting both handsets and tablets through configuration qualifiers and UI patterns like the action bar, workspace, dashboard, and slide navigation.