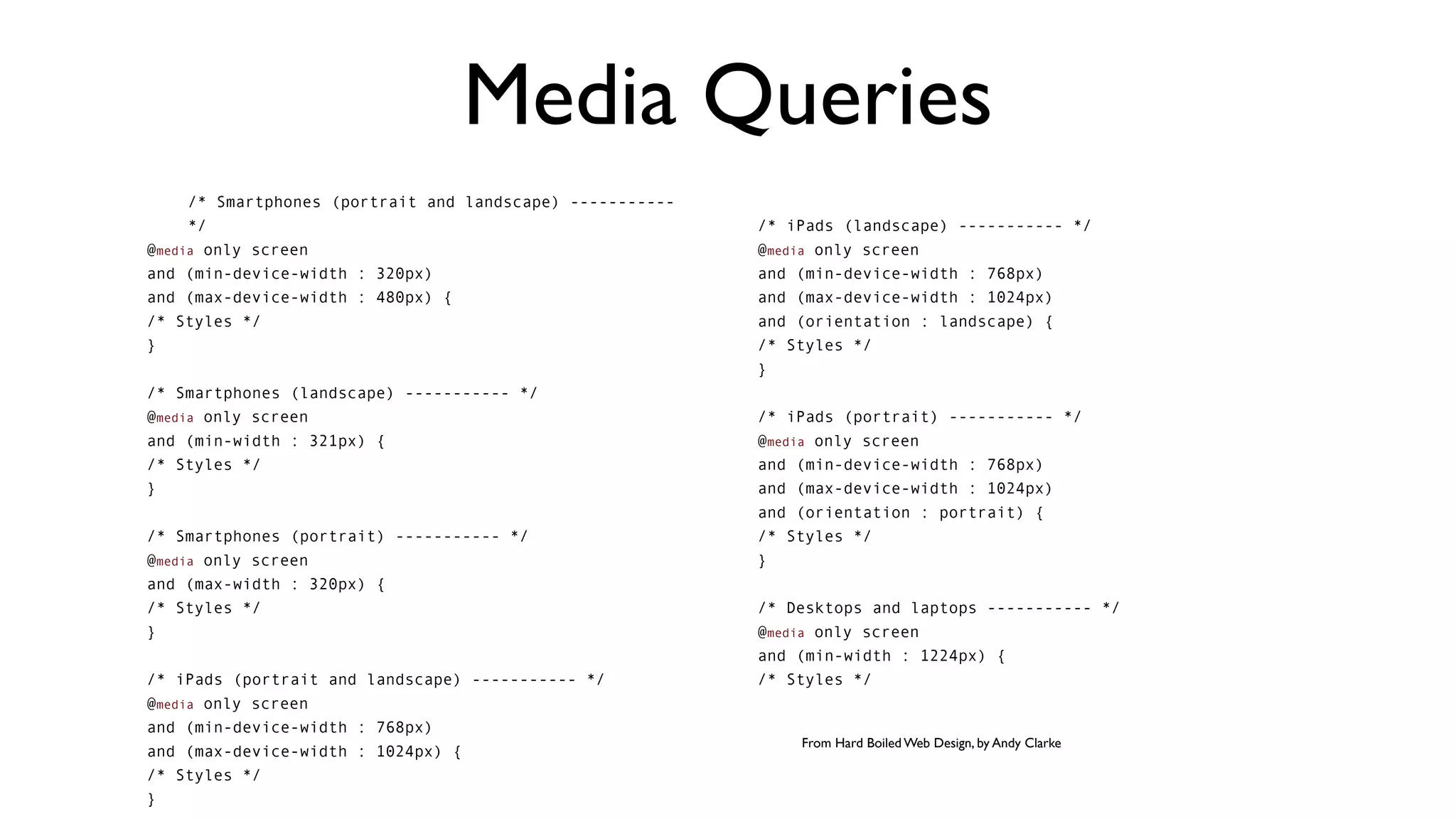
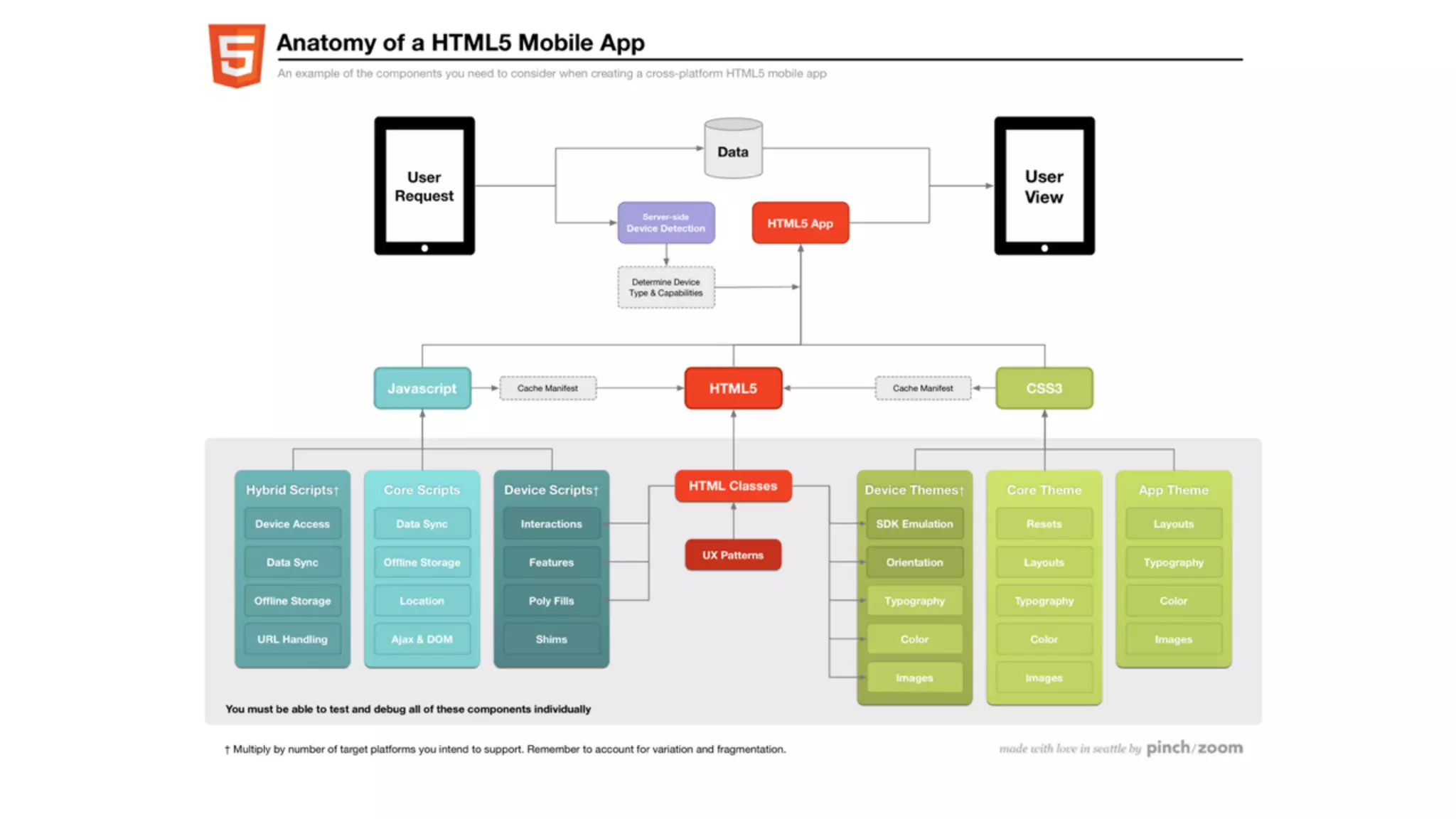
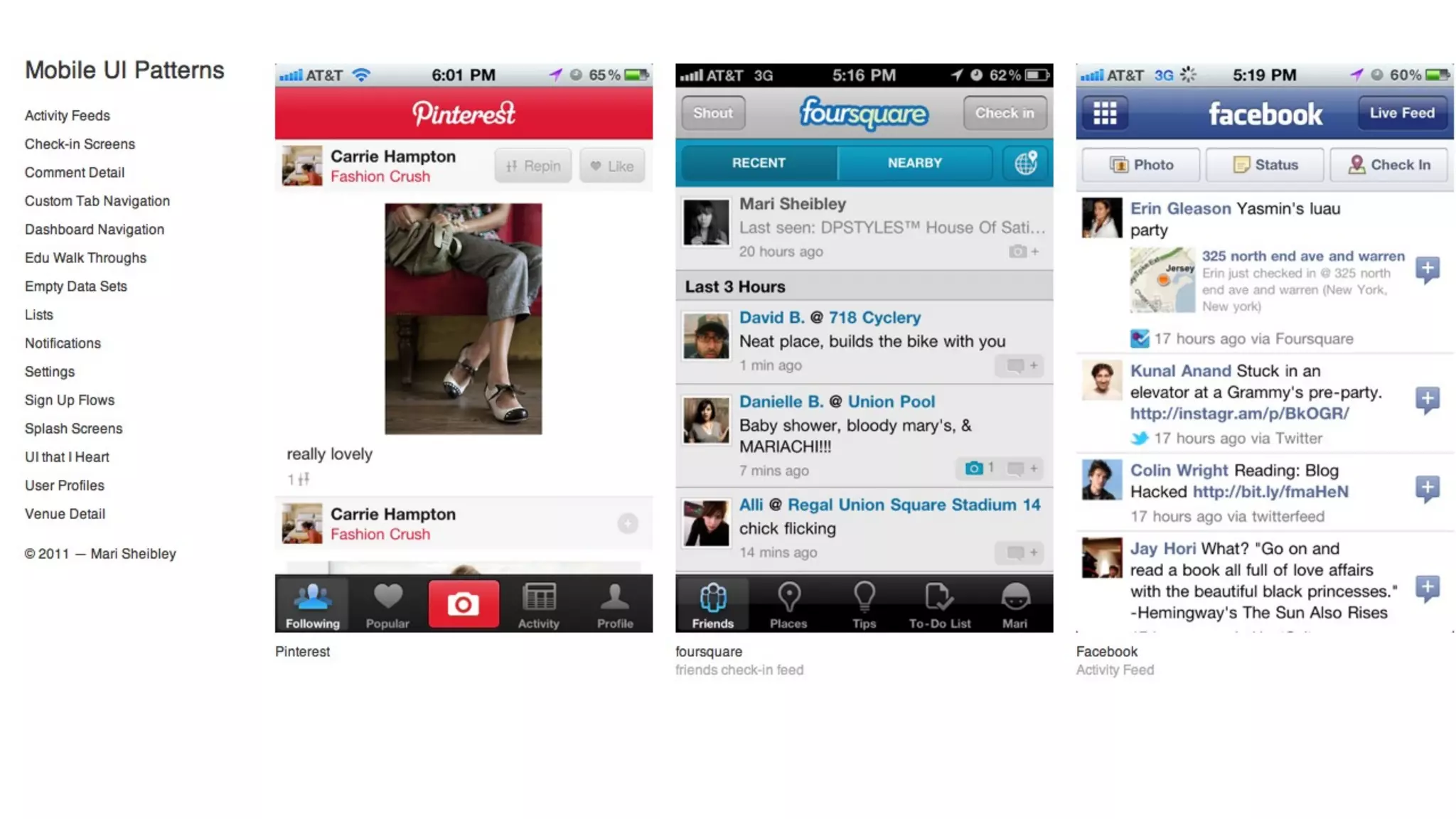
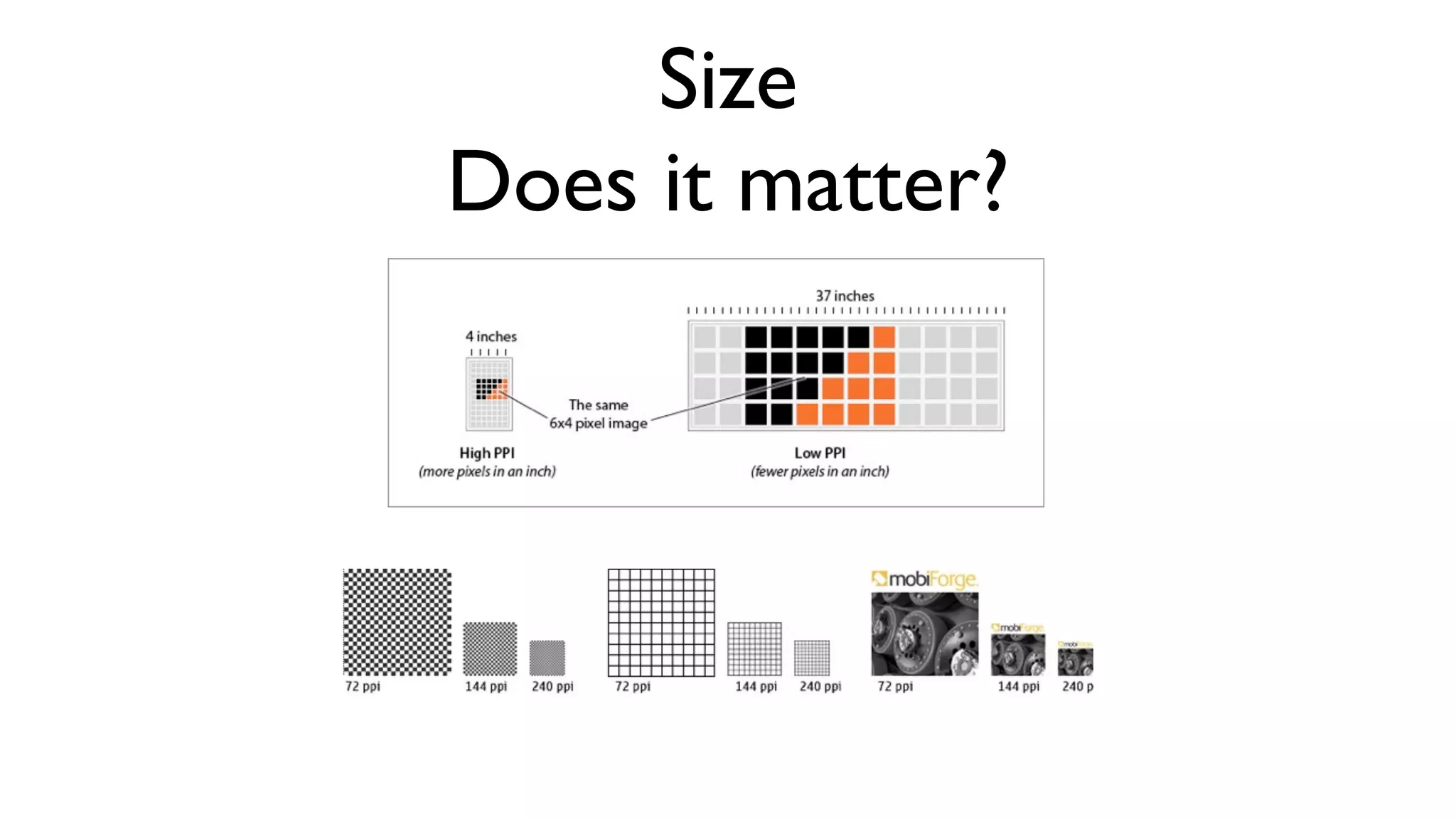
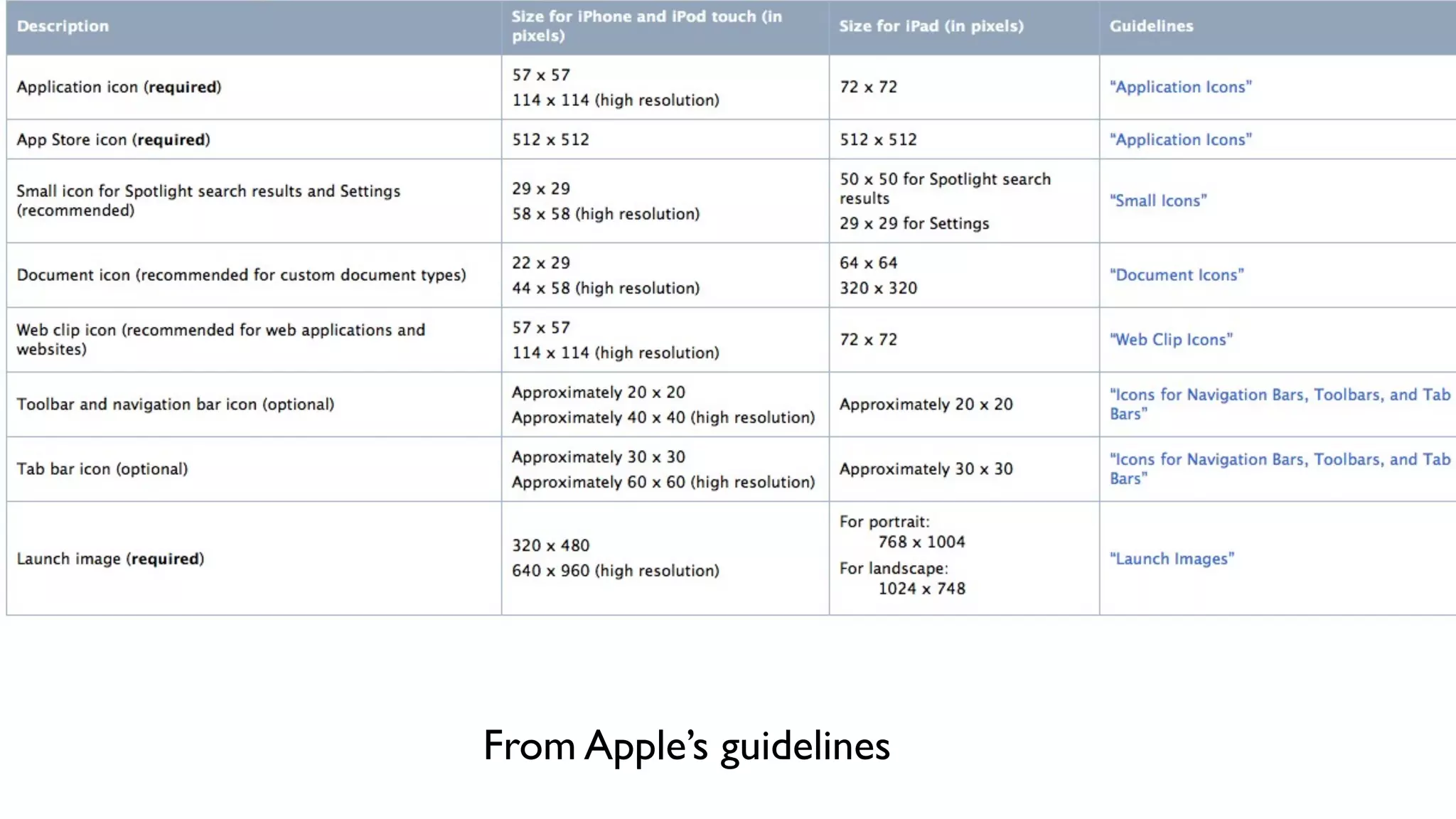
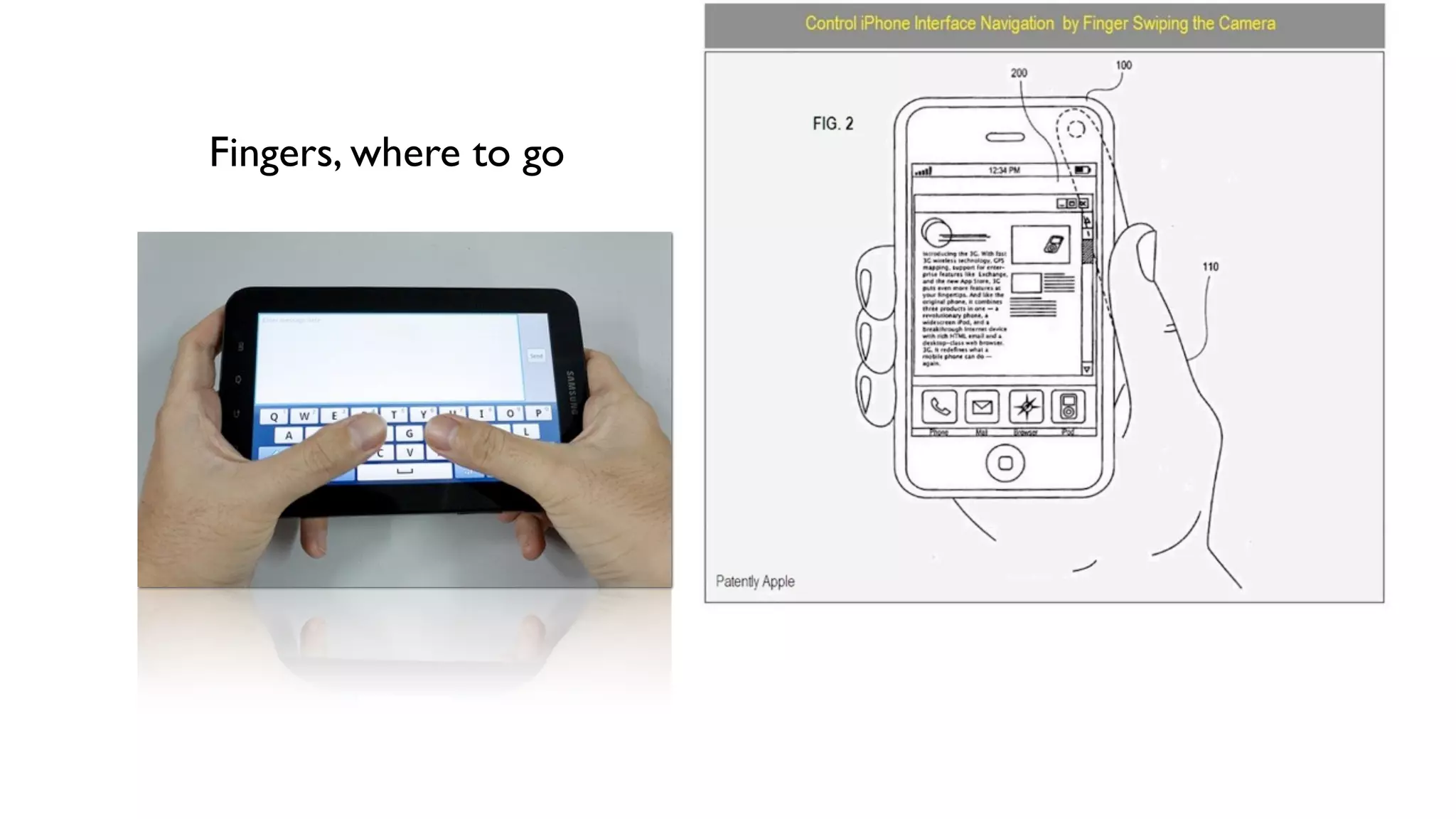
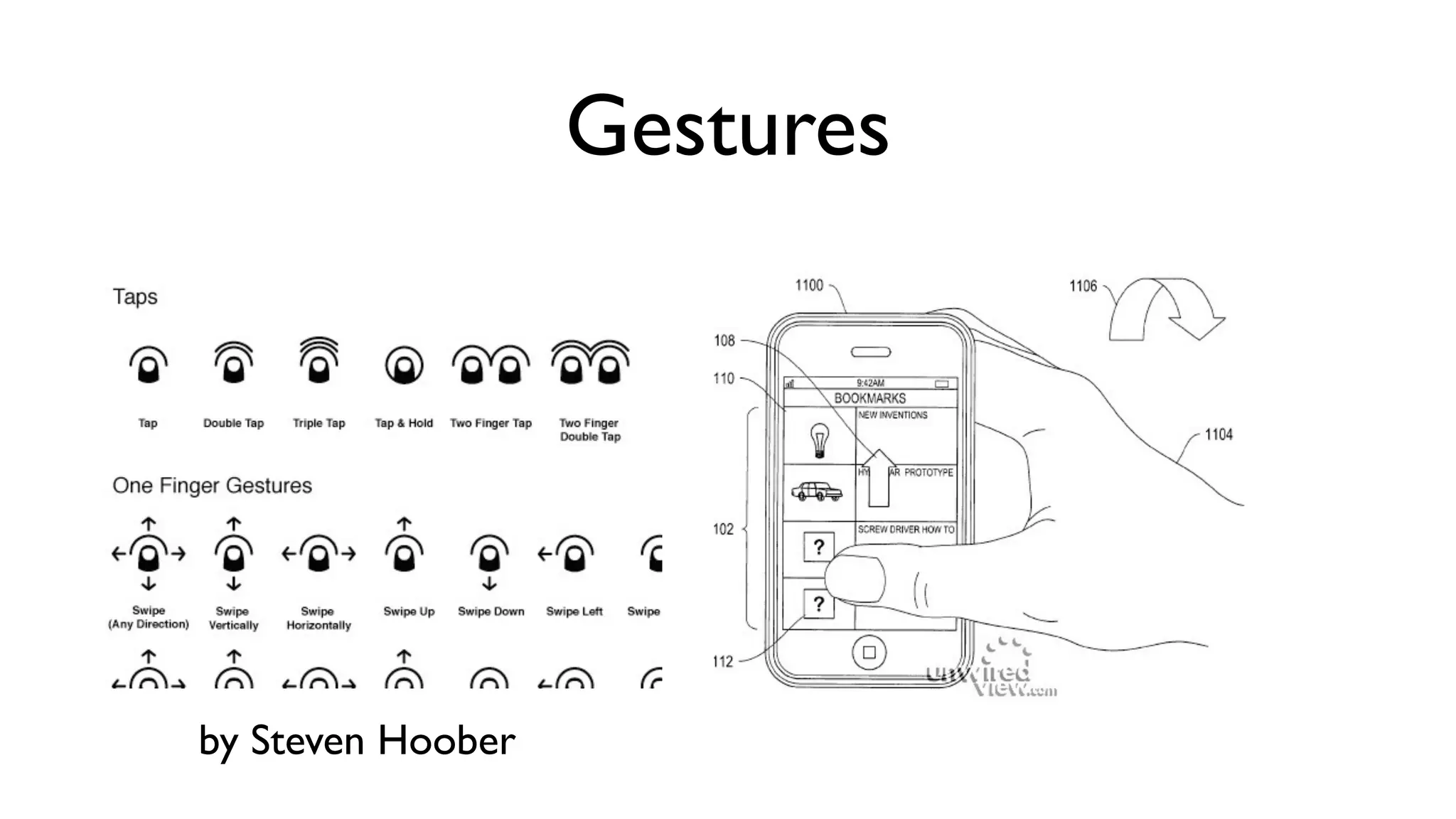
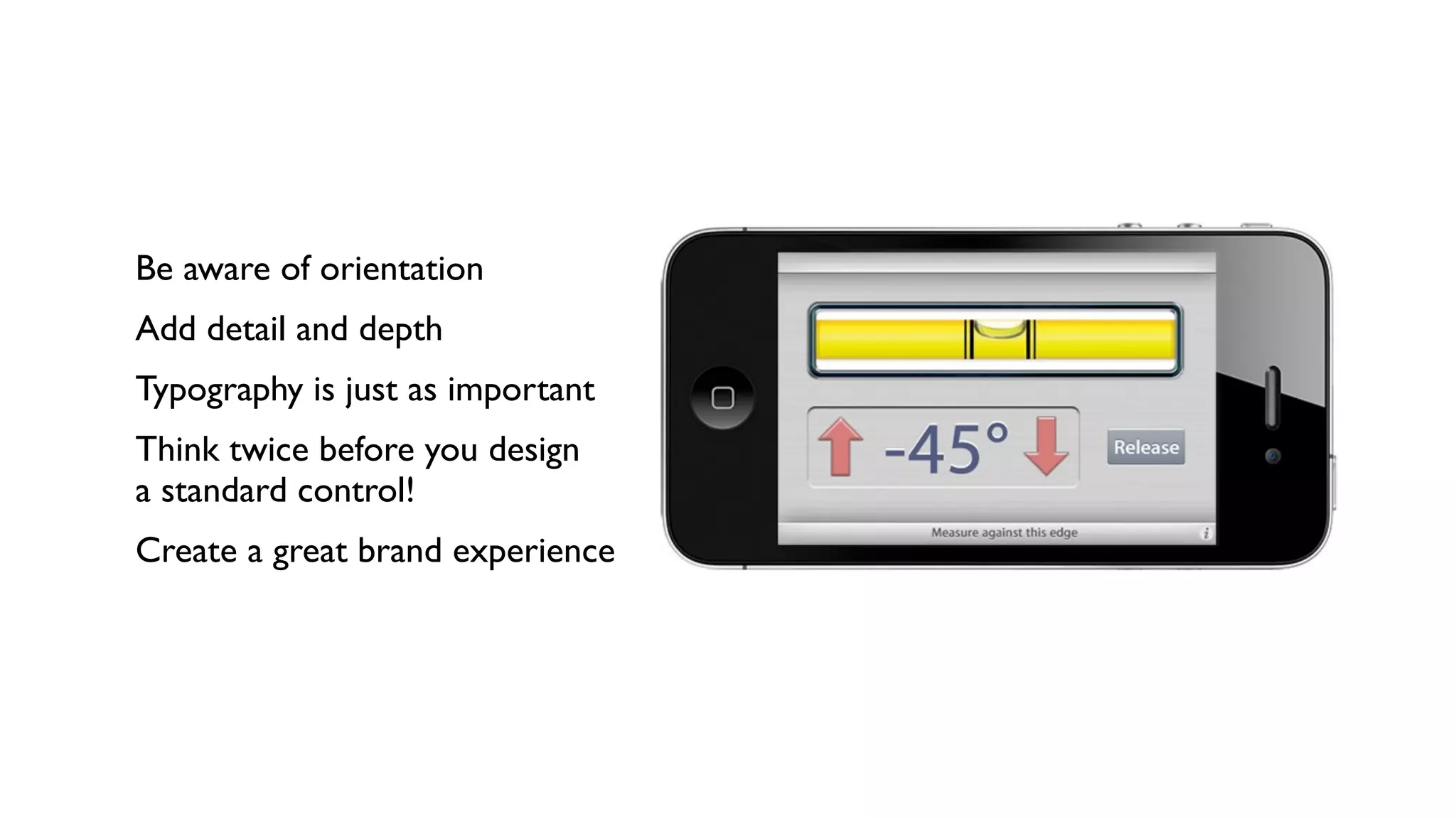
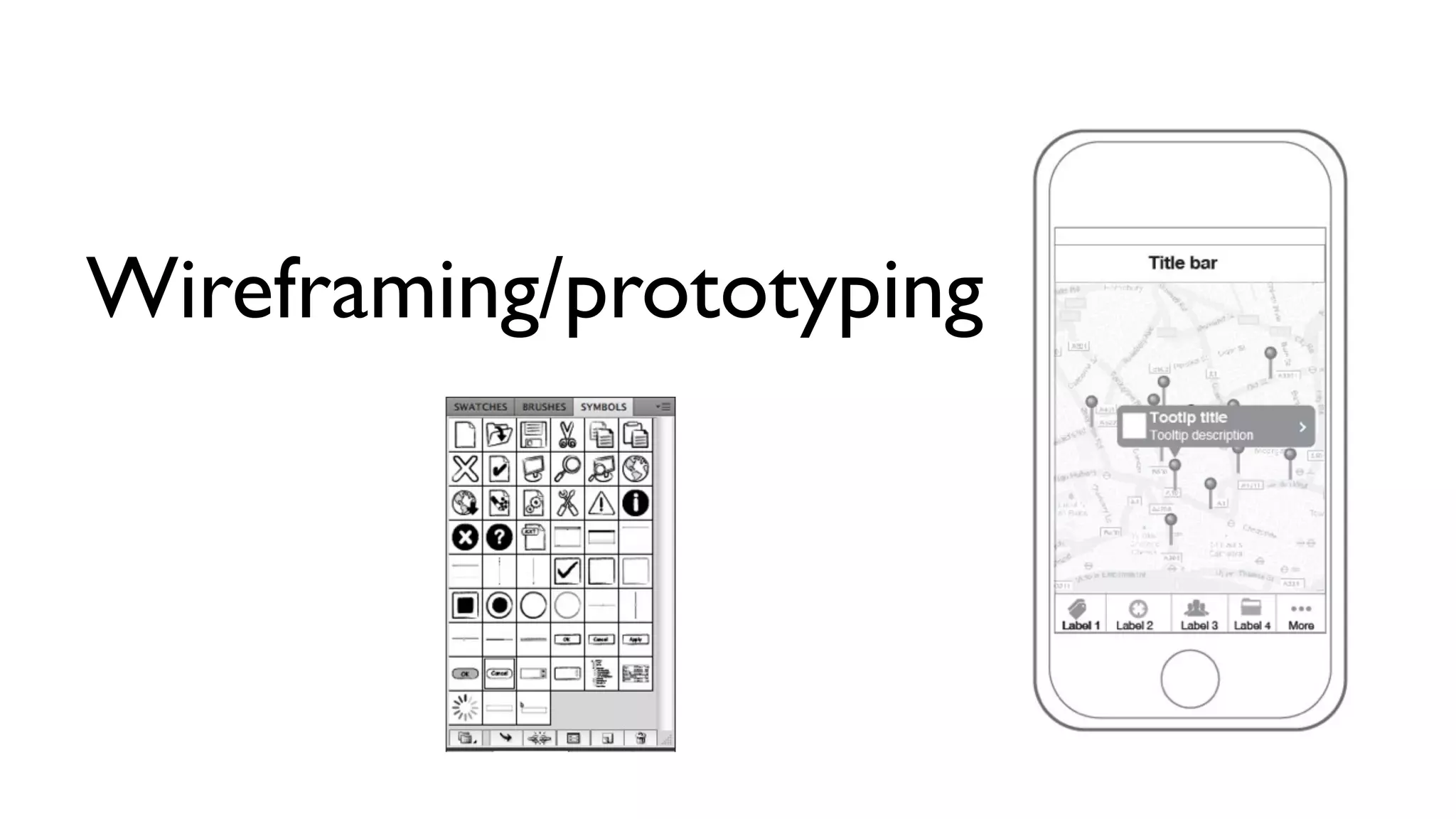
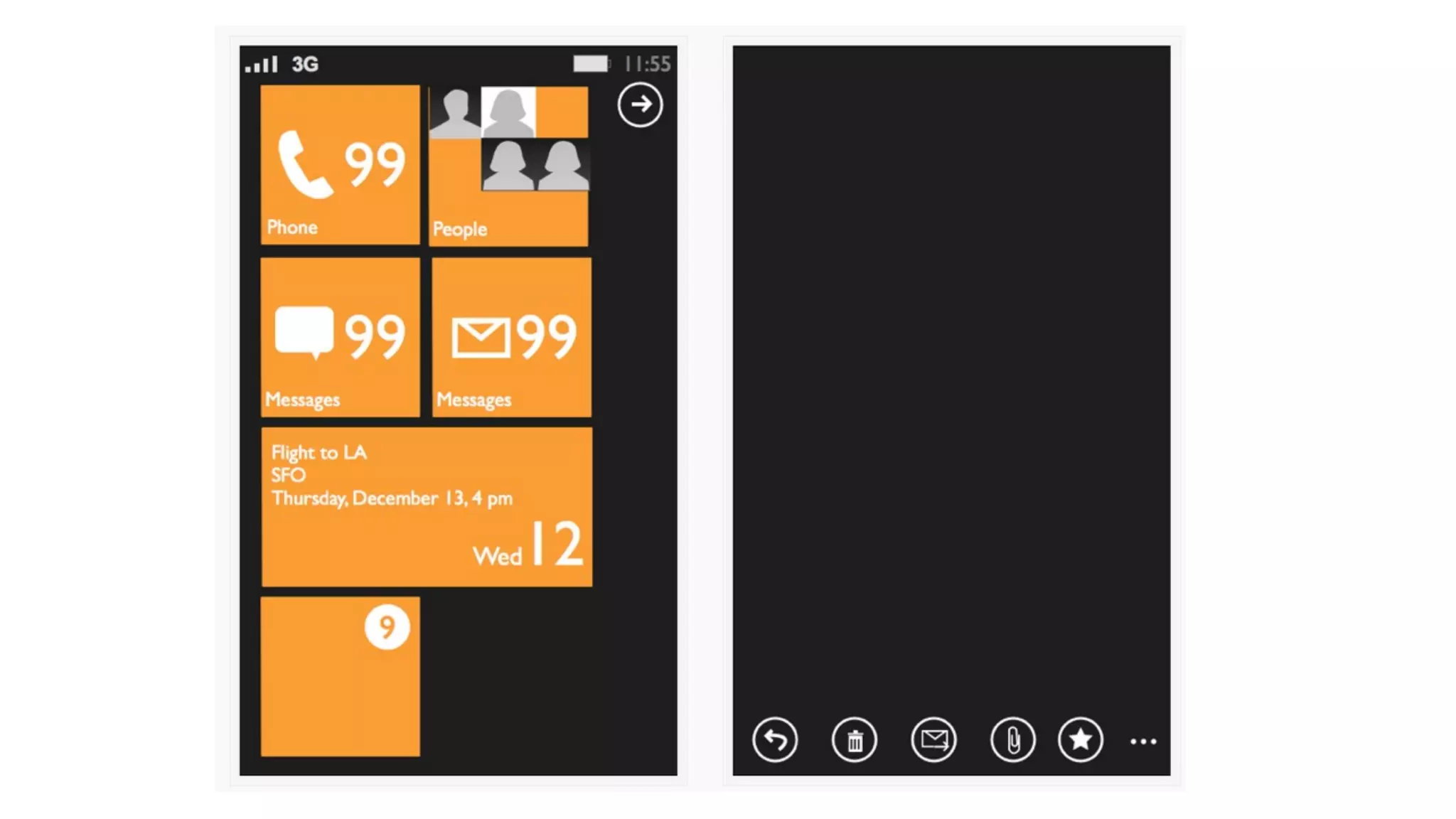
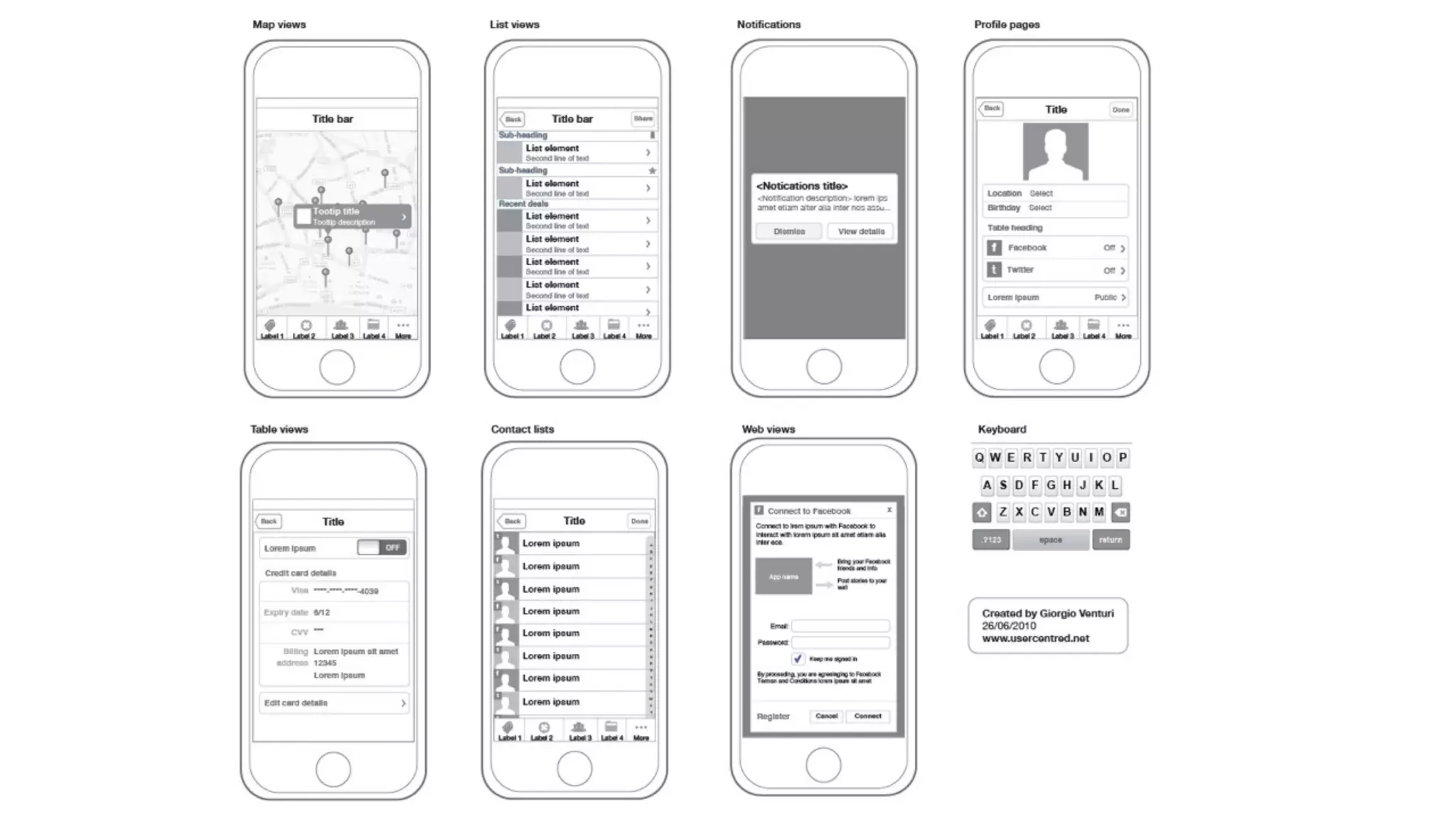
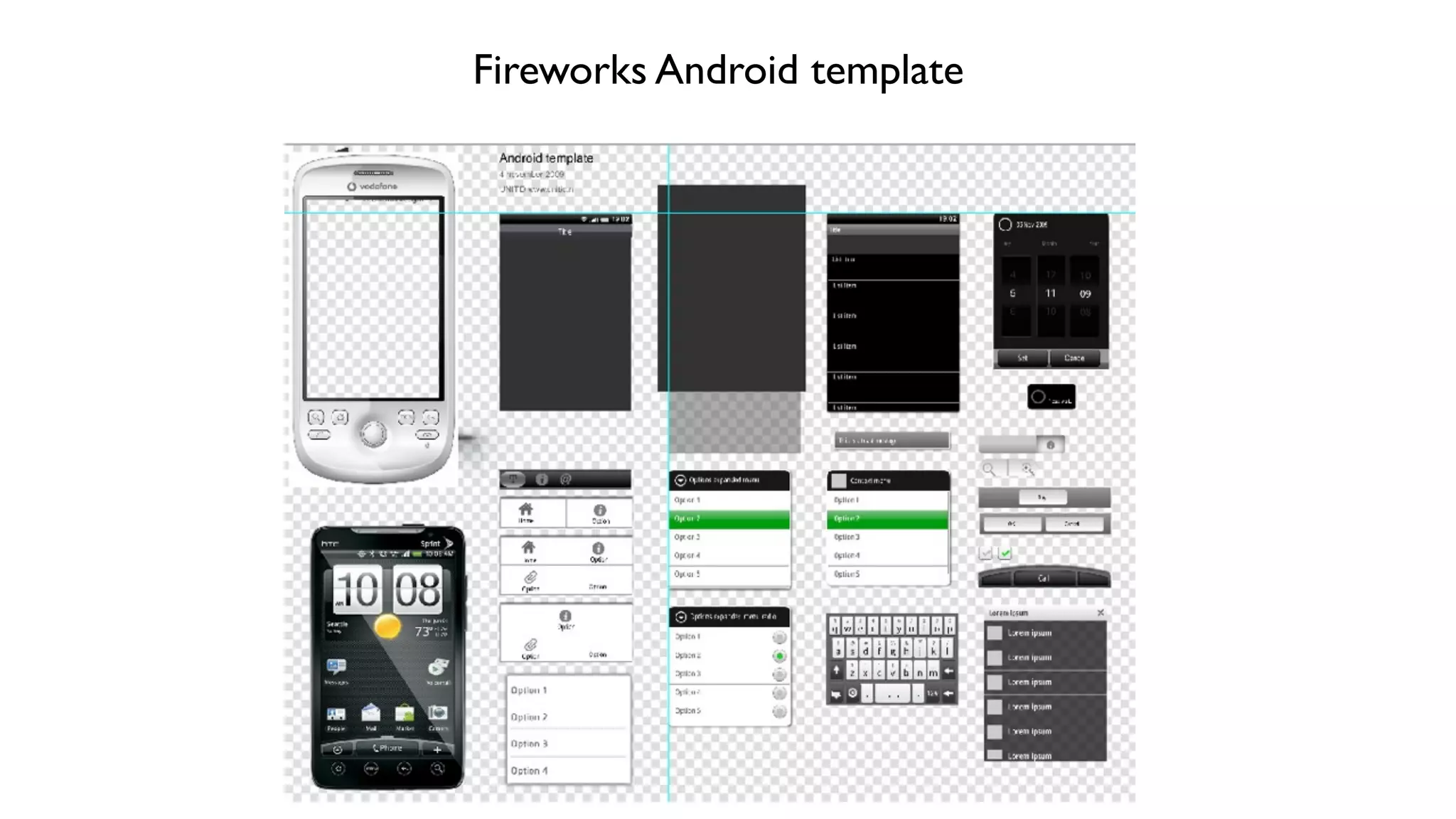
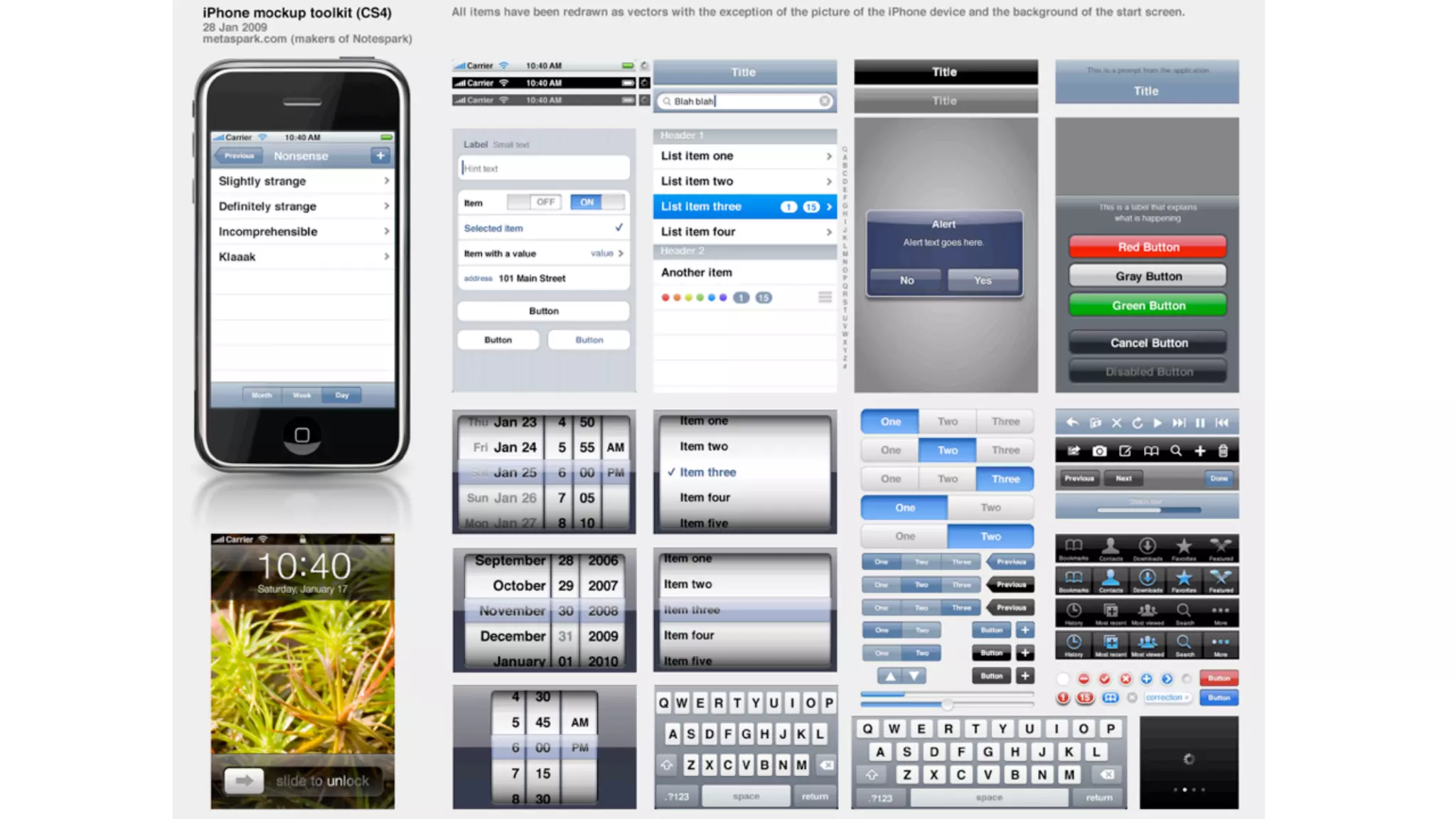
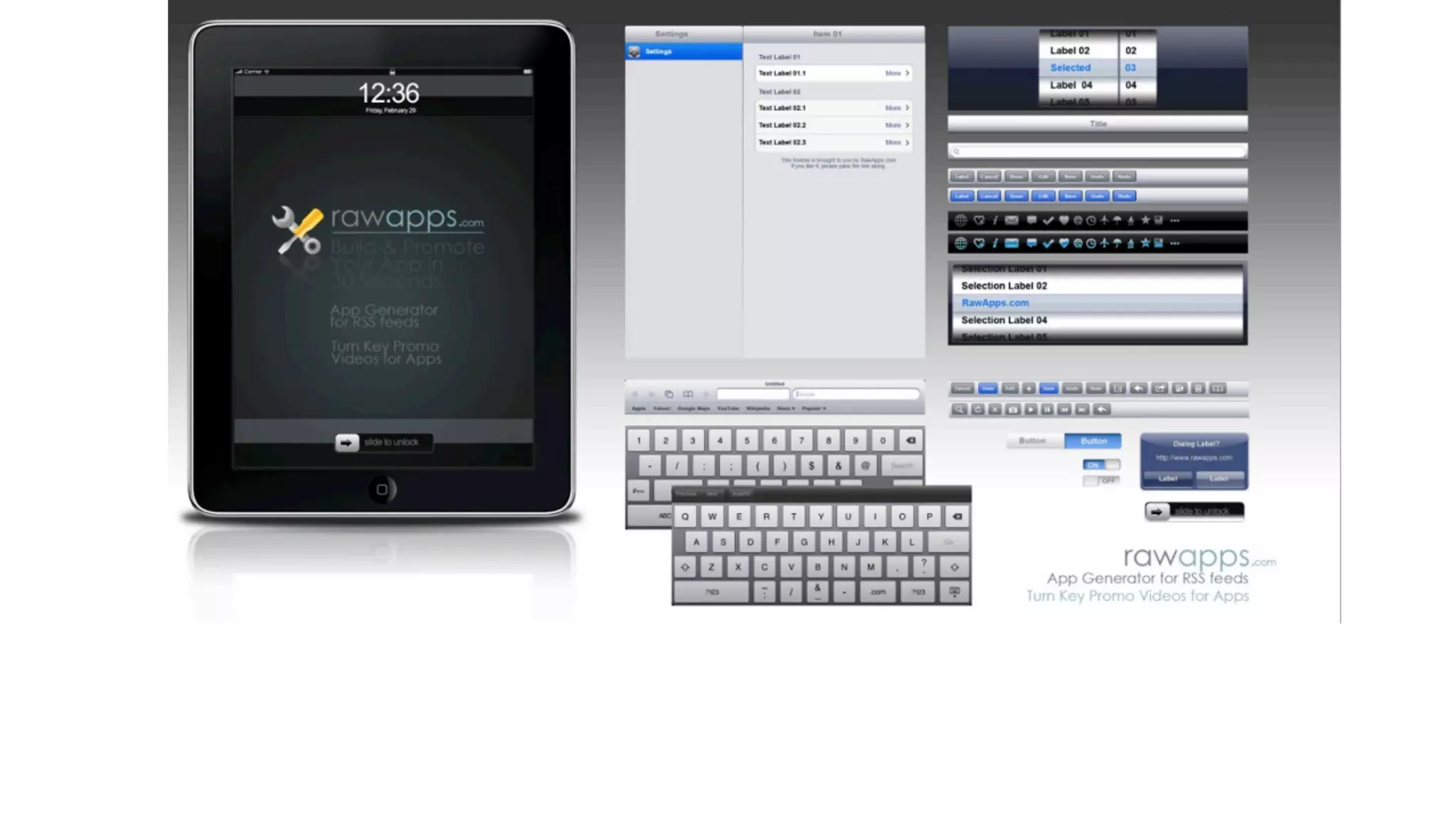
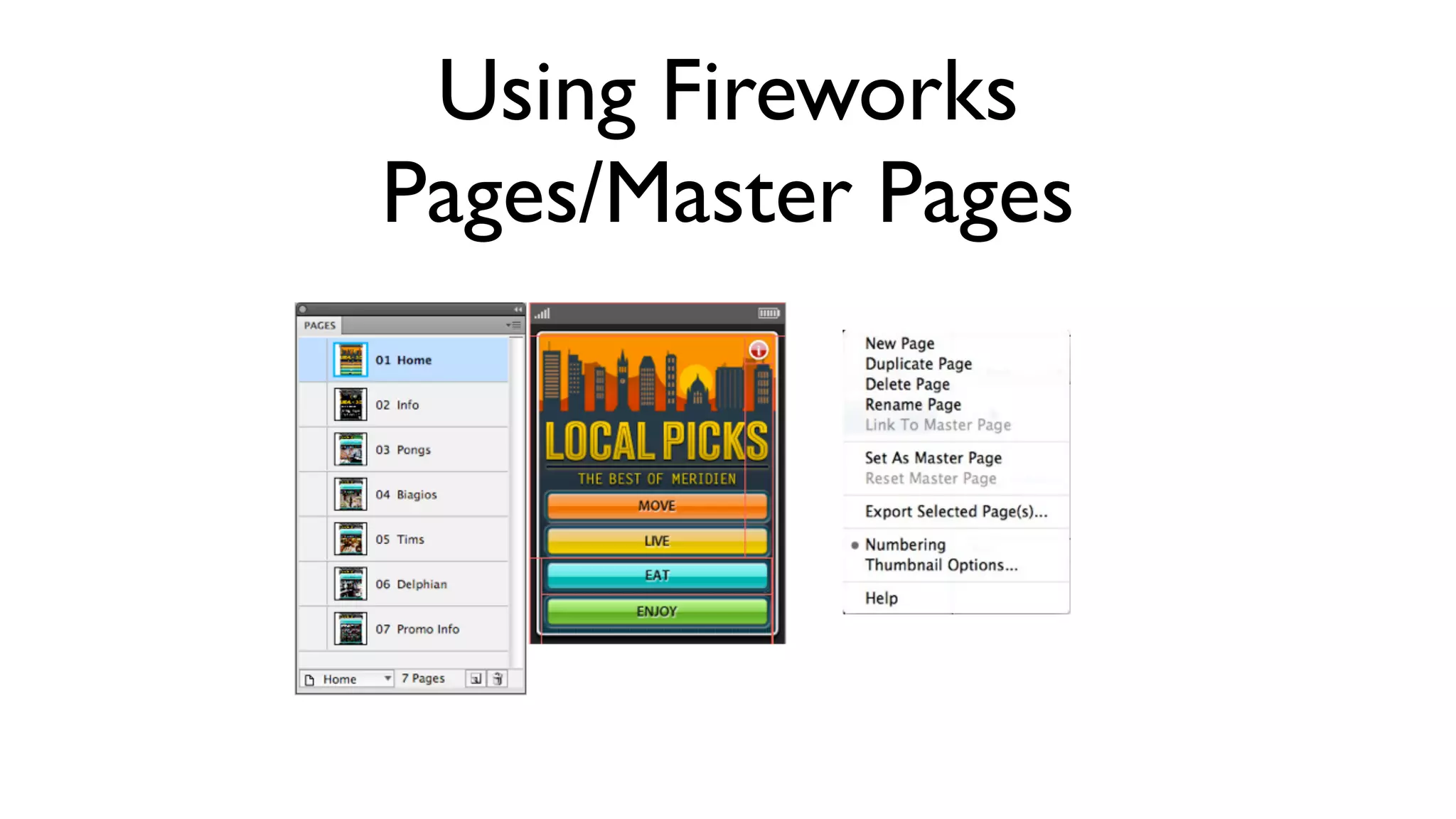
The document provides an overview of key considerations for designing mobile applications and websites. It discusses whether to build a mobile web or native app, addresses issues of screen size and resolution including pixel density, and emphasizes the importance of usability testing through wireframing and prototyping. Design decisions like whether to use vectors or raster images and how to handle orientation are covered. The document lists resources for mobile design patterns, guidelines and tools to use for wireframing prototypes.