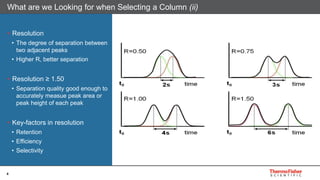
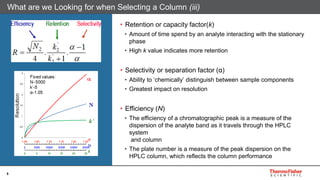
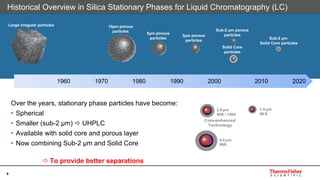
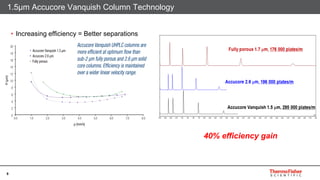
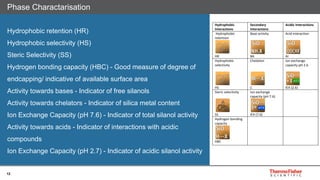
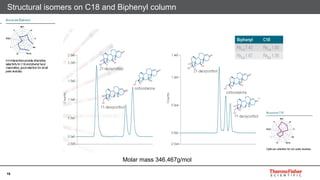
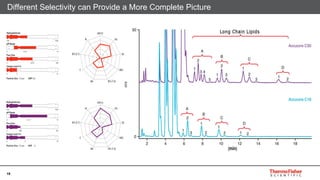
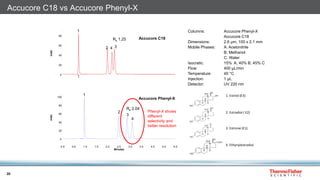
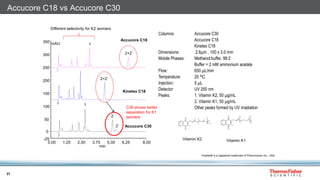
This document discusses selecting chromatography columns. It begins by outlining factors to consider like retention, resolution, selectivity and efficiency. It then discusses the popularity of C18 columns but notes other phases like C8, phenyl and HILIC may be better depending on the analytes. The document explores improvements in column technology over time through smaller particle sizes and core-shell designs. It highlights how different column phases provide unique selectivities that can better separate similar compounds. In the end, it recommends evaluating needs and considering alternative columns and vendors beyond the typical C18.