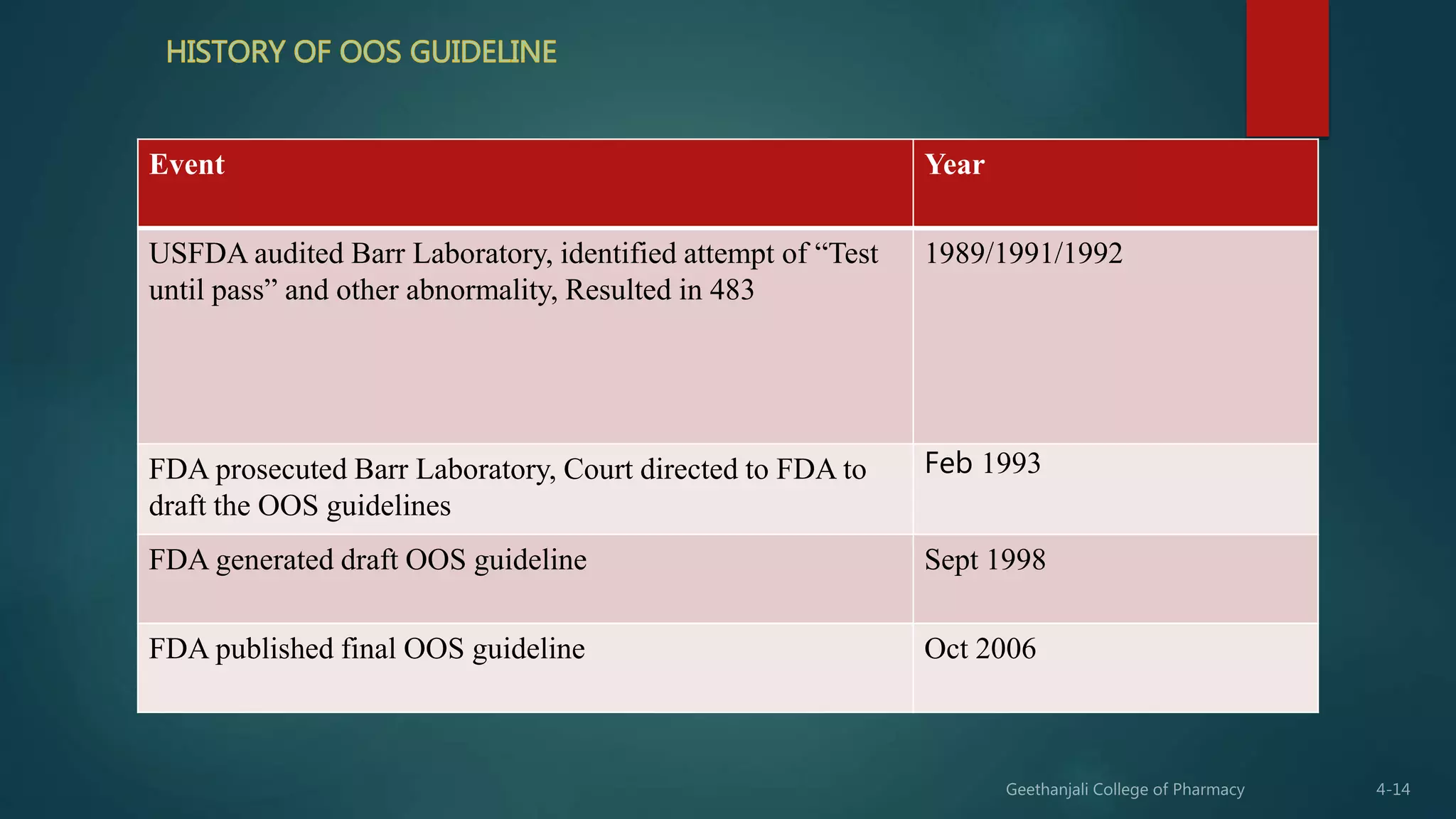
The document provides guidelines for handling out of specification test results as outlined by the USFDA. It defines an out of specification result as one that falls outside the defined test limits. It discusses the USFDA's OOS guidelines published in 2006 and notes that quality units should have a defined SOP for addressing OOS results. The SOP scope should be well defined and investigations into OOS results should be thorough, timely, unbiased, well documented, and scientifically sound. Laboratory investigations should check for errors and, if none are found, a phase II investigation including retesting and investigation at the plant may be initiated. Tools like 5M, 5 whys, DMAIC and root cause analysis should be used to identify