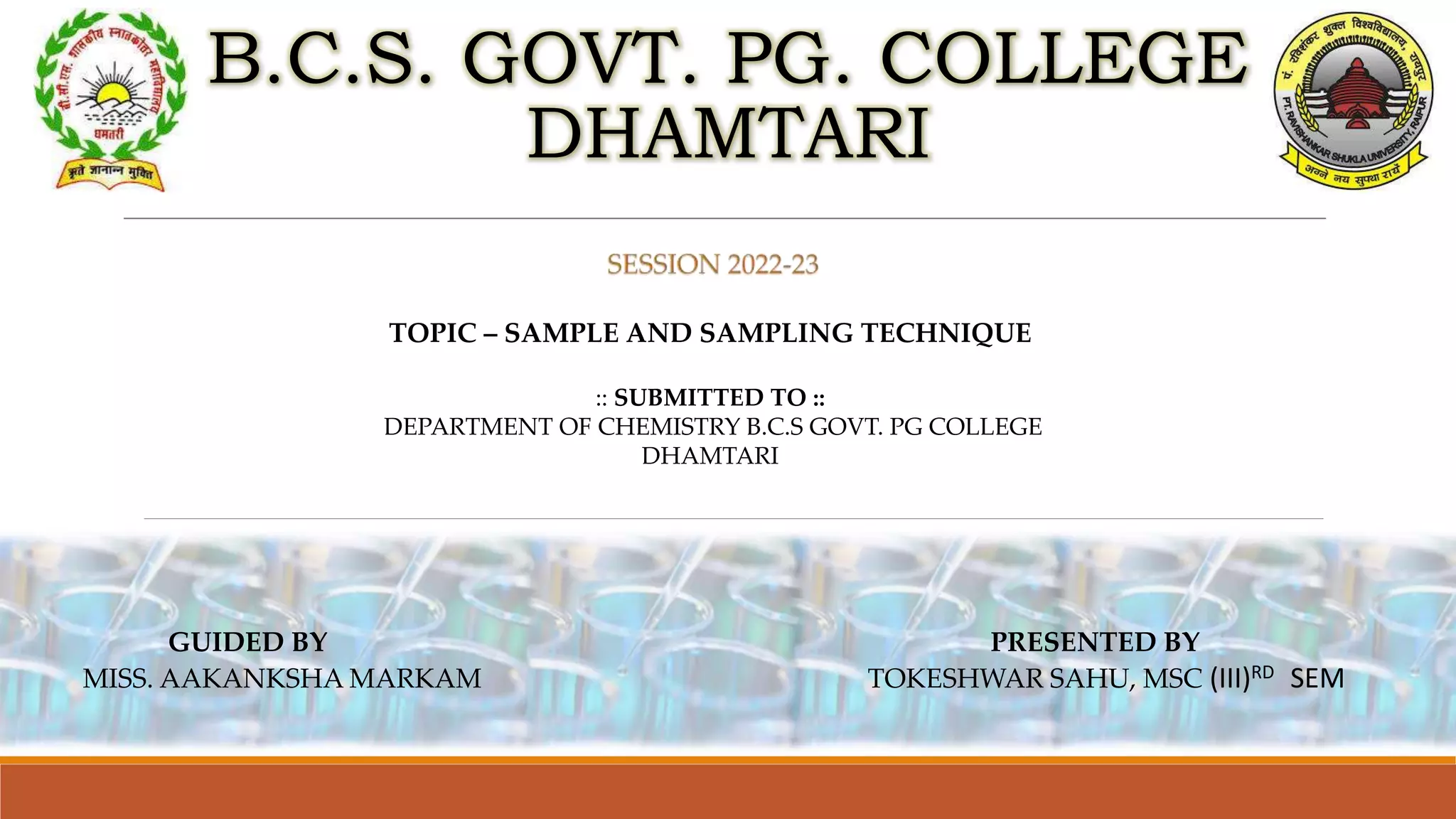
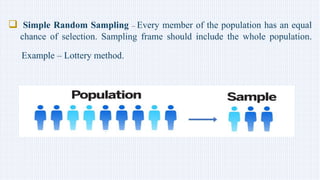
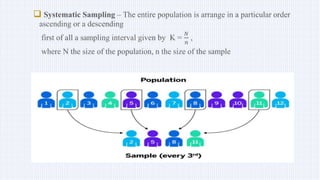
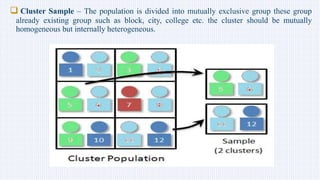
This document discusses sample and sampling techniques in analytical chemistry. It defines a sample as a smaller portion taken from a larger population that is meant to be representative of the whole. There are two main types of sampling: probability sampling, where every member has an equal chance of selection, and non-probability sampling, which does not use random selection. Some examples of probability sampling techniques provided are simple random sampling, stratified random sampling, systematic sampling, and cluster sampling. Non-probability sampling examples include convenience sampling, judgement sampling, quota sampling, and snowball sampling. Previous year exam questions on this topic are also mentioned.