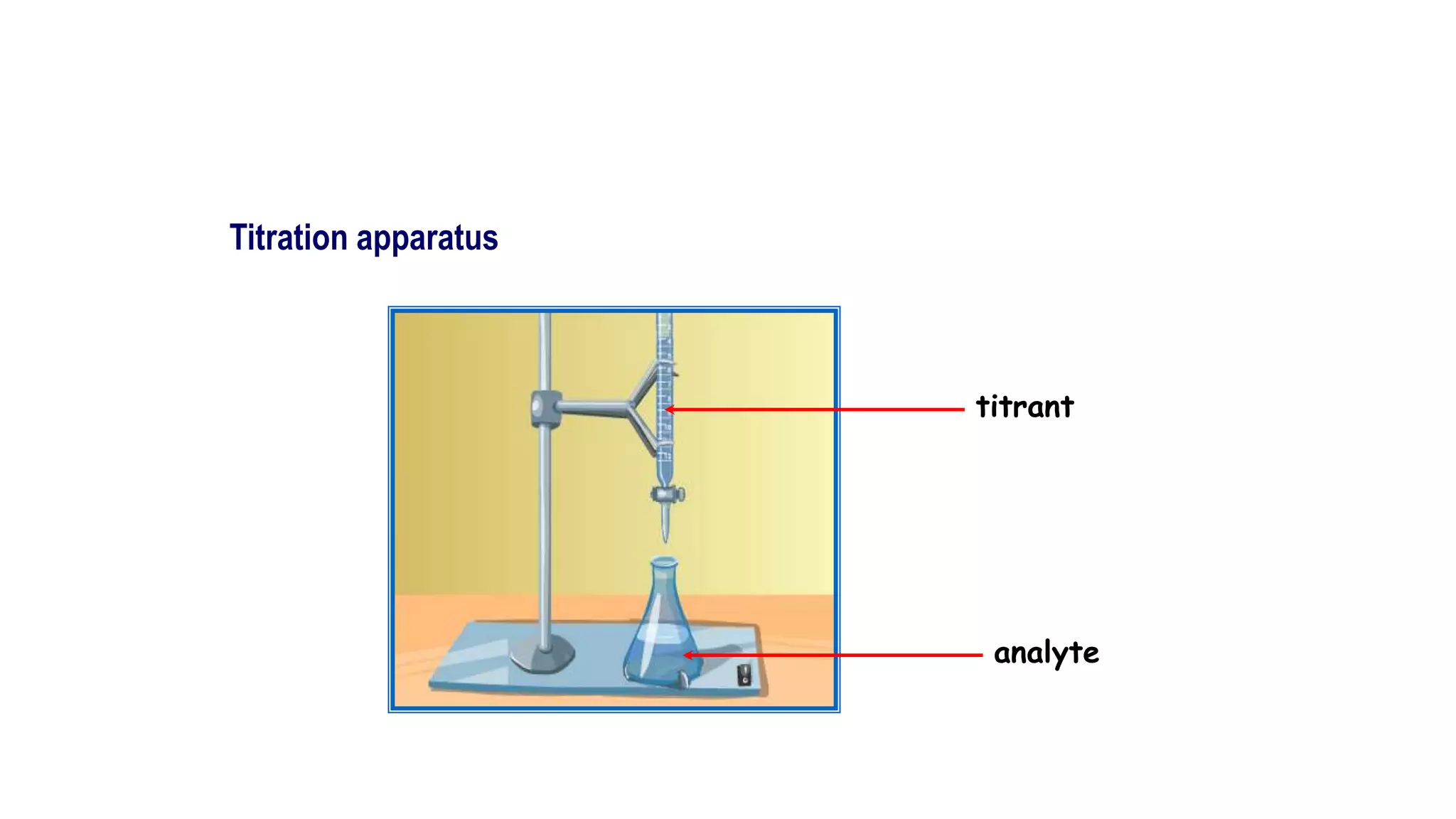
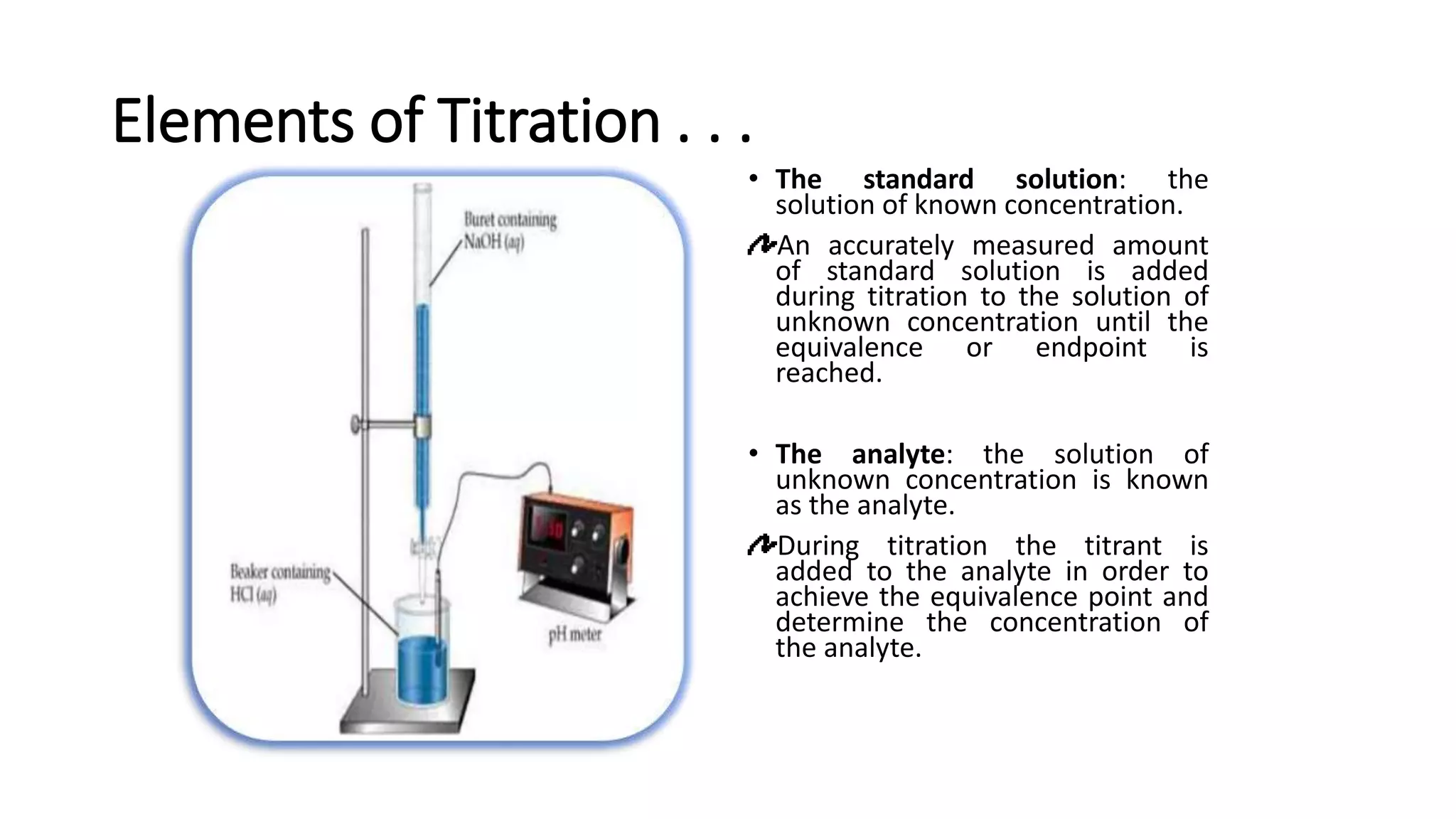
This document discusses titrimetric analysis and different types of titrations. It defines titration as the slow addition of a titrant of known concentration to an analyte of unknown concentration until neutralization. There are four main types of titrations: acid-base, complexometric, redox, and precipitation titrations. Acid-base titrations determine the concentration of an acid or base through neutralization of H3O+ and OH- ions at the equivalence point, which can be indicated by a color change in an added indicator.