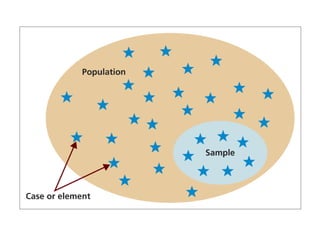
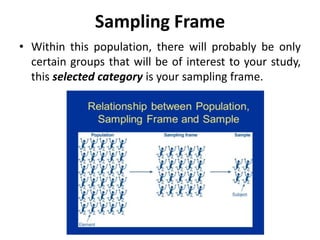
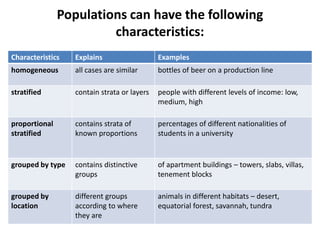
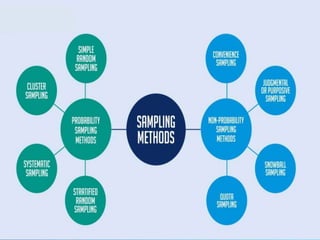
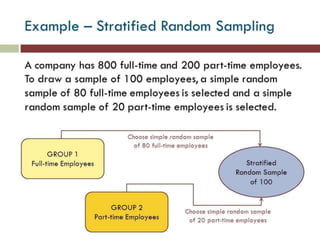
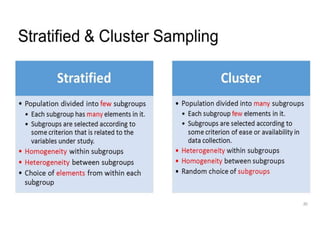
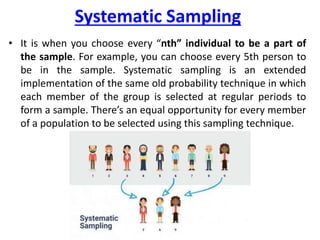
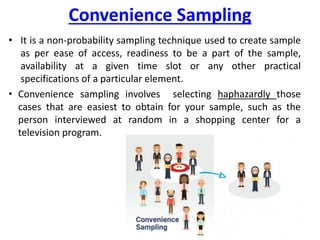
This document discusses sampling and different sampling methods. It defines sampling as selecting a small group from a larger population to make conclusions about the whole group. There are probability and non-probability sampling methods. Probability methods like simple random, stratified, cluster, and systematic sampling give reliable representations if everyone has an equal chance of selection. Non-probability methods like convenience, judgmental, snowball, and quota sampling rely on the researcher's judgment and cannot generalize to the full population. The document provides examples and explanations of each sampling method.