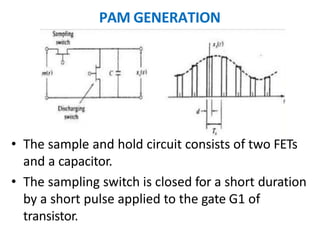
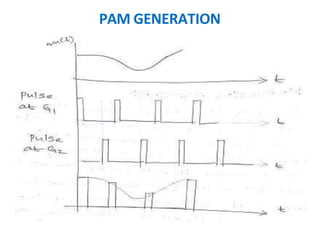
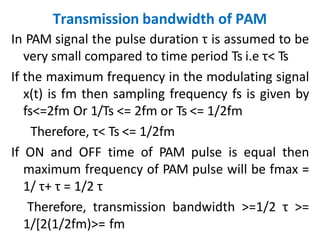
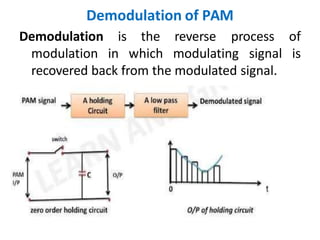
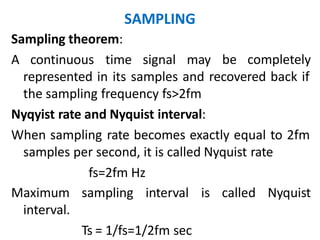
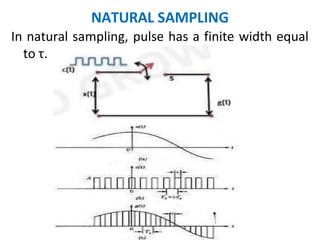
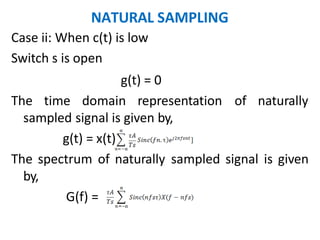
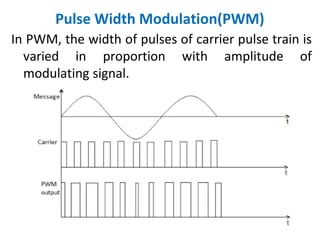
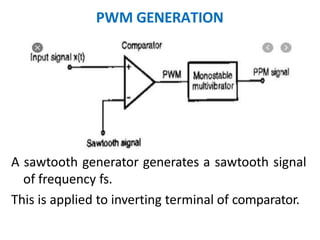
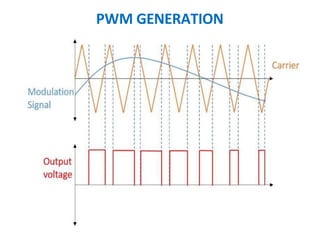
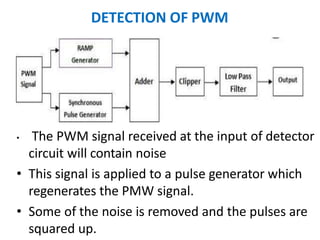
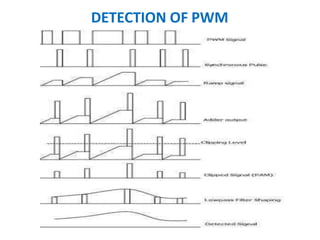
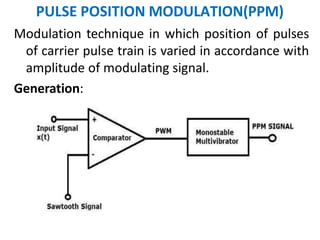
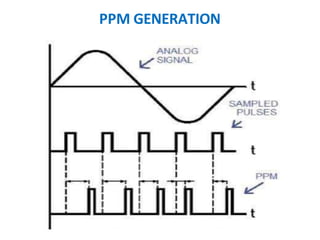
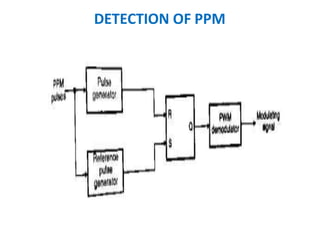
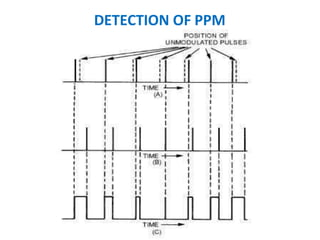
This document discusses various analog pulse modulation schemes, including pulse amplitude modulation (PAM), pulse width modulation (PWM), and pulse position modulation (PPM). PAM varies the amplitude of pulses in a carrier signal based on the modulating signal. PWM varies the width of pulses, while PPM varies the position of pulses. The document describes the generation and demodulation of these different modulation types. It also discusses sampling theory and the advantages and disadvantages of PAM.