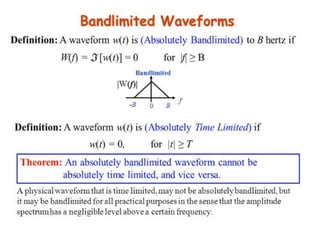
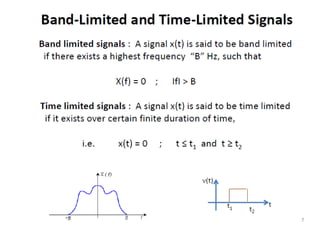
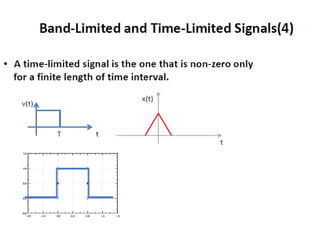
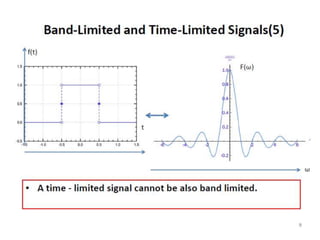
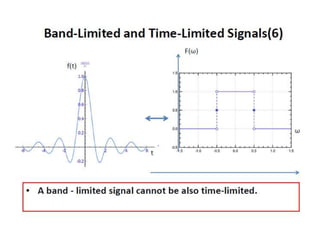
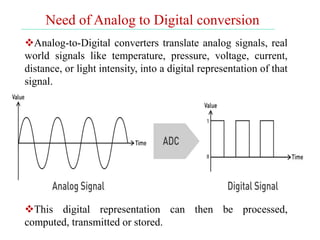
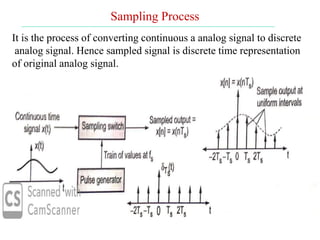
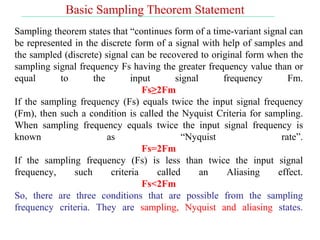
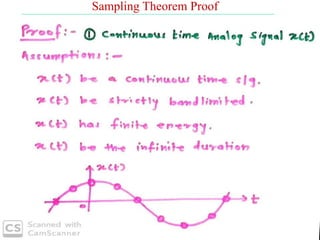
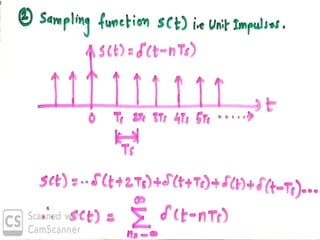
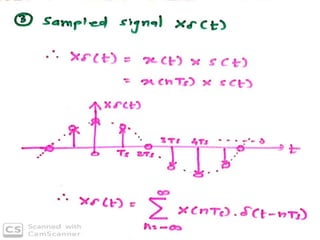
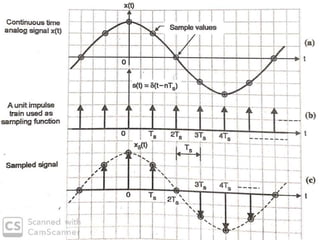
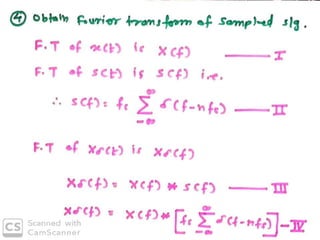
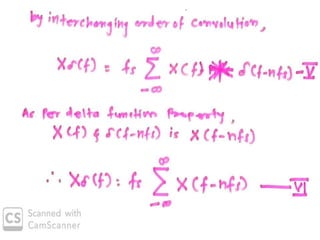
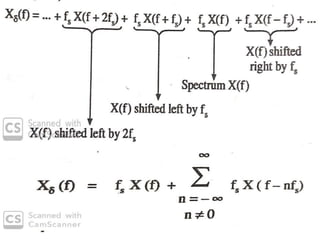
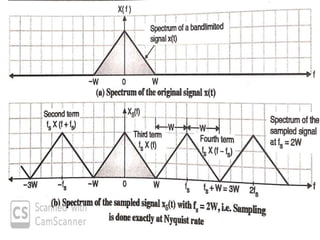
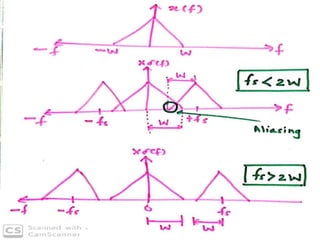
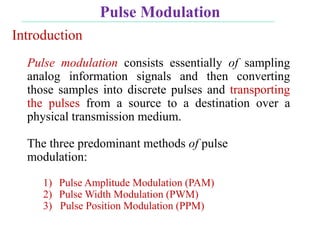
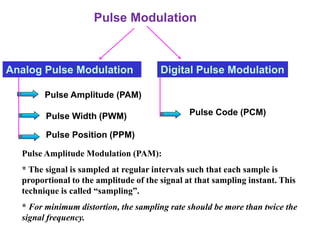
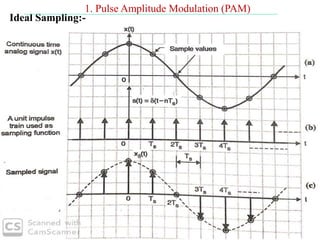
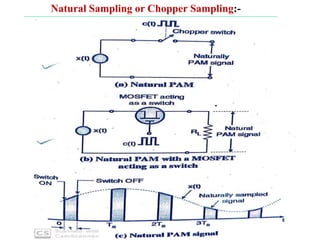
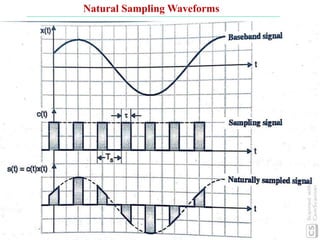
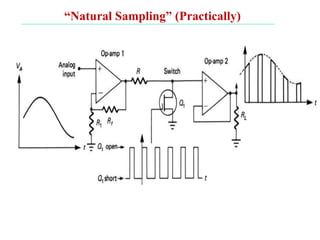
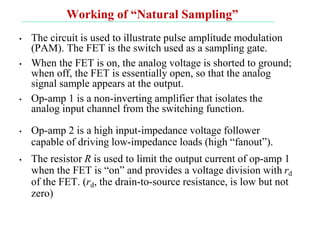
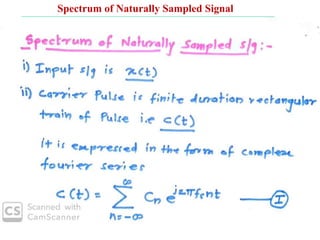
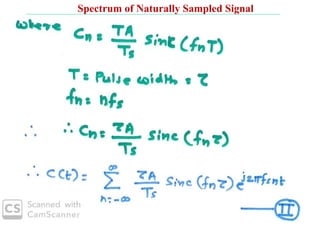
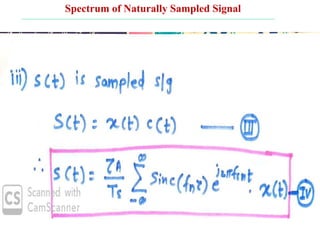
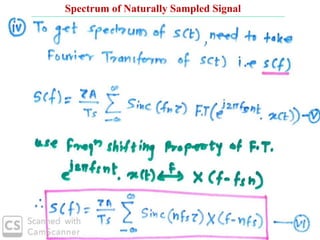
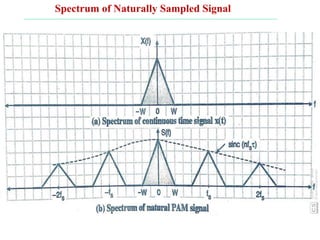
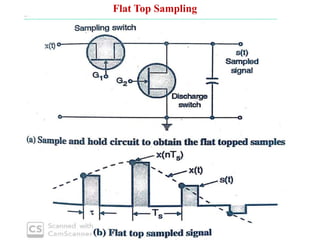
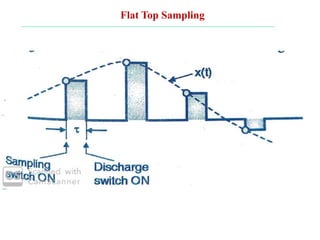
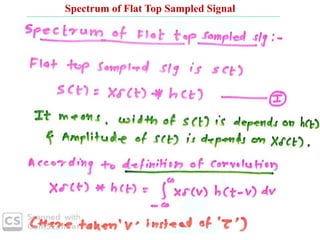
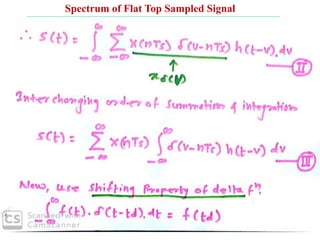
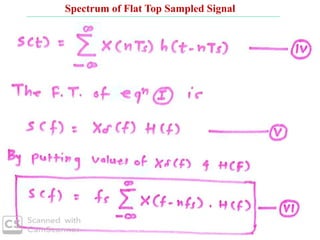
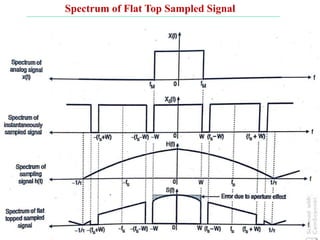
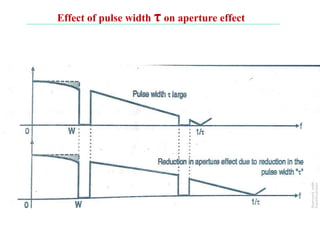
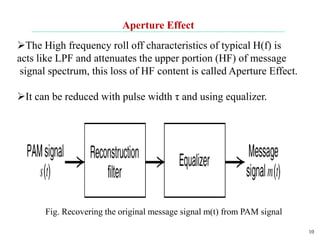
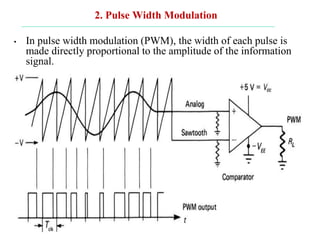
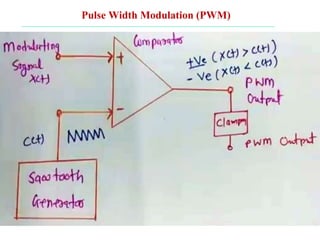
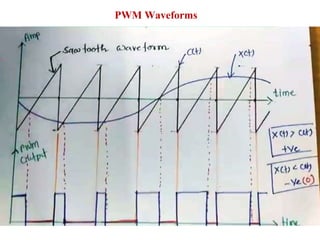
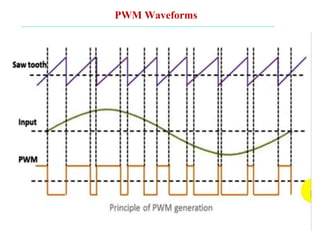
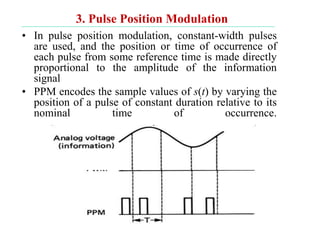
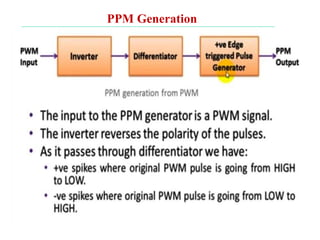
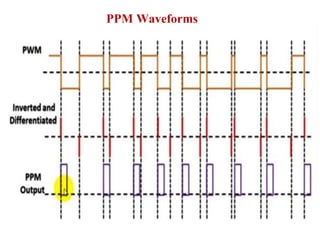
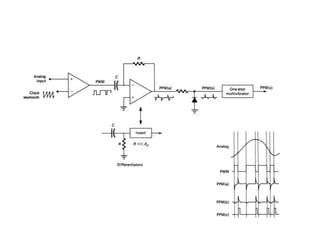
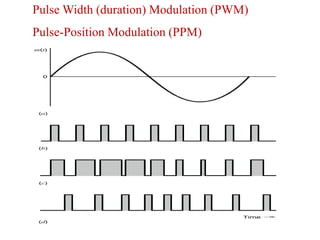
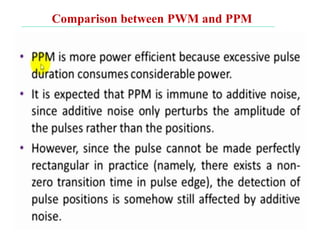
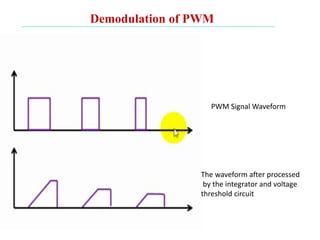
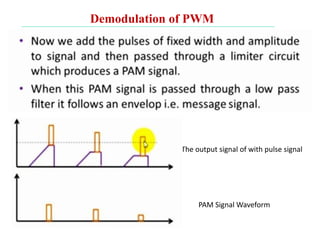
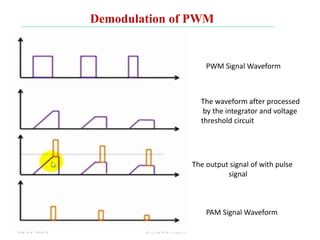
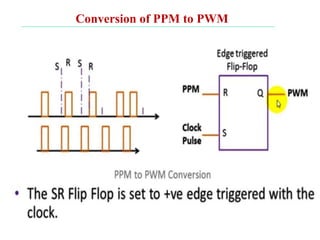
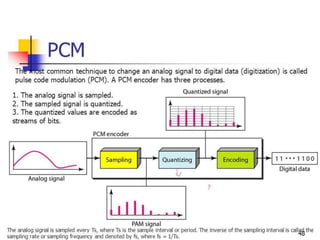
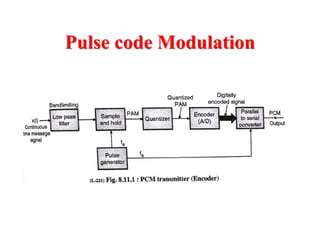
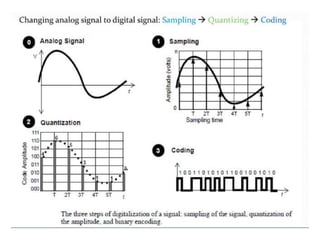
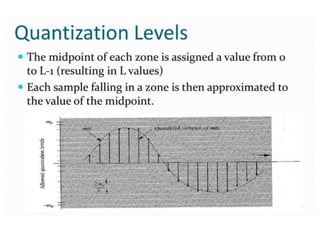
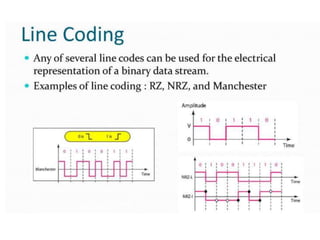
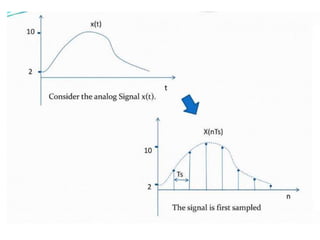
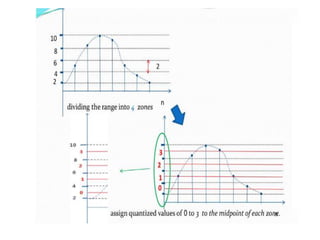
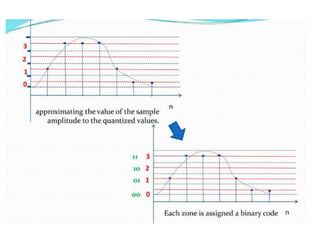
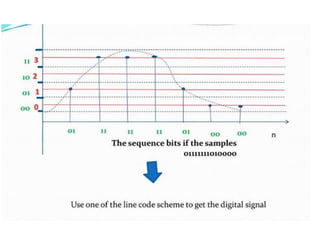
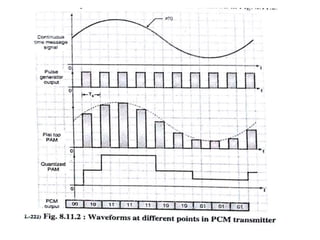
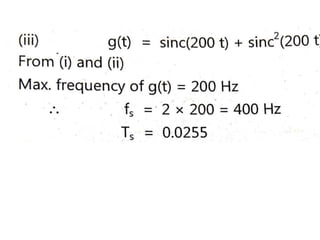The document discusses various types of pulse modulation techniques used to convert analog signals to digital signals. It describes pulse amplitude modulation (PAM), pulse width modulation (PWM), and pulse position modulation (PPM). PAM encodes information by varying the amplitude of pulses, PWM varies the width, and PPM varies the position. The key requirements for pulse modulation are that the sampling frequency must be at least twice the maximum input frequency to avoid aliasing, and techniques like flat top sampling and PWM help reduce the aperture effect by limiting high frequency roll-off. Pulse modulation allows analog signals to be transmitted and processed digitally.