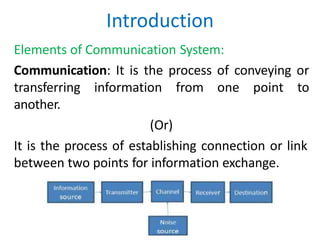
This document discusses the basic elements and concepts of analog communication systems. It defines communication as the process of conveying information from one point to another. The key elements are:
- Information source: The origin of the message or information to be communicated.
- Transmitter: Collects the message signal and modifies it so it can be transmitted through the channel.
- Channel: The physical medium that connects the transmitter and receiver, such as wires, cables, or free space.
- Receiver: Receives the modified signal from the channel and processes it to recreate the original message signal.
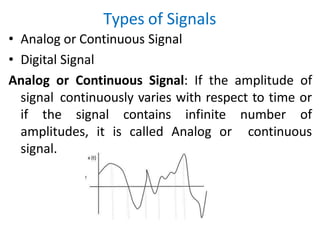
It also describes different types of signals, limitations of communication systems, and defines modulation as the process of