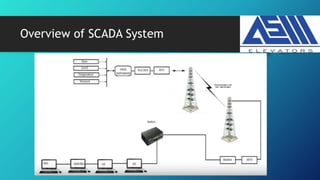
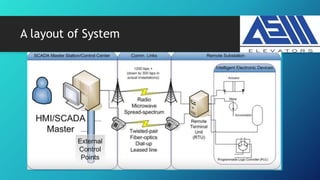
The document provides an overview of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC) for electrical engineers, covering their role in industrial automation, advantages, disadvantages, and components like CPU and memory. It also explains the differences between PLC, DCS, and SCADA, with emphasis on the communication aspects and real-time data processing capabilities. The instructor, Engr. Taimoor Muzaffar Gondal, highlights his experience and research interests in related fields.