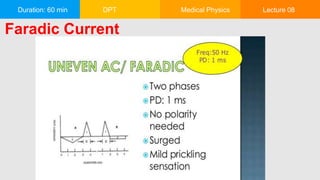
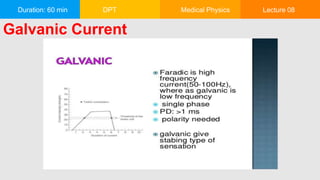
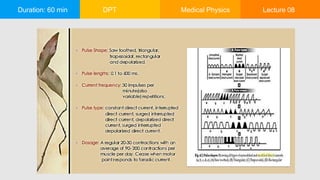
This document outlines a 60-minute medical physics lecture on the classification and therapeutic applications of low, medium, and high-frequency currents. It discusses current types based on direction, frequency, voltage, and amperage, as well as their effects, advantages, and disadvantages. Additionally, it covers specific treatments using these currents, including their application in various medical conditions and the types of electrodes used.