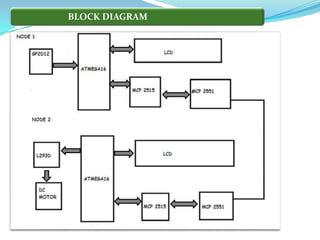
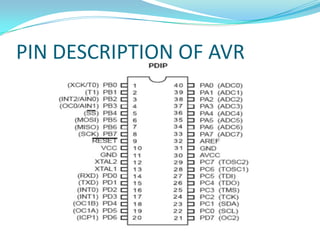
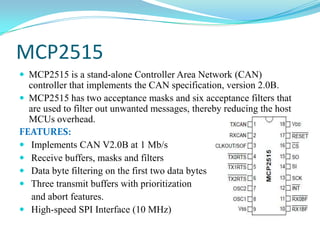
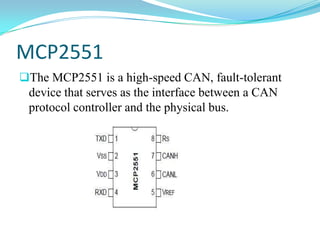
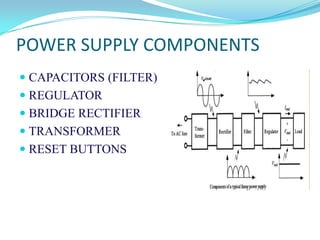
This project involves developing a CAN-based collision avoidance system for vehicles. The system uses a collision avoidance sensor to measure the distance to the vehicle ahead and warns the driver if the distance is unsafe or if the driver is not paying attention. It communicates between nodes using the Controller Area Network protocol to stop a DC motor if an object is detected by the sensor. The system requires hardware components like an AVR microcontroller, MCP2515 CAN controller, MCP2551 transceiver, collision avoidance sensor and power supply components. It also requires software programming in embedded C using development tools like CodeVision.