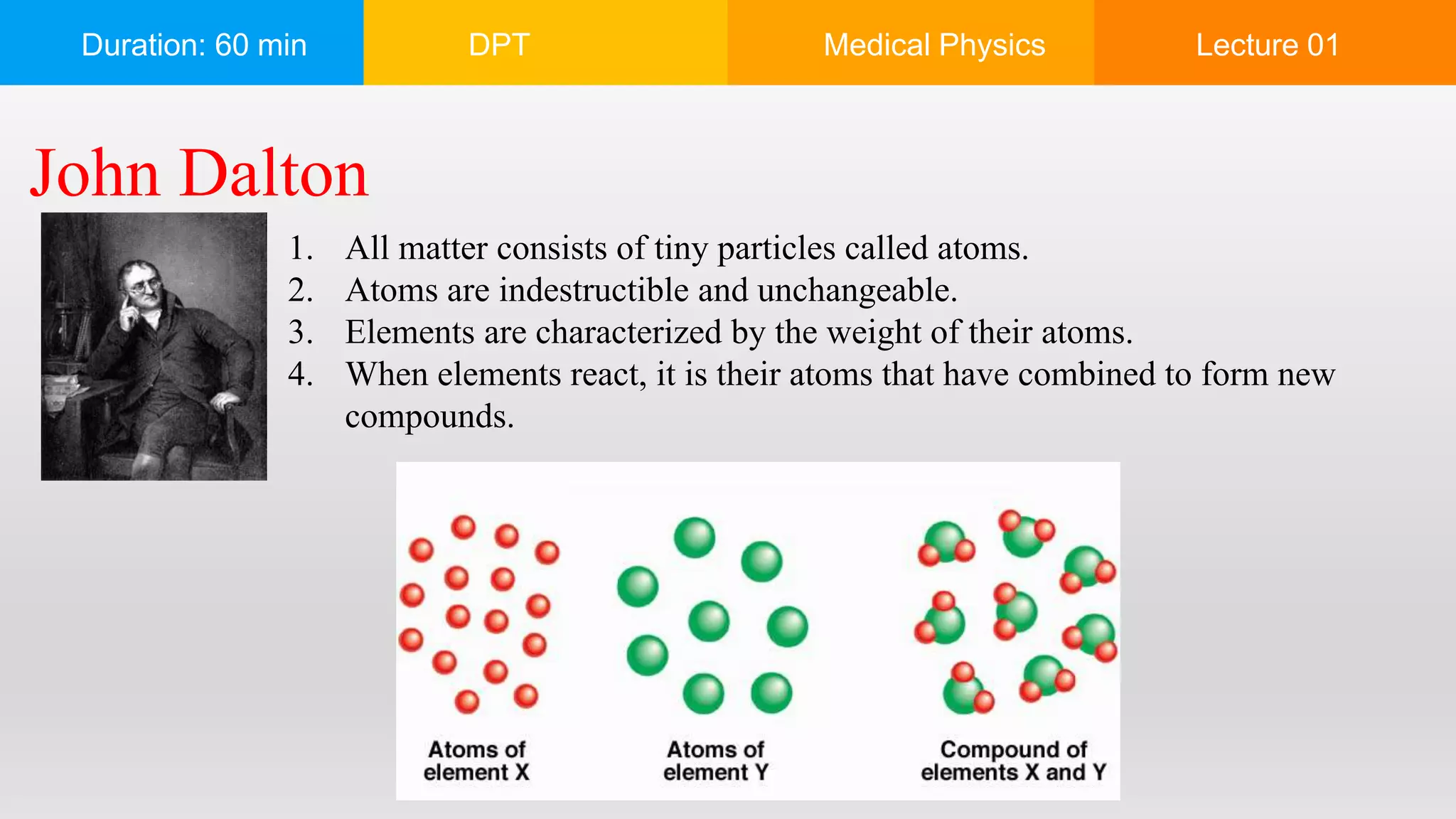
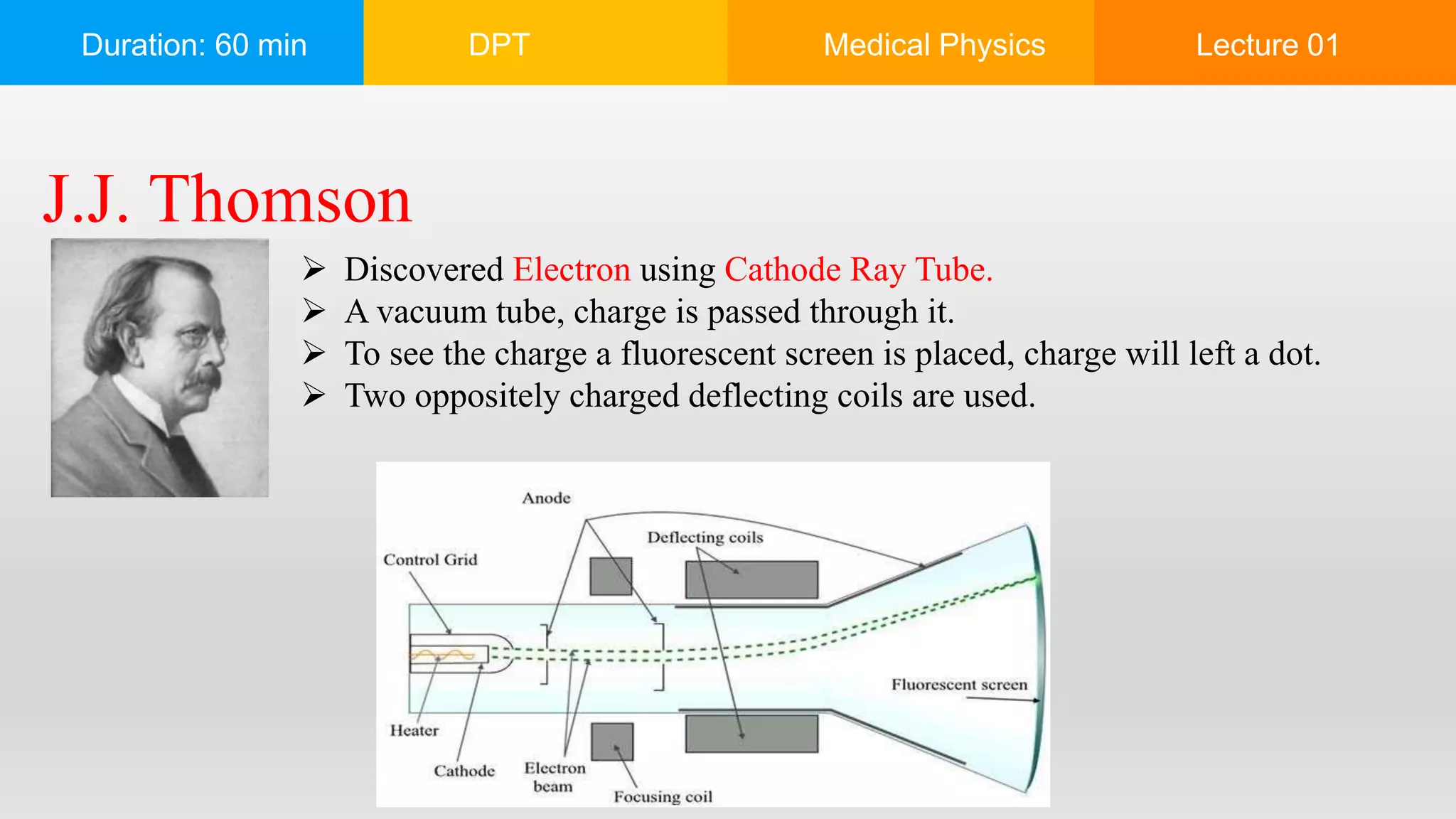
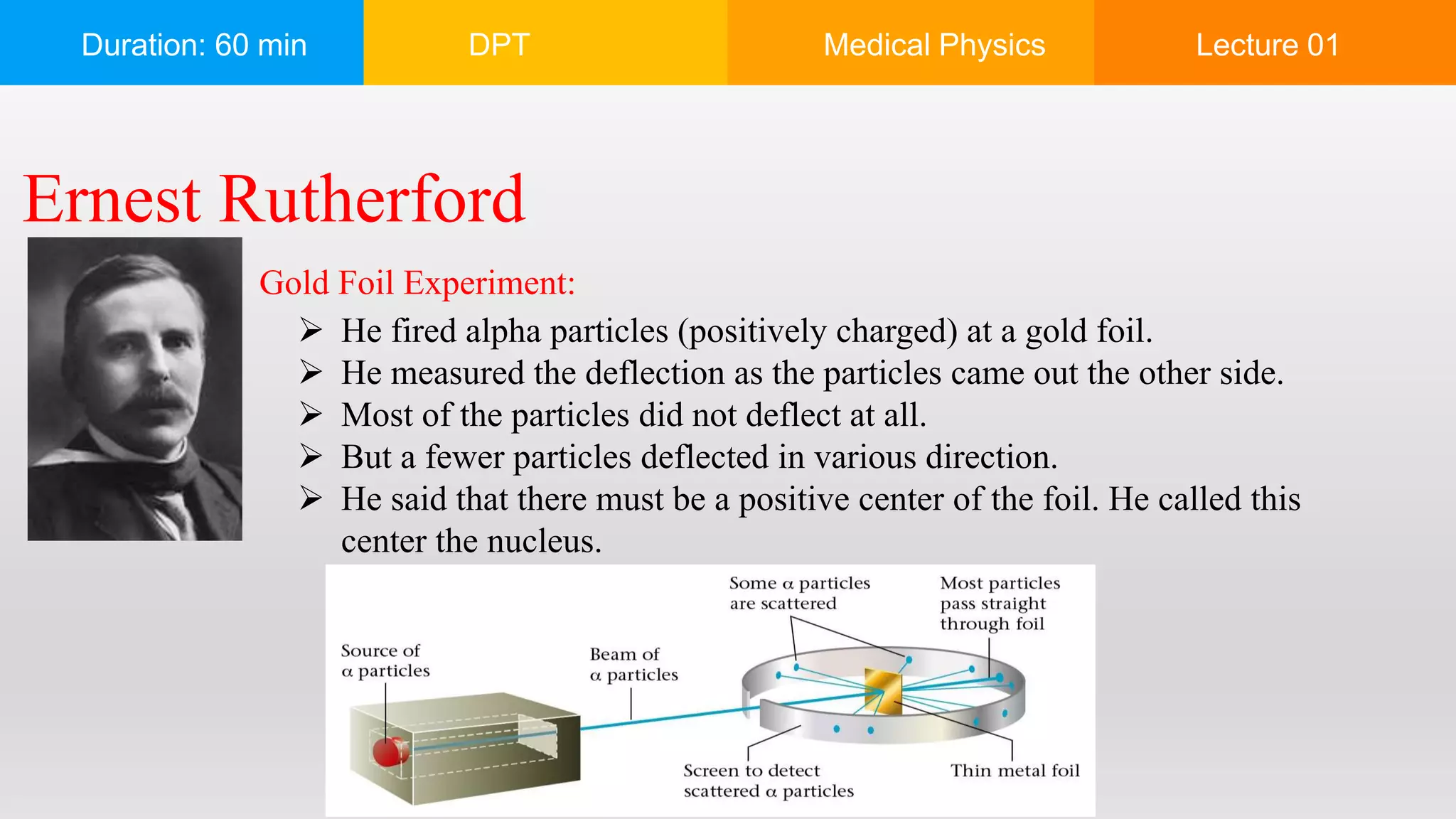
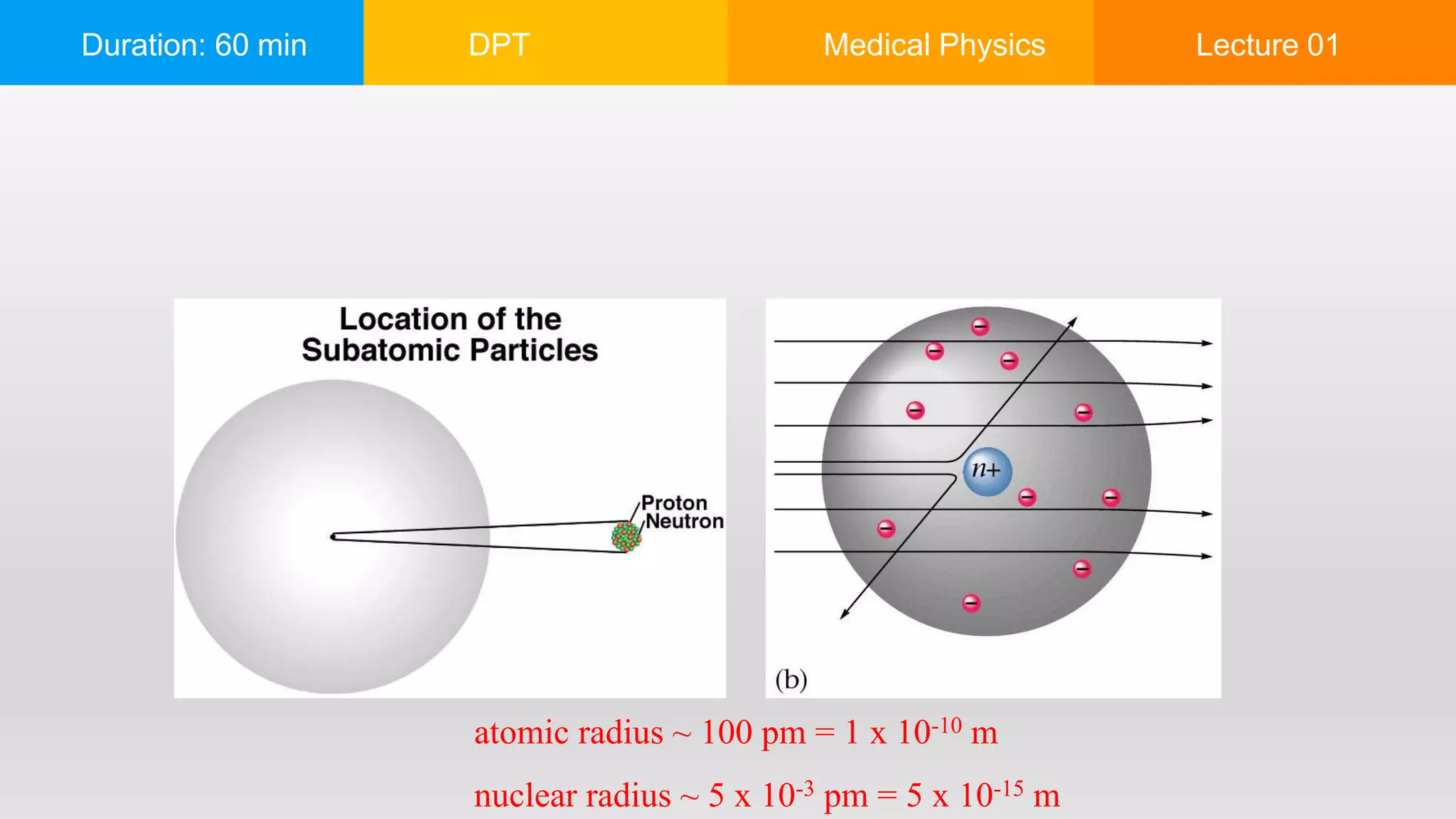
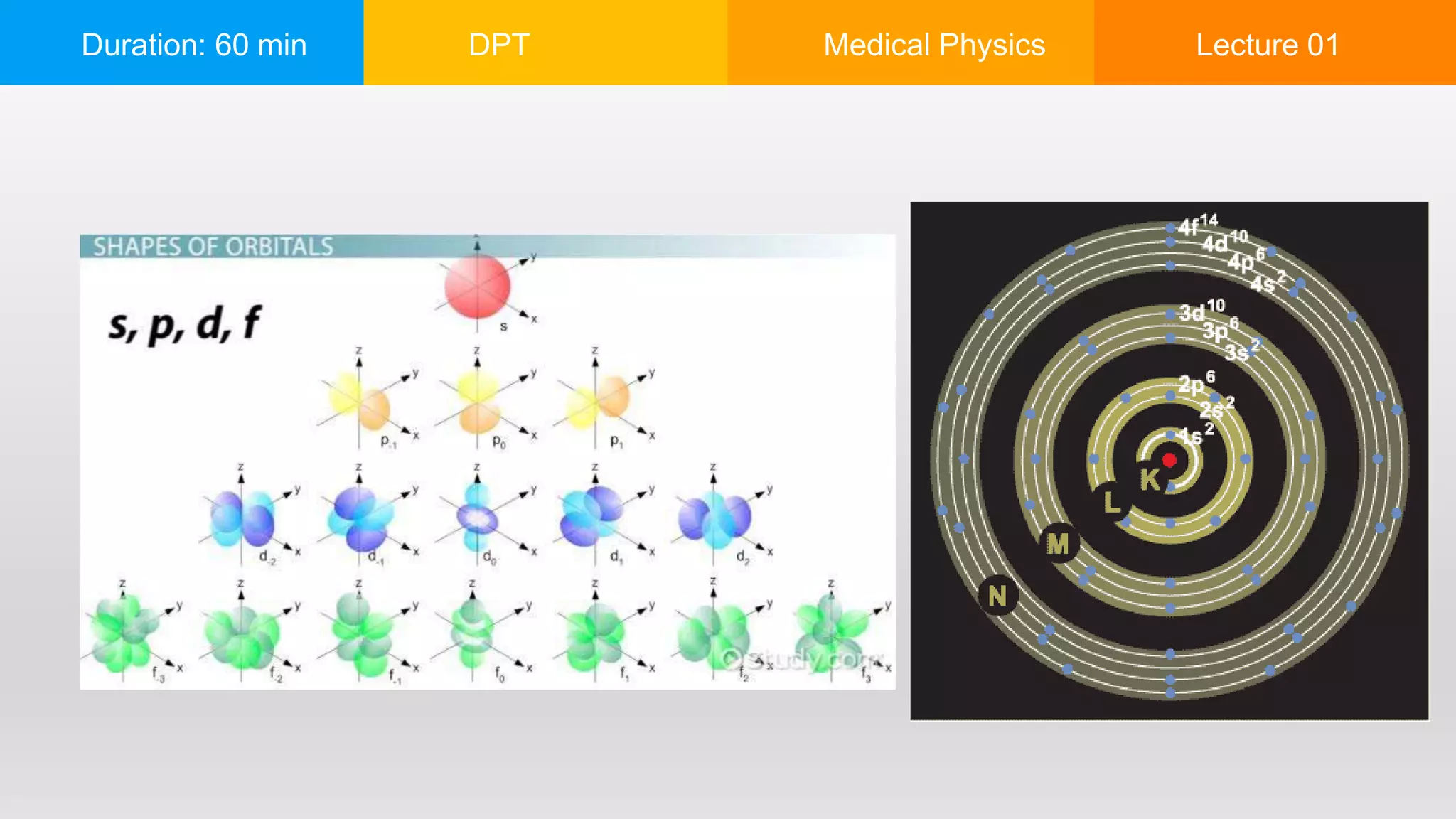
The document outlines a 60-minute lecture on the structure of atoms and the principles of medical physics, emphasizing the application of physics in medicine for diagnostics and therapy. Key historical figures in atomic theory, such as Democritus, John Dalton, J.J. Thomson, Ernest Rutherford, and Neil Bohr, are discussed regarding their contributions to atomic structure and the behavior of electrons. It also explains the concepts of conductors, insulators, and semiconductors based on electron stability and movement.