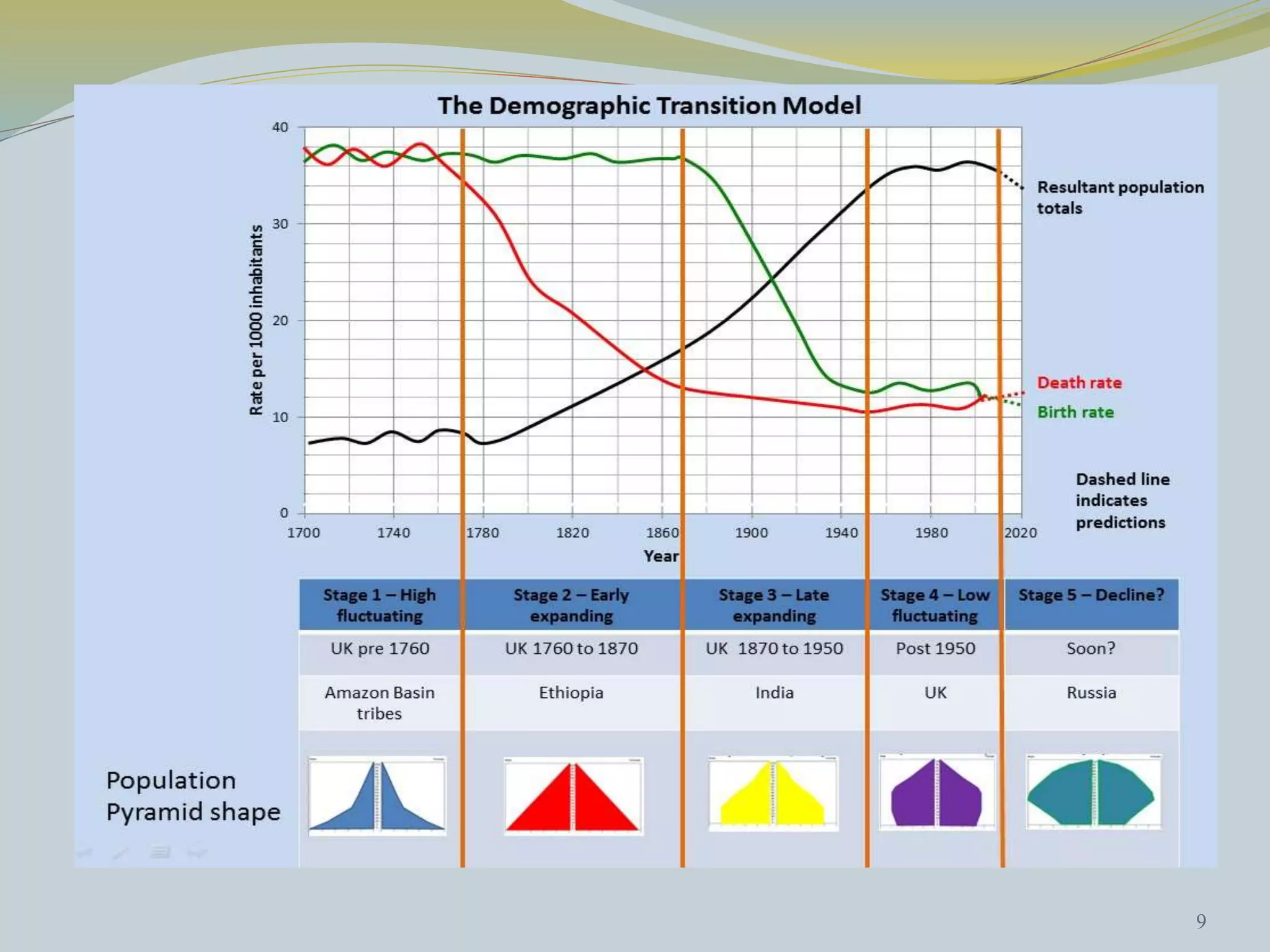
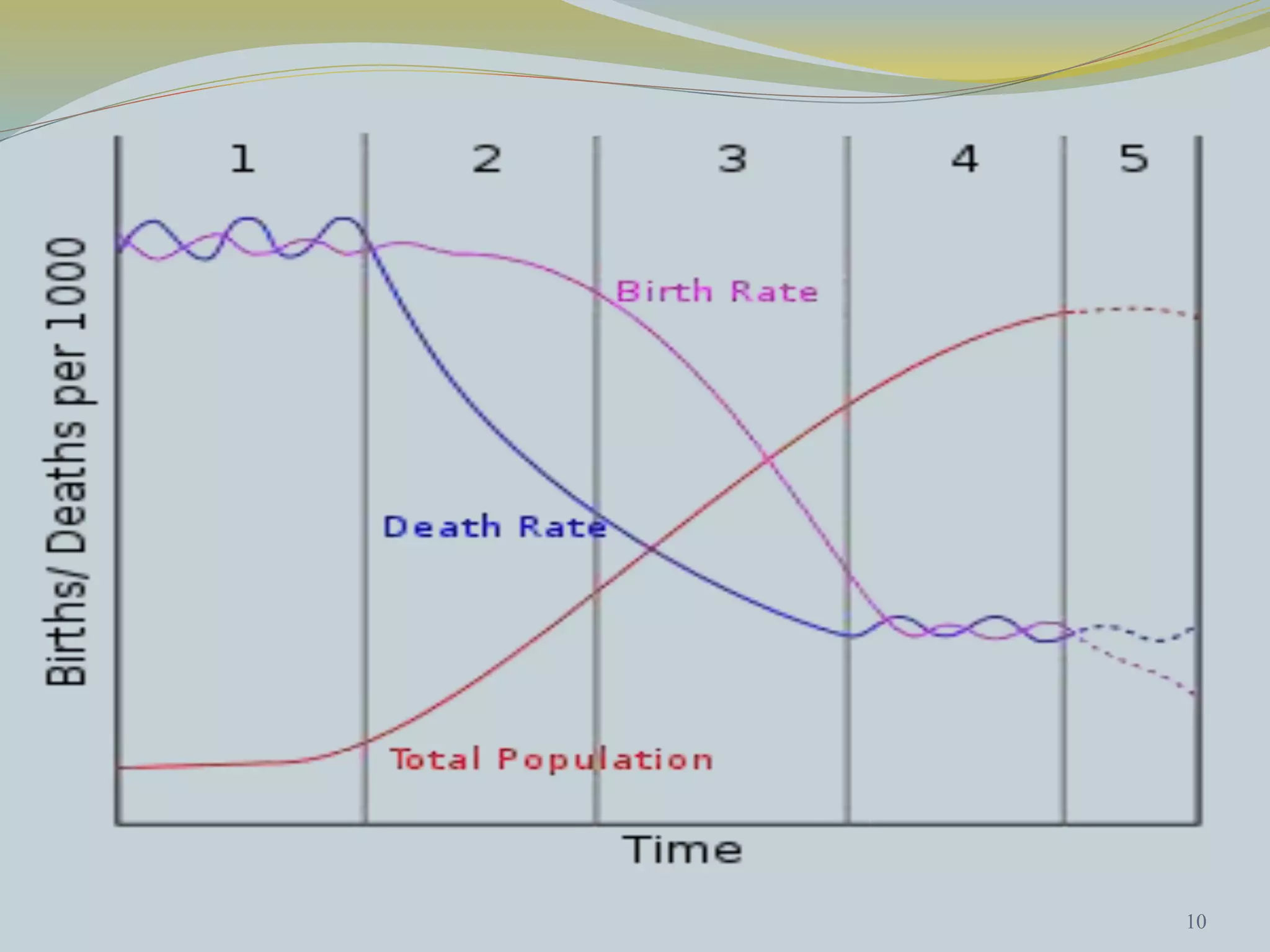
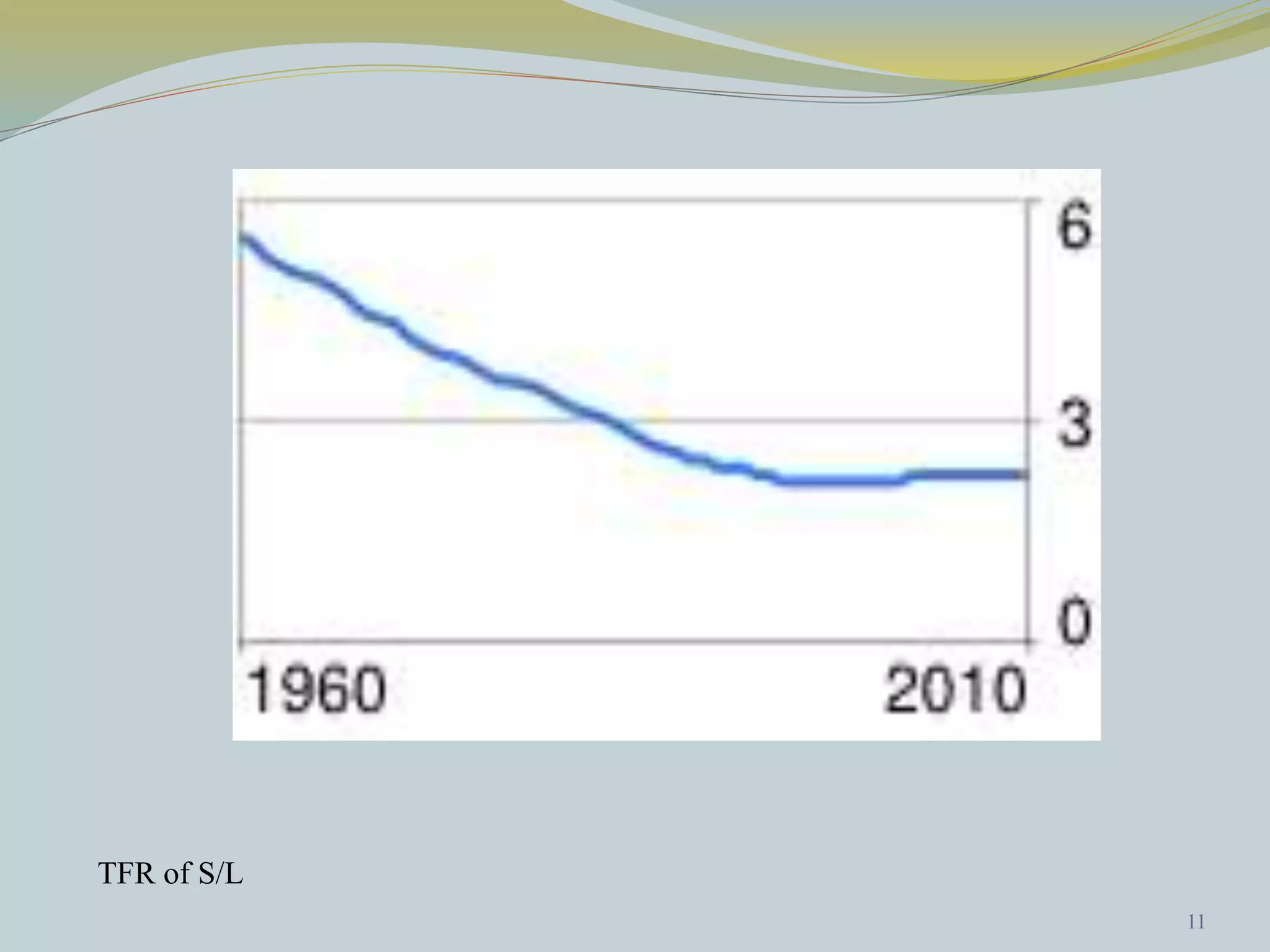
The document discusses crude birth rate and factors that influence population growth rates. It defines crude birth rate as the number of births per 1000 people per year. Crude birth rate minus crude death rate equals the rate of natural increase. Birth rates range from 10-20 births per 1000 being considered low and 40-50 being high. Factors that affect birth rates include government policies, availability of family planning services, economic conditions, education levels and urbanization. The total fertility rate is also discussed, which is the average number of children born to a woman over her lifetime.