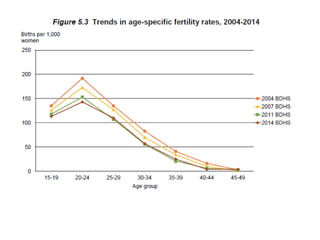
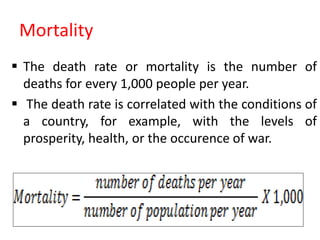
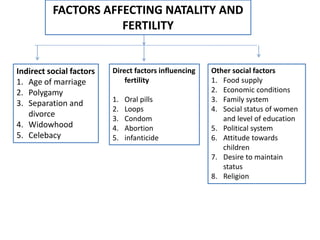
This document presents information on natality, related demographic terms, and measures of fertility. It defines natality as the birth rate, or number of births per 1000 people per year. It also discusses related concepts like mortality, fertility, and factors that affect birth rates. The document focuses on common measures used to quantify fertility, including the crude birth rate, general fertility rate, age-specific fertility rate, total fertility rate, gross reproduction rate, and net reproduction rate. It provides formulas and examples for calculating each measure and describes how they are used to analyze population changes over time.














![Calculating Mid-Year Population
•Mid-year population
= (P1 + P2) / 2
= [P1 + (P1 – D)] / 2
= P1 - ½ D
= P1 – ½ (P2 – P1)
• where:
• P1 = population on 1st January
• P2 = population on 1st January next year
• D = Deaths in a year](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentationonnatalitybyamin-170805152355/85/Presentation-on-natality-by-amin-17-320.jpg)