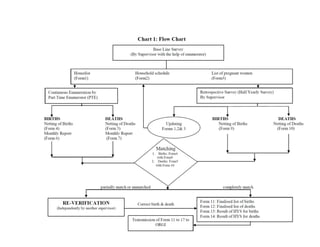
The Sample Registration System (SRS) was initiated in India in 1964-1965 to provide reliable demographic data for planning purposes, as birth and death registration was previously voluntary and incomplete. The SRS provides annual estimates of population composition, fertility, mortality, and medical attention at birth/death for India and major states. It covers about 8.1 million people based on a system of dual recording of births and deaths in representative sample units. Key estimates include population by age/sex, fertility rates, mortality rates, and maternal mortality. The SRS is implemented by the Office of the Registrar General and involves state census offices and part-time enumerators.