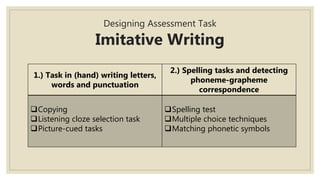
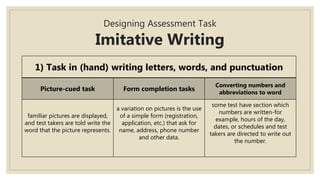
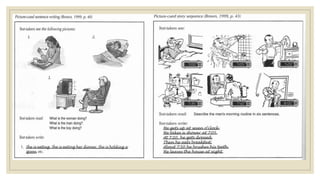
The document discusses assessing writing skills. It describes different types of writing like academic, job-related, and personal writing. It outlines micro skills like imitative and intensive writing, and macro skills like responsive and extensive writing. For micro skills, it provides examples of assessment tasks for imitative writing like spelling tests and dictation. For intensive writing, it discusses tasks like rewriting sentences and transforming grammar. For macro skills, it discusses designing assessment tasks for responsive and extensive writing like guided questions, paragraph construction, and scoring methods.