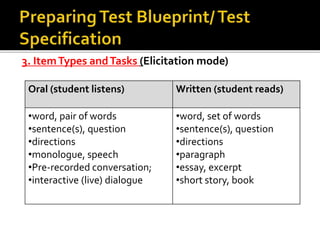
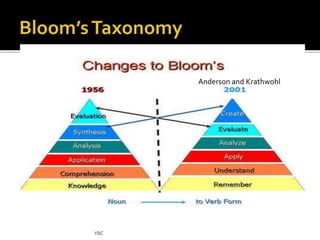
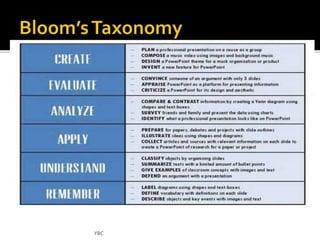
The document outlines the steps for developing a valid and reliable test: 1) determining test specifications, 2) planning by preparing a table of specifications, 3) writing test items, 4) preparing appropriate test formats, 5) reviewing test items, 6) pre-testing the test, and 7) validating test items through analyzing item difficulty, discrimination, and facility. The goal is to design a test that accurately measures the intended objectives and skills at an appropriate level of difficulty without cultural bias.









![7. Validating
To measure the facility or easiness of the item, the
following formula is used:
(Σc) - number of correct responses
(N) - total number of candidates
The results of such equations range from 0 – 1.
An item with a facility index of 0 is too difficult, and with 1
is too easy.
The ideal item is one with the value of (0.5) and the
acceptability range for item facility is between [0.37 →
0.63], i.e. less than 0.37 is difficult, and above 0.63 is easy.
Thus, tests which are too easy or too difficult for a given
sample population, often show low reliability.
YBC](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/designinglanguagetest-141014200404-conversion-gate01/85/Designing-language-test-10-320.jpg)