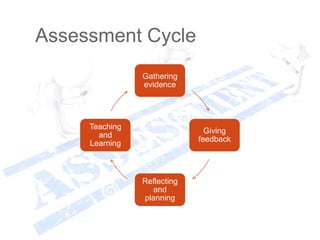
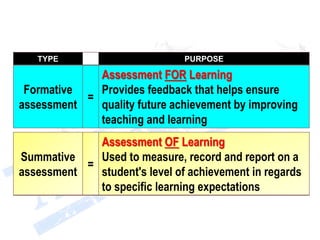
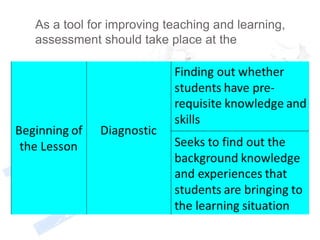
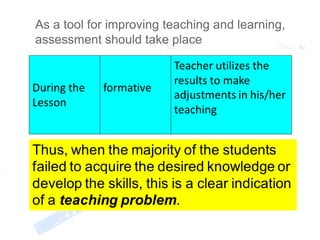
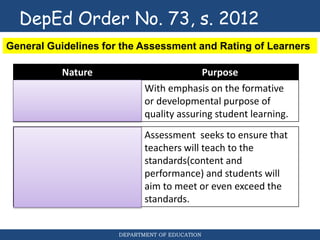
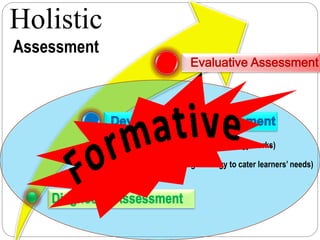
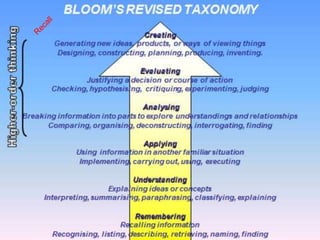
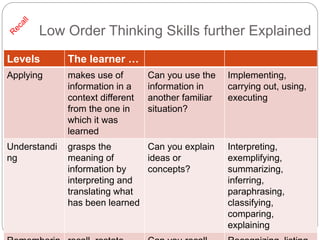
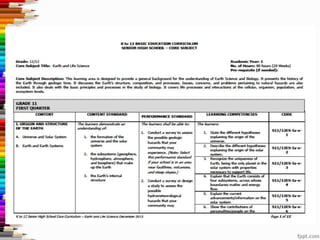
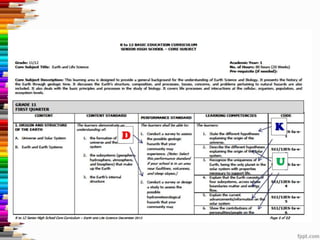
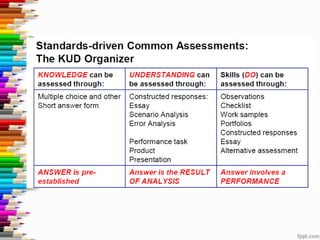
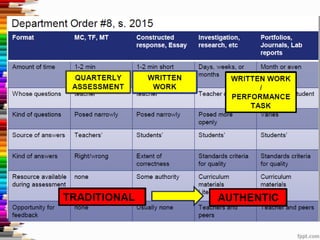
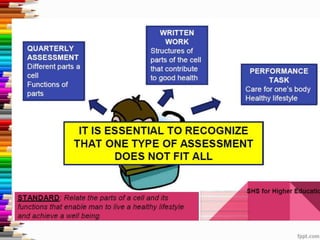
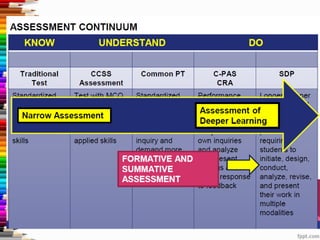
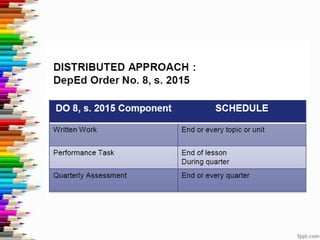
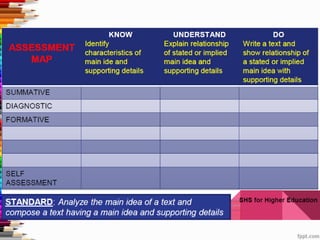
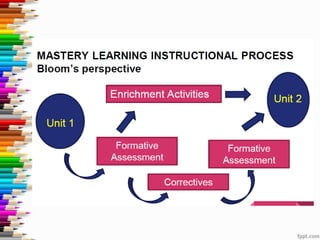
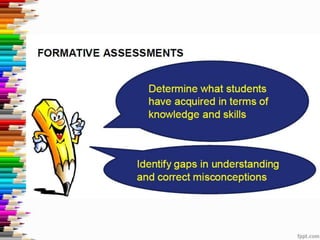
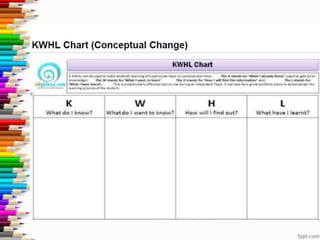
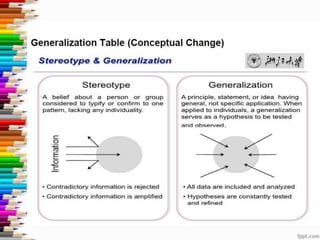
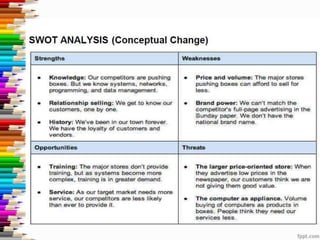
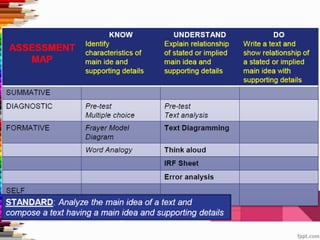
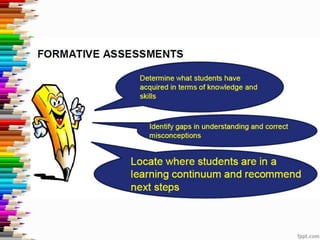
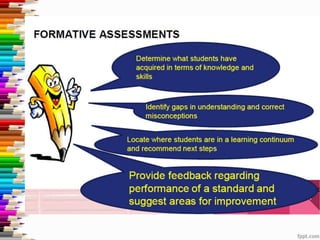
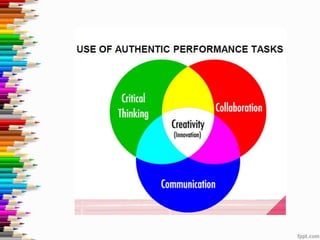
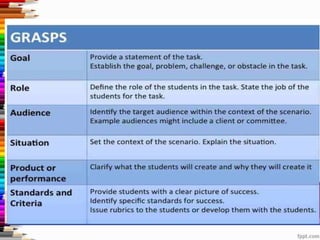
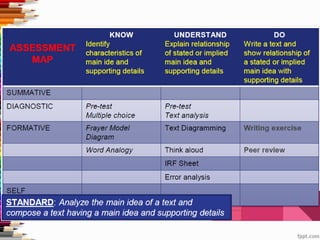
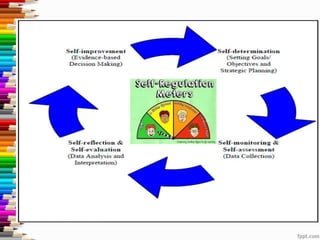
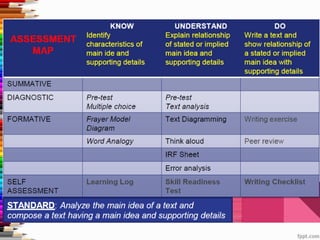
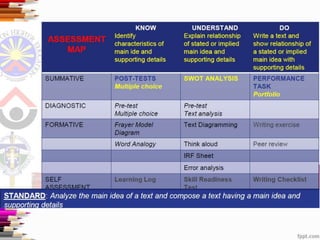
This document discusses assessment and learning outcomes. It provides an overview of assessment, including the assessment cycle and different types of assessment such as formative, summative, diagnostic, and standards-based assessment. The document discusses how to align assessment with learning outcomes and assess learning outcomes. It also discusses assessment for learning, of learning, and as learning. Key topics covered include the purpose of different assessments, developing students' ability to self-assess, and using formative assessment results to improve teaching and learning.